[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7y0d: Cryo-EM structure of the Mycobacterium smegmatis DNA integrity sc... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7y0d | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the Mycobacterium smegmatis DNA integrity scanning protein (MsDisA). | |||||||||
 Components Components | DNA integrity scanning protein DisA | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / second messengers / stress response / c-di-AMP / cryo-EM | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdiadenylate cyclase / diadenylate cyclase activity / adenylate cyclase activity / DNA repair / DNA binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gautam, S. / Vinothkumar, K.R. / Chatterji, D. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  India, 2items India, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Protein Sci / Year: 2023 Journal: Protein Sci / Year: 2023Title: Regulatory mechanisms of c-di-AMP synthase from Mycobacterium smegmatis revealed by a structure: Function analysis. Authors: Sudhanshu Gautam / Avisek Mahapa / Lahari Yeramala / Apoorv Gandhi / Sushma Krishnan / Vinothkumar Kutti R / Dipankar Chatterji /  Abstract: Cyclic-di-nucleotide-based secondary messengers regulate various physiological functions, including stress responses in bacteria. Cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) has recently emerged as a ...Cyclic-di-nucleotide-based secondary messengers regulate various physiological functions, including stress responses in bacteria. Cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) has recently emerged as a crucial second messenger with implications in processes including osmoregulation, antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation, virulence, DNA repair, ion homeostasis, and sporulation, and has potential therapeutic applications. The contrasting activities of the enzymes diadenylate cyclase (DAC) and phosphodiesterase (PDE) determine the equilibrium levels of c-di-AMP. Although c-di-AMP is suspected of playing an essential role in the pathophysiology of bacterial infections and in regulating host-pathogen interactions, the mechanisms of its regulation remain relatively unexplored in mycobacteria. In this report, we biochemically and structurally characterize the c-di-AMP synthase (MsDisA) from Mycobacterium smegmatis. The enzyme activity is regulated by pH and substrate concentration; conditions of significance in the homoeostasis of c-di-AMP levels. Substrate binding stimulates conformational changes in the protein, and pApA and ppApA are synthetic intermediates detectable when enzyme efficiency is low. Unlike the orthologous Bacillus subtilis enzyme, MsDisA does not bind to, and its activity is not influenced in the presence of DNA. Furthermore, we have determined the cryo-EM structure of MsDisA, revealing asymmetry in its structure in contrast to the symmetric crystal structure of Thermotoga maritima DisA. We also demonstrate that the N-terminal minimal region alone is sufficient and essential for oligomerization and catalytic activity. Our data shed light on the regulation of mycobacterial DisA and possible future directions to pursue. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7y0d.cif.gz 7y0d.cif.gz | 456 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7y0d.ent.gz pdb7y0d.ent.gz | 382.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7y0d.json.gz 7y0d.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y0/7y0d https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y0/7y0d ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y0/7y0d ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y0/7y0d | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33540MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 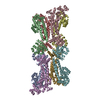
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41844.199 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)Gene: disA, MSMEG_6080, MSMEI_5920 / Plasmid: pET28A / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of the Mycobacterium smegmatis DNA integrity scanning protein (MsDisA). Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.33 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: Buffer were made freshly with 75mM NaCl and 50mM Tris (pH 7.5) |
| Buffer component | Conc.: 75 mM / Name: Sodium Chloride / Formula: NaCl |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: The protein sample was made on a holey carbon grid with an additional layer of thin carbon. |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Details: blotted for 3.5s |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Calibrated magnification: 130841 X / Nominal defocus max: 3300 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2100 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 60 sec. / Electron dose: 27.75 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 1587 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 14 µm / Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 973755 Details: Template Picker from cryoSparc 3.0 were used to pick total particles in the first extraction. Three rounds of reference-free 2d classification were carried to remove bad particles followed by NU-refinement. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 204932 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 4 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 138.7 / Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL Details: Model from AlphaFold was used as the starting point (AF-A0R564-F1-model_v2.pdb). |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj
