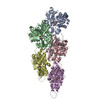
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vec | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of F-actin/Plastin2-ABD2 complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / F-actin / Plastin 2 / Helical reconstruction | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationactin filament network formation / actin crosslink formation / T cell activation involved in immune response / : / cortical actin cytoskeleton organization / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / regulation of intracellular protein transport / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle ...actin filament network formation / actin crosslink formation / T cell activation involved in immune response / : / cortical actin cytoskeleton organization / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / regulation of intracellular protein transport / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / animal organ regeneration / glial cell projection / phagocytic cup / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / ruffle / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / Gene and protein expression by JAK-STAT signaling after Interleukin-12 stimulation / actin filament / filopodium / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / integrin binding / ruffle membrane / calcium-dependent protein binding / actin filament binding / cell junction / cell migration / actin cytoskeleton / lamellipodium / actin binding / cell body / GTPase binding / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / focal adhesion / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / magnesium ion binding / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / ATP binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zheng, W. / Kudryashov, D.S. / Egelman, E.H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Bone Res / Year: 2020 Journal: Bone Res / Year: 2020Title: Osteogenesis imperfecta mutations in plastin 3 lead to impaired calcium regulation of actin bundling. Authors: Christopher L Schwebach / Elena Kudryashova / Weili Zheng / Matthew Orchard / Harper Smith / Lucas A Runyan / Edward H Egelman / Dmitri S Kudryashov /  Abstract: Mutations in actin-bundling protein plastin 3 (PLS3) emerged as a cause of congenital osteoporosis, but neither the role of PLS3 in bone development nor the mechanisms underlying PLS3-dependent ...Mutations in actin-bundling protein plastin 3 (PLS3) emerged as a cause of congenital osteoporosis, but neither the role of PLS3 in bone development nor the mechanisms underlying PLS3-dependent osteoporosis are understood. Of the over 20 identified osteoporosis-linked PLS3 mutations, we investigated all five that are expected to produce full-length protein. One of the mutations distorted an actin-binding loop in the second actin-binding domain of PLS3 and abolished F-actin bundling as revealed by cryo-EM reconstruction and protein interaction assays. Surprisingly, the remaining four mutants fully retained F-actin bundling ability. However, they displayed defects in Ca sensitivity: two of the mutants lost the ability to be inhibited by Ca, while the other two became hypersensitive to Ca. Each group of the mutants with similar biochemical properties showed highly characteristic cellular behavior. Wild-type PLS3 was distributed between lamellipodia and focal adhesions. In striking contrast, the Ca-hyposensitive mutants were not found at the leading edge but localized exclusively at focal adhesions/stress fibers, which displayed reinforced morphology. Consistently, the Ca-hypersensitive PLS3 mutants were restricted to lamellipodia, while chelation of Ca caused their redistribution to focal adhesions. Finally, the bundling-deficient mutant failed to co-localize with any F-actin structures in cells despite a preserved F-actin binding through a non-mutation-bearing actin-binding domain. Our findings revealed that severe osteoporosis can be caused by a mutational disruption of the Ca-controlled PLS3's cycling between adhesion complexes and the leading edge. Integration of the structural, biochemical, and cell biology insights enabled us to propose a molecular mechanism of plastin activity regulation by Ca. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
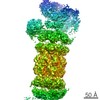
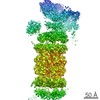
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vec.cif.gz 6vec.cif.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vec.ent.gz pdb6vec.ent.gz | 954.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vec.json.gz 6vec.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ve/6vec https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ve/6vec ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ve/6vec ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ve/6vec | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21155MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| Symmetry | Helical symmetry: (Circular symmetry: 1 / Dyad axis: no / N subunits divisor: 1 / Num. of operations: 11 / Rise per n subunits: 28 Å / Rotation per n subunits: -166.5 °) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42096.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 11 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 47983.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 11 / Fragment: UNP residues 385-625 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HEL-S-37 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HEL-S-37Production host:  References: UniProt: V9HWJ7, UniProt: P13796*PLUS #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -166.5 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 28 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 248184 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 124092 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5ONV Accession code: 5ONV / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj