+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wlb | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
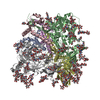
| Title | Structure of homotrimeric poplar cellulose synthase isoform 8 | |||||||||
 Components Components | Cellulose synthase | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Cellulose / polysaccharide / cell wall / glycosyltransferase / translocation | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellulose synthase (UDP-forming) / cellulose synthase (UDP-forming) activity / cellulose biosynthetic process / cell wall organization / zinc ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
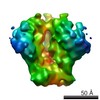
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zimmer, J. / Pallinti, P. / Ho, R. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2020 Journal: Science / Year: 2020Title: Architecture of a catalytically active homotrimeric plant cellulose synthase complex. Authors: Pallinti Purushotham / Ruoya Ho / Jochen Zimmer /  Abstract: Cellulose is an essential plant cell wall component and represents the most abundant biopolymer on Earth. Supramolecular plant cellulose synthase complexes organize multiple linear glucose polymers ...Cellulose is an essential plant cell wall component and represents the most abundant biopolymer on Earth. Supramolecular plant cellulose synthase complexes organize multiple linear glucose polymers into microfibrils as load-bearing wall components. We determined the structure of a poplar cellulose synthase CesA homotrimer that suggests a molecular basis for cellulose microfibril formation. This complex, stabilized by cytosolic plant-conserved regions and helical exchange within the transmembrane segments, forms three channels occupied by nascent cellulose polymers. Secretion steers the polymers toward a common exit point, which could facilitate protofibril formation. CesA's N-terminal domains assemble into a cytosolic stalk that interacts with a microtubule-tethering protein and may thus be involved in CesA localization. Our data suggest how cellulose synthase complexes assemble and provide the molecular basis for plant cell wall engineering. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wlb.cif.gz 6wlb.cif.gz | 723.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wlb.ent.gz pdb6wlb.ent.gz | 596.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wlb.json.gz 6wlb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6wlb_validation.pdf.gz 6wlb_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6wlb_full_validation.pdf.gz 6wlb_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6wlb_validation.xml.gz 6wlb_validation.xml.gz | 58.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6wlb_validation.cif.gz 6wlb_validation.cif.gz | 89.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlb | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21820MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10552 (Title: Architecture of a catalytically active homotrimeric plant cellulose synthase complex EMPIAR-10552 (Title: Architecture of a catalytically active homotrimeric plant cellulose synthase complexData size: 3.4 TB Data #1: Unaligned movie frames of poplar cellulose synthase-8 [micrographs - multiframe] Data #2: Unaligned movie frames of poplar cellulose synthase-8 [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 112483.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: CesA3-1 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q6J8X0, cellulose synthase (UDP-forming) #2: Polysaccharide | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: CesA / Type: COMPLEX Details: Poplar cellulose synthase containing a nascent cellulose chain Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 110 kDa/nm / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: -2250 nm / Nominal defocus min: -750 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 3.96 sec. / Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 11532 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 5760 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C3 (3 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 65665 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj