+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7xml | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of PEIP-Bs_enolase complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LYASE/LYASE INHIBITOR / Enolase inhibitor / Glycolysis / Bacteriophage / ANTIMICROBIAL PROTEIN / LYASE-LYASE INHIBITOR complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphosphopyruvate hydratase / phosphopyruvate hydratase complex / phosphopyruvate hydratase activity / sporulation resulting in formation of a cellular spore / glycolytic process / cell surface / magnesium ion binding / extracellular region Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Bacillus phage SP01 (virus) Bacillus phage SP01 (virus) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li, S. / Zhang, K. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2022 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2022Title: Bacteriophage protein PEIP is a potent Bacillus subtilis enolase inhibitor. Authors: Kaining Zhang / Shanshan Li / Yawen Wang / Zhihao Wang / Nancy Mulvenna / Hang Yang / Peipei Zhang / Huan Chen / Yan Li / Hongliang Wang / Yongxiang Gao / Sivaramesh Wigneshweraraj / Steve ...Authors: Kaining Zhang / Shanshan Li / Yawen Wang / Zhihao Wang / Nancy Mulvenna / Hang Yang / Peipei Zhang / Huan Chen / Yan Li / Hongliang Wang / Yongxiang Gao / Sivaramesh Wigneshweraraj / Steve Matthews / Kaiming Zhang / Bing Liu /   Abstract: Enolase is a highly conserved enzyme that presents in all organisms capable of glycolysis or fermentation. Its immediate product phosphoenolpyruvate is essential for other important processes like ...Enolase is a highly conserved enzyme that presents in all organisms capable of glycolysis or fermentation. Its immediate product phosphoenolpyruvate is essential for other important processes like peptidoglycan synthesis and the phosphotransferase system in bacteria. Therefore, enolase inhibitors are of great interest. Here, we report that Gp60, a phage-encoded enolase inhibitor protein (PEIP) of bacteriophage SPO1 for Bacillus subtilis, is an enolase inhibitor. PEIP-expressing bacteria exhibit growth attenuation, thinner cell walls, and safranin color in Gram staining owing to impaired peptidoglycan synthesis. We solve the structure of PEIP-enolase tetramer and show that PEIP disassembles enolase by disrupting the basic dimer unit. The structure reveals that PEIP does not compete for substrate binding but induces a cascade of conformational changes that limit accessibility to the enolase catalytic site. This phage-inspired disassembly of enolase represents an alternative strategy for the development of anti-microbial drugs. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7xml.cif.gz 7xml.cif.gz | 175.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7xml.ent.gz pdb7xml.ent.gz | 139.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7xml.json.gz 7xml.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xm/7xml https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xm/7xml ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xm/7xml ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xm/7xml | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33300MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 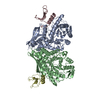
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 46626.148 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: eno, BSU33900 / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 8558.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Bacillus phage SP01 (virus) / Gene: 60 / Production host: Bacillus phage SP01 (virus) / Gene: 60 / Production host:  #3: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.1 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2300 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.13_2998: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 553242 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj


