+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7x59 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | A Cbc-ParM filament with GTP or GDPPi | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | ParM/StbA family protein | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / ParM actin-like plasmid segregation | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology | GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / :  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Koh, A. / Ali, S. / Robinson, R. / Narita, A. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 3items Japan, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2025 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2025Title: Bacterial genome-encoded ParMs. Authors: Samson Ali / Adrian Koh / David Popp / Kotaro Tanaka / Yoshihito Kitaoku / Naoyuki Miyazaki / Kenji Iwasaki / Kaoru Mitsuoka / Robert C Robinson / Akihiro Narita /    Abstract: ParMs generally exist on low-copy number plasmids where they contribute to plasmid segregation and stable inheritance. We carried out bioinformatics analysis, which indicated that ParM genes are not ...ParMs generally exist on low-copy number plasmids where they contribute to plasmid segregation and stable inheritance. We carried out bioinformatics analysis, which indicated that ParM genes are not only confined to plasmids but are also occasionally found on genomes. Here we report the discovery and characterization of two chromosome-encoded ParMs (cParMs) from the genomes of Desulfitobacterium hafniense (Dh-cParM1) and Clostridium botulinum (Cb-cParM). Both cParMs form filaments, exhibit nucleotide hydrolysis, and possess characteristic ParM subunit structures. Dh-cParM1 forms single and tightly coupled double filaments and is highly conserved on the chromosomes of five of six Desulfitobacterium species. Interestingly, these bacteria have not been reported to harbor plasmids. Cb-cParM possesses unique properties. Its filaments were stable after nucleotide hydrolysis and Pi release, and its ParR (Cb-cParR) did not affect the initial phase of Cb-cParM polymerization but displayed properties of a depolymerization factor for mature filaments. These results indicate functional, polymerizing ParMs can be encoded on genomes, suggesting that ParM roles may extend to other functions beyond plasmid segregation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7x59.cif.gz 7x59.cif.gz | 256.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7x59.ent.gz pdb7x59.ent.gz | 211 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7x59.json.gz 7x59.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x5/7x59 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x5/7x59 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x5/7x59 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x5/7x59 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33012MC  7x54C  7x55C  7x56C  8x1iC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 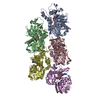
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 32545.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: CBg-ParM filament with GTP or GDPPi / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.7 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 45 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 165.7 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 22.6 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 70754 / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj

