[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7ram: Cryo-EM Structure of the HCMV gHgLgO Trimer Derived from AD169 an... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ram | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of the HCMV gHgLgO Trimer Derived from AD169 and TR strains in complex with PDGFRalpha | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / viral entry glycoprotein in complex with receptor | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationImatinib-resistant PDGFR mutants / Sunitinib-resistant PDGFR mutants / Regorafenib-resistant PDGFR mutants / Sorafenib-resistant PDGFR mutants / PDGFR mutants bind TKIs / platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha signaling pathway / platelet-derived growth factor receptor-ligand complex / platelet-derived growth factor alpha-receptor activity / metanephric glomerular capillary formation / regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation ...Imatinib-resistant PDGFR mutants / Sunitinib-resistant PDGFR mutants / Regorafenib-resistant PDGFR mutants / Sorafenib-resistant PDGFR mutants / PDGFR mutants bind TKIs / platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha signaling pathway / platelet-derived growth factor receptor-ligand complex / platelet-derived growth factor alpha-receptor activity / metanephric glomerular capillary formation / regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation / luteinization / positive regulation of cell proliferation by VEGF-activated platelet derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / platelet-derived growth factor binding / vascular endothelial growth factor binding / embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis / retina vasculature development in camera-type eye / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity / embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis / Leydig cell differentiation / cardiac myofibril assembly / cell activation / Signaling by PDGF / male genitalia development / positive regulation of chemotaxis / embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis / phospholipase C activator activity / platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding / estrogen metabolic process / signal transduction involved in regulation of gene expression / face morphogenesis / adrenal gland development / platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth / microvillus / roof of mouth development / white fat cell differentiation / negative regulation of platelet activation / hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / Signaling by PDGFRA transmembrane, juxtamembrane and kinase domain mutants / Signaling by PDGFRA extracellular domain mutants / extracellular matrix organization / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / Downstream signal transduction / lung development / peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / cell surface receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway / host cell endosome membrane / cell chemotaxis / regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / wound healing / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / platelet aggregation / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / Constitutive Signaling by Aberrant PI3K in Cancer / cell junction / cell migration / PIP3 activates AKT signaling / protein autophosphorylation / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / in utero embryonic development / host cell Golgi apparatus / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / protein kinase activity / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / receptor complex / cilium / nuclear body / positive regulation of cell migration / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / external side of plasma membrane / viral envelope / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / symbiont entry into host cell / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / Golgi apparatus / protein homodimerization activity / protein-containing complex / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / membrane / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Human herpesvirus 5 strain AD169 Human herpesvirus 5 strain AD169  Human betaherpesvirus 5 Human betaherpesvirus 5 Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.43 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Liu, J. / Vanarsdall, A.L. / Chen, D. / Johnson, D.C. / Jardetzky, T.S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2021 Journal: mBio / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure and Interactions of the Human Cytomegalovirus gHgLgO Trimer with Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Alpha. Authors: Jing Liu / Adam Vanarsdall / Dong-Hua Chen / Andrea Chin / David Johnson / Theodore S Jardetzky /  Abstract: Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a herpesvirus that produces disease in transplant patients and newborn children. Entry of HCMV into cells relies on gH/gL trimer (gHgLgO) and pentamer (gHgLUL128-131) ...Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a herpesvirus that produces disease in transplant patients and newborn children. Entry of HCMV into cells relies on gH/gL trimer (gHgLgO) and pentamer (gHgLUL128-131) complexes that bind cellular receptors. Here, we studied the structure and interactions of the HCMV trimer, formed by AD169 strain gH and gL and TR strain gO proteins, with the human platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRα). Three trimer surfaces make extensive contacts with three PDGFRα N-terminal domains, causing PDGFRα to wrap around gO in a structure similar to a human hand, explaining the high-affinity interaction. gO is among the least conserved HCMV proteins, with 8 distinct genotypes. We observed high conservation of residues mediating gO-gL interactions but more extensive gO variability in the PDGFRα interface. Comparisons between our trimer structure and a previously determined structure composed of different subunit genotypes indicate that gO variability is accommodated by adjustments in the gO-PDGFRα interface. We identified two loops within gO that were disordered and apparently glycosylated, which could be deleted without disrupting PDGFRα binding. We also identified four gO residues that contact PDGFRα, which when mutated produced markedly reduced receptor binding. These residues fall within conserved contact sites of gO with PDGFRα and may represent key targets for anti-trimer neutralizing antibodies and HCMV vaccines. Finally, we observe that gO mutations distant from the gL interaction site impact trimer expression, suggesting that the intrinsic folding or stability of gO can impact the efficiency of trimer assembly. HCMV is a herpesvirus that infects a large percentage of the adult population and causes significant levels of disease in immunocompromised individuals and birth defects in the developing fetus. The virus encodes a complex protein machinery that coordinates infection of different cell types in the body, including a trimer formed of gH, gL, and gO subunits. Here, we studied the interactions of the HCMV trimer with its receptor on cells, the platelet derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRα), to better understand how HCMV coordinates virus entry into cells. Our results add to our understanding of HCMV strain-specific differences and identify sites on the trimer that represent potential targets for therapeutic antibodies or vaccine development. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ram.cif.gz 7ram.cif.gz | 291.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ram.ent.gz pdb7ram.ent.gz | 221 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ram.json.gz 7ram.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ra/7ram https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ra/7ram ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ra/7ram ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ra/7ram | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  24369MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 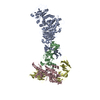
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 80435.430 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP Residues 41-718 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Human herpesvirus 5 strain AD169 / Strain: AD169 / Gene: gH, UL75 / Production host: Human herpesvirus 5 strain AD169 / Strain: AD169 / Gene: gH, UL75 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P12824 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P12824 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 27138.018 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP Residues 31-278 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Human herpesvirus 5 strain AD169 / Strain: AD169 / Gene: gL, UL115 / Plasmid: pTT5 / Cell line (production host): HEK293-6E / Production host: Human herpesvirus 5 strain AD169 / Strain: AD169 / Gene: gL, UL115 / Plasmid: pTT5 / Cell line (production host): HEK293-6E / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P16832 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P16832 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 53937.715 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Human betaherpesvirus 5 / Gene: UL74 / Production host: Human betaherpesvirus 5 / Gene: UL74 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8AZ32 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8AZ32 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 59370.016 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PDGFRA, PDGFR2, RHEPDGFRA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PDGFRA, PDGFR2, RHEPDGFRA / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P16234, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 / Details: 300mM NaCl and 20mM HEPES7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 96 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 75 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.43 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 345997 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 94.19 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj






