[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
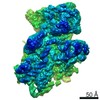
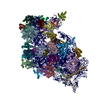
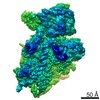
Yorodumi- PDB-7kts: Negative stain EM structure of the human SAGA coactivator complex... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7kts | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Negative stain EM structure of the human SAGA coactivator complex (TRRAP, core, splicing module) | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / splicing / gene regulation / chromatin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationSAGA-type complex / regulation of somatic stem cell population maintenance / SAGA complex assembly / lateral mesodermal cell differentiation / allantois development / regulation of cellular response to stress / transcription factor TFTC complex / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization / hepatocyte differentiation ...SAGA-type complex / regulation of somatic stem cell population maintenance / SAGA complex assembly / lateral mesodermal cell differentiation / allantois development / regulation of cellular response to stress / transcription factor TFTC complex / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization / hepatocyte differentiation / U12-type spliceosomal complex / maintenance of protein location in nucleus / RNA splicing, via transesterification reactions / splicing factor binding / U2-type precatalytic spliceosome / RNA polymerase binding / U2-type prespliceosome assembly / U2-type spliceosomal complex / limb development / SAGA complex / U2 snRNP / transcription preinitiation complex / RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity / precatalytic spliceosome / negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / transcription factor TFIID complex / nucleus organization / HIV Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II HIV Promoter Escape / Transcription of the HIV genome / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / regulation of RNA splicing / histone deacetylase complex / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / U2 snRNA binding / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / embryonic placenta development / somitogenesis / regulation of DNA repair / RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex assembly / catalytic step 2 spliceosome / gastrulation / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / visual perception / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / RNA splicing / TBP-class protein binding / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / transcription coregulator activity / male germ cell nucleus / spliceosomal complex / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / promoter-specific chromatin binding / DNA-templated transcription initiation / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / autophagy / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / multicellular organism growth / nuclear matrix / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / transcription corepressor activity / HATs acetylate histones / microtubule cytoskeleton / positive regulation of cell growth / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / transcription coactivator activity / Ub-specific processing proteases / protein stabilization / nuclear speck / chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / focal adhesion / apoptotic process / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / protein-containing complex binding / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / Golgi apparatus / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) unclassified Rhodococcus (bacteria) unclassified Rhodococcus (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 19.09 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Herbst, D.A. / Esbin, M.N. / Nogales, E. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, European Union, United States, European Union,  Switzerland, 6items Switzerland, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2021Title: Structure of the human SAGA coactivator complex. Authors: Dominik A Herbst / Meagan N Esbin / Robert K Louder / Claire Dugast-Darzacq / Gina M Dailey / Qianglin Fang / Xavier Darzacq / Robert Tjian / Eva Nogales /   Abstract: The SAGA complex is a regulatory hub involved in gene regulation, chromatin modification, DNA damage repair and signaling. While structures of yeast SAGA (ySAGA) have been reported, there are ...The SAGA complex is a regulatory hub involved in gene regulation, chromatin modification, DNA damage repair and signaling. While structures of yeast SAGA (ySAGA) have been reported, there are noteworthy functional and compositional differences for this complex in metazoans. Here we present the cryogenic-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of human SAGA (hSAGA) and show how the arrangement of distinct structural elements results in a globally divergent organization from that of yeast, with a different interface tethering the core module to the TRRAP subunit, resulting in a dramatically altered geometry of functional elements and with the integration of a metazoan-specific splicing module. Our hSAGA structure reveals the presence of an inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP) binding site in TRRAP and an unusual property of its pseudo-(Ψ)PIKK. Finally, we map human disease mutations, thus providing the needed framework for structure-guided drug design of this important therapeutic target for human developmental diseases and cancer. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7kts.cif.gz 7kts.cif.gz | 2.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7kts.ent.gz pdb7kts.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7kts.json.gz 7kts.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kt/7kts https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kt/7kts ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kt/7kts ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kt/7kts | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 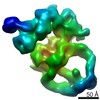 23028MC  7ktrC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 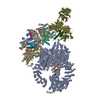
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 8 types, 8 molecules ABCDFIJN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 419168.094 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: F2Z2U4 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HeLa / References: UniProt: F2Z2U4 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 66223.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75529 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75529 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 88129.070 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8NEM7 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8NEM7 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 83013.664 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.) Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.)  unclassified Rhodococcus (bacteria) unclassified Rhodococcus (bacteria)Gene: SUPT7L, KIAA0764 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O94864 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O94864 |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 62027.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9Y6J9 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9Y6J9 |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 35447.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75486 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75486 |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 37432.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q96BN2 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q96BN2 |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 95597.742 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15265 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15265 |
-Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit ... , 3 types, 3 molecules EGH
| #5: Protein | Mass: 27654.861 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9HBM6 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9HBM6 |
|---|---|
| #7: Protein | Mass: 17948.467 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16514 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16514 |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 21731.248 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q12962 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q12962 |
-Splicing factor 3B subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules ST
| #12: Protein | Mass: 135718.844 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15393 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15393 |
|---|---|
| #13: Protein | Mass: 10149.369 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BWJ5 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BWJ5 |
-Details
| Sequence details | Portions of chains A, D, F and I were not fully discernible in the map, and so many of the residues ...Portions of chains A, D, F and I were not fully discernible in the map, and so many of the residues were modeled as unknown (UNK) due to not knowing the register in these regions. The full sequence of the chains are as follows. Chain A: MAFVATQGAT |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera






 PDBj
PDBj





