+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6xl0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
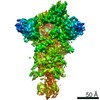
| Title | Caulobacter crescentus FljK filament | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Flagellin | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / flagellum / flagellin / filament / helical / Caulobacter / motility | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbacterial-type flagellum / structural molecule activity / extracellular region Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Caulobacter vibrioides (bacteria) Caulobacter vibrioides (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Montemayor, E.J. / Ploscariu, N.T. / Sanchez, J.C. / Parrell, D. / Dillard, R.S. / Shebelut, C.W. / Ke, Z. / Guerrero-Ferreira, R.C. / Wright, E.R. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 6items United States, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Bacteriol / Year: 2021 Journal: J Bacteriol / Year: 2021Title: Flagellar Structures from the Bacterium Caulobacter crescentus and Implications for Phage CbK Predation of Multiflagellin Bacteria. Authors: Eric J Montemayor / Nicoleta T Ploscariu / Juan C Sanchez / Daniel Parrell / Rebecca S Dillard / Conrad W Shebelut / Zunlong Ke / Ricardo C Guerrero-Ferreira / Elizabeth R Wright /  Abstract: is a Gram-negative alphaproteobacterium that commonly lives in oligotrophic fresh- and saltwater environments. is a host to many bacteriophages, including ϕCbK and ϕCbK-like bacteriophages, which ... is a Gram-negative alphaproteobacterium that commonly lives in oligotrophic fresh- and saltwater environments. is a host to many bacteriophages, including ϕCbK and ϕCbK-like bacteriophages, which require interaction with the bacterial flagellum and pilus complexes during adsorption. It is commonly thought that the six paralogs of the flagellin gene present in are important for bacteriophage evasion. Here, we show that deletion of specific flagellins in can indeed attenuate ϕCbK adsorption efficiency, although no single deletion completely ablates ϕCbK adsorption. Thus, the bacteriophage ϕCbK likely recognizes a common motif among the six known flagellins in with various degrees of efficiency. Interestingly, we observe that most deletion strains still generate flagellar filaments, with the exception of a strain that contains only the most divergent flagellin, FljJ, or a strain that contains only FljN and FljO. To visualize the surface residues that are likely recognized by ϕCbK, we determined two high-resolution structures of the FljK filament, with and without an amino acid substitution that induces straightening of the filament. We observe posttranslational modifications on conserved surface threonine residues of FljK that are likely O-linked glycans. The possibility of interplay between these modifications and ϕCbK adsorption is discussed. We also determined the structure of a filament composed of a heterogeneous mixture of FljK and FljL, the final resolution of which was limited to approximately 4.6 Å. Altogether, this work builds a platform for future investigations of how phage ϕCbK infects at the molecular level. Bacterial flagellar filaments serve as an initial attachment point for many bacteriophages to bacteria. Some bacteria harbor numerous flagellin genes and are therefore able to generate flagellar filaments with complex compositions, which is thought to be important for evasion from bacteriophages. This study characterizes the importance of the six flagellin genes in for infection by bacteriophage ϕCbK. We find that filaments containing the FljK flagellin are the preferred substrate for bacteriophage ϕCbK. We also present a high-resolution structure of a flagellar filament containing only the FljK flagellin, which provides a platform for future studies on determining how bacteriophage ϕCbK attaches to flagellar filaments at the molecular level. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6xl0.cif.gz 6xl0.cif.gz | 827.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6xl0.ent.gz pdb6xl0.ent.gz | 689.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6xl0.json.gz 6xl0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xl/6xl0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xl/6xl0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xl/6xl0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xl/6xl0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  22231MC  6xkyC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera


 PDBj
PDBj