[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7l1k: Cryo-EM structure of S. Pombe NatC complex with a Bisubstrate inh... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7l1k | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
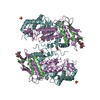
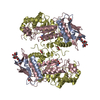
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of S. Pombe NatC complex with a Bisubstrate inhibitor and inositol hexaphosphate | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / NatB / NAA20 / NAA25 | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationN-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatC / NatC complex / Sm-like protein family complex / protein N-terminal-methionine acetyltransferase activity / protein-N-terminal amino-acid acetyltransferase activity / inositol hexakisphosphate binding / protein maturation / endoplasmic reticulum / RNA binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.16 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Deng, S. / Marmorstein, R. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2021 Journal: Structure / Year: 2021Title: Molecular mechanism of N-terminal acetylation by the ternary NatC complex. Authors: Sunbin Deng / Leah Gottlieb / Buyan Pan / Julianna Supplee / Xuepeng Wei / E James Petersson / Ronen Marmorstein /  Abstract: Protein N-terminal acetylation is predominantly a ribosome-associated modification, with NatA-E serving as the major enzymes. NatC is the most unusual of these enzymes, containing one Naa30 catalytic ...Protein N-terminal acetylation is predominantly a ribosome-associated modification, with NatA-E serving as the major enzymes. NatC is the most unusual of these enzymes, containing one Naa30 catalytic subunit and two auxiliary subunits, Naa35 and Naa38; and substrate selectivity profile that overlaps with NatE. Here, we report the cryoelectron microscopy structure of S. pombe NatC with a NatE/C-type bisubstrate analog and inositol hexaphosphate (IP), and associated biochemistry studies. We find that the presence of three subunits is a prerequisite for normal NatC acetylation activity in yeast and that IP binds tightly to NatC to stabilize the complex. We also describe the molecular basis for IP-mediated NatC complex stabilization and the overlapping yet distinct substrate profiles of NatC and NatE. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7l1k.cif.gz 7l1k.cif.gz | 184.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7l1k.ent.gz pdb7l1k.ent.gz | 142 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7l1k.json.gz 7l1k.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/7l1k https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/7l1k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/7l1k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/7l1k | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23110MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-N-alpha-acetyltransferase ... , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 17721.350 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: naa30, mak3, SPBC15D4.06 / Production host:  References: UniProt: O74311, N-terminal methionine Nalpha-acetyltransferase NatC |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 80541.312 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: mak10, naa35, SPBC1861.03 / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 13258.555 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: naa38, mak31, SPBC947.03c / Production host:  |
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules D
| #4: Protein/peptide | Mass: 416.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules 
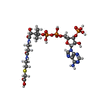
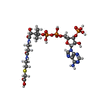
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-IHP / |
|---|---|
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-CMC / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Units: MEGADALTONS / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 289 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS | ||||||||||||
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM | ||||||||||||
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD | ||||||||||||
| Image recording |
|
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Details: 5397 images | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3289528 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.16 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 607131 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj