[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
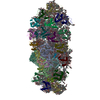
Yorodumi- PDB-6mti: Synaptotagmin-1 C2A, C2B domains and SNARE-pin proteins (5CCI) in... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6mti | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
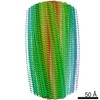
| Title | Synaptotagmin-1 C2A, C2B domains and SNARE-pin proteins (5CCI) individually docked into Cryo-EM map of C2AB-SNARE complexes helically organized on lipid nanotube surface in presence of Mg2+ | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | EXOCYTOSIS / SNARE / lipid nanotubes | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationexocytic insertion of neurotransmitter receptor to postsynaptic membrane / trans-Golgi Network Vesicle Budding / regulation of vesicle fusion / regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / synchronous neurotransmitter secretion / fast, calcium ion-dependent exocytosis of neurotransmitter / syntaxin-3 binding / spontaneous neurotransmitter secretion / regulation of regulated secretory pathway / positive regulation of vesicle fusion ...exocytic insertion of neurotransmitter receptor to postsynaptic membrane / trans-Golgi Network Vesicle Budding / regulation of vesicle fusion / regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / synchronous neurotransmitter secretion / fast, calcium ion-dependent exocytosis of neurotransmitter / syntaxin-3 binding / spontaneous neurotransmitter secretion / regulation of regulated secretory pathway / positive regulation of vesicle fusion / BLOC-1 complex / calcium-dependent activation of synaptic vesicle fusion / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / myosin head/neck binding / positive regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis of neurotransmitter / chromaffin granule membrane / zymogen granule membrane / storage vacuole / synaptic vesicle fusion to presynaptic active zone membrane / Other interleukin signaling / synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a-complexin II complex / synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a complex / presynaptic dense core vesicle exocytosis / synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a-complexin I complex / extrinsic component of presynaptic membrane / calcium ion-regulated exocytosis of neurotransmitter / regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis / Glutamate Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / calcium ion sensor activity / Norepinephrine Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / Acetylcholine Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / Serotonin Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / GABA synthesis, release, reuptake and degradation / positive regulation of norepinephrine secretion / positive regulation of catecholamine secretion / regulated exocytosis / Dopamine Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / synaptic vesicle docking / eosinophil degranulation / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / regulation of synaptic vesicle priming / regulation of establishment of protein localization / vesicle-mediated transport in synapse / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / exocytic vesicle / positive regulation of intracellular protein transport / positive regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis / vesicle organization / vesicle docking / protein heterooligomerization / ribbon synapse / positive regulation of dendrite extension / regulation of vesicle-mediated transport / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / secretion by cell / positive regulation of dopamine secretion / regulation of exocytosis / SNAP receptor activity / chloride channel inhibitor activity / SNARE complex / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / vesicle fusion / calcium-ion regulated exocytosis / actomyosin / LGI-ADAM interactions / hormone secretion / dense core granule / Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport / positive regulation of hormone secretion / calcium-dependent phospholipid binding / neuron projection terminus / membraneless organelle assembly / ATP-dependent protein binding / neurotransmitter secretion / protein localization to membrane / regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling / syntaxin binding / clathrin-coated vesicle / presynaptic active zone / syntaxin-1 binding / insulin secretion / endosomal transport / Neutrophil degranulation / SNARE complex assembly / low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding / positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / clathrin binding / neurotransmitter transport / phosphatidylserine binding / synaptic vesicle priming / regulation of synapse assembly / response to gravity / myosin binding / regulation of neuron projection development / regulation of dopamine secretion / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / exocytosis / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / positive regulation of exocytosis / synaptic vesicle exocytosis Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 10.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Grushin, K. / Wang, J. / Coleman, J. / Rothman, J. / Sindelar, C. / Krishnakumar, S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Structural basis for the clamping and Ca activation of SNARE-mediated fusion by synaptotagmin. Authors: Kirill Grushin / Jing Wang / Jeff Coleman / James E Rothman / Charles V Sindelar / Shyam S Krishnakumar /   Abstract: Synapotagmin-1 (Syt1) interacts with both SNARE proteins and lipid membranes to synchronize neurotransmitter release to calcium (Ca) influx. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of ...Synapotagmin-1 (Syt1) interacts with both SNARE proteins and lipid membranes to synchronize neurotransmitter release to calcium (Ca) influx. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Syt1-SNARE complex on anionic-lipid containing membranes. Under resting conditions, the Syt1 C2 domains bind the membrane with a magnesium (Mg)-mediated partial insertion of the aliphatic loops, alongside weak interactions with the anionic lipid headgroups. The C2B domain concurrently interacts the SNARE bundle via the 'primary' interface and is positioned between the SNAREpins and the membrane. In this configuration, Syt1 is projected to sterically delay the complete assembly of the associated SNAREpins and thus, contribute to clamping fusion. This Syt1-SNARE organization is disrupted upon Ca-influx as Syt1 reorients into the membrane, likely displacing the attached SNAREpins and reversing the fusion clamp. We thus conclude that the cation (Mg/Ca) dependent membrane interaction is a key determinant of the dual clamp/activator function of Synaptotagmin-1. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6mti.cif.gz 6mti.cif.gz | 574.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6mti.ent.gz pdb6mti.ent.gz | 473.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6mti.json.gz 6mti.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6mti_validation.pdf.gz 6mti_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6mti_full_validation.pdf.gz 6mti_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.7 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6mti_validation.xml.gz 6mti_validation.xml.gz | 96.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6mti_validation.cif.gz 6mti_validation.cif.gz | 136.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mt/6mti https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mt/6mti ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mt/6mti ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mt/6mti | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9231MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Synaptotagmin- ... , 2 types, 6 molecules 162345
| #1: Protein | Mass: 14654.769 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: C2A domain, residues 141-267 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 32247.197 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: C2A and C2B domains, residues 141-421 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Protein , 2 types, 12 molecules AEIMQUBFJNRV
| #3: Protein | Mass: 7231.061 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Fragment: residues 28-89 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #4: Protein | Mass: 7837.957 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Fragment: residues 191-256 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Synaptosomal-associated protein ... , 2 types, 12 molecules CGKOSWDHLPTX
| #5: Protein | Mass: 9030.114 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Fragment: residues 7-83 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #6: Protein | Mass: 7471.368 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Fragment: residues 141-204 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 10 molecules 
| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Synaptotagmin-1 C2A and C2B domains in the complex with SNARE proteins on the surface of lipid membrane nanotube Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 44 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: Situs / Category: model fitting |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 78.48 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 7.3 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 10.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 2082 / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5CCI Accession code: 5CCI / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj










