+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ufm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | VchTnsC AAA+ with DNA (double heptamer) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA / transposon / AAA+ / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology | P-loop containing nucleotide triphosphate hydrolases / Rossmann fold / 3-Layer(aba) Sandwich / Alpha Beta / ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / DNA / DNA (> 10) Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Fernandez, I.S. / Sternberg, S.H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Selective TnsC recruitment enhances the fidelity of RNA-guided transposition. Authors: Florian T Hoffmann / Minjoo Kim / Leslie Y Beh / Jing Wang / Phuc Leo H Vo / Diego R Gelsinger / Jerrin Thomas George / Christopher Acree / Jason T Mohabir / Israel S Fernández / Samuel H Sternberg /   Abstract: Bacterial transposons are pervasive mobile genetic elements that use distinct DNA-binding proteins for horizontal transmission. For example, Escherichia coli Tn7 homes to a specific attachment site ...Bacterial transposons are pervasive mobile genetic elements that use distinct DNA-binding proteins for horizontal transmission. For example, Escherichia coli Tn7 homes to a specific attachment site using TnsD, whereas CRISPR-associated transposons use type I or type V Cas effectors to insert downstream of target sites specified by guide RNAs. Despite this targeting diversity, transposition invariably requires TnsB, a DDE-family transposase that catalyses DNA excision and insertion, and TnsC, a AAA+ ATPase that is thought to communicate between transposase and targeting proteins. How TnsC mediates this communication and thereby regulates transposition fidelity has remained unclear. Here we use chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing to monitor in vivo formation of the type I-F RNA-guided transpososome, enabling us to resolve distinct protein recruitment events before integration. DNA targeting by the TniQ-Cascade complex is surprisingly promiscuous-hundreds of genomic off-target sites are sampled, but only a subset of those sites is licensed for TnsC and TnsB recruitment, revealing a crucial proofreading checkpoint. To advance the mechanistic understanding of interactions responsible for transpososome assembly, we determined structures of TnsC using cryogenic electron microscopy and found that ATP binding drives the formation of heptameric rings that thread DNA through the central pore, thereby positioning the substrate for downstream integration. Collectively, our results highlight the molecular specificity imparted by consecutive factor binding to genomic target sites during RNA-guided transposition, and provide a structural roadmap to guide future engineering efforts. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ufm.cif.gz 7ufm.cif.gz | 768.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ufm.ent.gz pdb7ufm.ent.gz | 648.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ufm.json.gz 7ufm.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uf/7ufm https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uf/7ufm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uf/7ufm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uf/7ufm | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  26477MC  7rzyC  7ufiC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 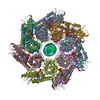
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 35065.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 14 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: DNA chain | | Mass: 11055.130 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) #3: DNA chain | | Mass: 11099.121 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: VchTnsC AAA+ with DNA (double heptamer) / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.2 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Homemade |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NITROGEN |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 125000 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj








































