[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7vay: V1EG domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus at saturated ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7vay | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | V1EG domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus at saturated ATP-gamma-S condition, state2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (V-type ATP synthase ...) x 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / rotary ATPase / V-type ATPase / ATP synthase / Thermus thermophilus / chemo-mechanical coupling | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kishikawa, J. / Nakanishi, A. / Nakano, A. / Saeki, S. / Furuta, A. / Kato, T. / Mitsuoka, K. / Yokoyama, K. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 6items Japan, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structural snapshots of V/A-ATPase reveal the rotary catalytic mechanism of rotary ATPases. Authors: J Kishikawa / A Nakanishi / A Nakano / S Saeki / A Furuta / T Kato / K Mistuoka / K Yokoyama /  Abstract: V/A-ATPase is a motor protein that shares a common rotary catalytic mechanism with FF ATP synthase. When powered by ATP hydrolysis, the V domain rotates the central rotor against the AB hexamer, ...V/A-ATPase is a motor protein that shares a common rotary catalytic mechanism with FF ATP synthase. When powered by ATP hydrolysis, the V domain rotates the central rotor against the AB hexamer, composed of three catalytic AB dimers adopting different conformations (AB, AB, and AB). Here, we report the atomic models of 18 catalytic intermediates of the V domain of V/A-ATPase under different reaction conditions, determined by single particle cryo-EM. The models reveal that the rotor does not rotate immediately after binding of ATP to the V. Instead, three events proceed simultaneously with the 120˚ rotation of the shaft: hydrolysis of ATP in AB, zipper movement in AB by the binding ATP, and unzipper movement in AB with release of both ADP and Pi. This indicates the unidirectional rotation of V/A-ATPase by a ratchet-like mechanism owing to ATP hydrolysis in AB, rather than the power stroke model proposed previously for F-ATPase. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7vay.cif.gz 7vay.cif.gz | 640.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7vay.ent.gz pdb7vay.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7vay.json.gz 7vay.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/va/7vay https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/va/7vay ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/va/7vay ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/va/7vay | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  31871MC  7vaiC  7vajC  7vakC  7valC  7vamC  7vanC  7vaoC  7vapC  7vaqC  7varC  7vasC  7vatC  7vauC  7vavC  7vawC  7vaxC 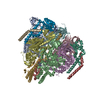 7vb0C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type ATP synthase ... , 6 types, 12 molecules ABCDEFGHIKJL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63669.957 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8References: UniProt: Q56403, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 53219.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: Q56404 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: Q56404#3: Protein | | Mass: 24715.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: O87880 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: O87880#4: Protein | | Mass: 11294.904 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: P74903 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: P74903#5: Protein | Mass: 13166.218 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: Q5SIT5 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: Q5SIT5#6: Protein | Mass: 20645.582 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: P74901 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: P74901 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 5 molecules 




| #7: Chemical | | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | #9: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Sequence details | For V-ATPase subunit A, the bacterium has two mutations in its genome (S232A and T235S). |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: V1EG domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus at saturated ATP-gamma-S condition, state2 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.5 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: Buffer contains 4mM ATP-gamma-S. |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: MOLYBDENUM / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: JEOL CRYO ARM 300 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 60000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 5 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 4677284 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 35300 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL Details: The atomic model built in this study was used as an initial model. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj






