[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6xw7: Crystal structure of murine norovirus P domain in complex with Na... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6xw7 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of murine norovirus P domain in complex with Nanobody NB-5829 and glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDCA) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / MNV / neutralizing nanobody / VHH / norovirus | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |   Murine norovirus 1 Murine norovirus 1 | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.15 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.15 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kilic, T. / Sabin, C. / Hansman, G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2020 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2020Title: Nanobody-Mediated Neutralization Reveals an Achilles Heel for Norovirus. Authors: Anna D Koromyslova / Jessica M Devant / Turgay Kilic / Charles D Sabin / Virginie Malak / Grant S Hansman /  Abstract: Human norovirus frequently causes outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis. Although discovered more than five decades ago, antiviral development has, until recently, been hampered by the lack of a ...Human norovirus frequently causes outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis. Although discovered more than five decades ago, antiviral development has, until recently, been hampered by the lack of a reliable human norovirus cell culture system. Nevertheless, a lot of pathogenesis studies were accomplished using murine norovirus (MNV), which can be grown routinely in cell culture. In this study, we analyzed a sizeable library of nanobodies that were raised against the murine norovirus virion with the main purpose of developing nanobody-based inhibitors. We discovered two types of neutralizing nanobodies and analyzed the inhibition mechanisms using X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), and cell culture techniques. The first type bound on the top region of the protruding (P) domain. Interestingly, this nanobody binding region closely overlapped the MNV receptor-binding site and collectively shared numerous P domain-binding residues. In addition, we showed that these nanobodies competed with the soluble receptor, and this action blocked virion attachment to cultured cells. The second type bound at a dimeric interface on the lower side of the P dimer. We discovered that these nanobodies disrupted a structural change in the capsid associated with binding cofactors (i.e., metal cations/bile acid). Indeed, we found that capsids underwent major conformational changes following addition of Mg or Ca Ultimately, these nanobodies directly obstructed a structural modification reserved for a postreceptor attachment stage. Altogether, our new data show that nanobody-based inhibition could occur by blocking functional and structural capsid properties. This research discovered and analyzed two different types of MNV-neutralizing nanobodies. The top-binding nanobodies sterically inhibited the receptor-binding site, whereas the dimeric-binding nanobodies interfered with a structural modification associated with cofactor binding. Moreover, we found that the capsid contained a number of vulnerable regions that were essential for viral replication. In fact, the capsid appeared to be organized in a state of flux, which could be important for cofactor/receptor-binding functions. Blocking these capsid-binding events with nanobodies directly inhibited essential capsid functions. Moreover, a number of MNV-specific nanobody binding epitopes were comparable to human norovirus-specific nanobody inhibitors. Therefore, this additional structural and inhibition information could be further exploited in the development of human norovirus antivirals. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6xw7.cif.gz 6xw7.cif.gz | 354.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6xw7.ent.gz pdb6xw7.ent.gz | 284.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6xw7.json.gz 6xw7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xw/6xw7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xw/6xw7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xw/6xw7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xw/6xw7 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6xw4C  6xw5C  6xw6C  3lq6S S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 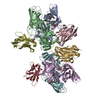
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 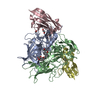
| ||||||||
| 2 | 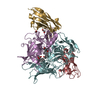
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||
| Components on special symmetry positions |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein / Antibody , 2 types, 8 molecules ABEFCDGH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 33683.980 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Murine norovirus 1 / Production host: Murine norovirus 1 / Production host:  #2: Antibody | Mass: 13447.881 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 912 molecules 





| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-EDO / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-CHO / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | #6: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.92 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 57.84 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 291 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: 0.2 M Sodium chloride, 0.1M Phosphate-citrate pH 4.2, 20% PEG8000 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ESRF ESRF  / Beamline: ID30B / Wavelength: 0.97856 Å / Beamline: ID30B / Wavelength: 0.97856 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: May 12, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.97856 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.15→49.21 Å / Num. obs: 114707 / % possible obs: 96.9 % / Redundancy: 6.886 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 38.879 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.998 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.096 / Rrim(I) all: 0.104 / Χ2: 0.959 / Net I/σ(I): 14.36 / Num. measured all: 789862 / Scaling rejects: 36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 3LQ6 Resolution: 2.15→49.21 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.962 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.943 / SU B: 5.049 / SU ML: 0.127 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / ESU R: 0.193 / ESU R Free: 0.169 Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS U VALUES : REFINED INDIVIDUALLY
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 146.38 Å2 / Biso mean: 33.609 Å2 / Biso min: 12.07 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 2.15→49.21 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.15→2.202 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj





