[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
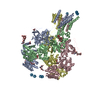
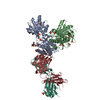
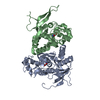
Yorodumi- PDB-6mmu: Triheteromeric NMDA receptor GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2A* in the '2-Knuck... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6mmu | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Triheteromeric NMDA receptor GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2A* in the '2-Knuckle-Asymmetric' conformation, in complex with glycine and glutamate, in the presence of 1 micromolar zinc chloride, and at pH 7.4 | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Ligand-gated Ion Channel / NMDA Receptor / ionotropic Glutamate Receptors / membrane protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationneurotransmitter receptor transport, plasma membrane to endosome / regulation of response to alcohol / response to ammonium ion / receptor recycling / response to environmental enrichment / directional locomotion / positive regulation of Schwann cell migration / pons maturation / regulation of cell communication / EPHB-mediated forward signaling ...neurotransmitter receptor transport, plasma membrane to endosome / regulation of response to alcohol / response to ammonium ion / receptor recycling / response to environmental enrichment / directional locomotion / positive regulation of Schwann cell migration / pons maturation / regulation of cell communication / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / response to hydrogen sulfide / auditory behavior / olfactory learning / conditioned taste aversion / dendritic branch / regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange / response to other organism / regulation of ARF protein signal transduction / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / cellular response to magnesium ion / serotonin metabolic process / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / positive regulation of inhibitory postsynaptic potential / response to methylmercury / suckling behavior / response to manganese ion / response to glycine / response to carbohydrate / propylene metabolic process / sleep / dendritic spine organization / cellular response to dsRNA / locomotion / regulation of NMDA receptor activity / cellular response to lipid / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / regulation of monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / NMDA glutamate receptor activity / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / response to glycoside / NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex / glutamate binding / neurotransmitter receptor complex / ligand-gated sodium channel activity / response to morphine / glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of axonogenesis / neuromuscular process / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / protein heterotetramerization / male mating behavior / regulation of synapse assembly / spinal cord development / response to amine / glycine binding / cellular response to zinc ion / startle response / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / dopamine metabolic process / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / response to lithium ion / positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol / cellular response to glycine / response to light stimulus / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / action potential / associative learning / conditioned place preference / excitatory synapse / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / monoatomic ion channel complex / social behavior / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / monoatomic cation transport / glutamate receptor binding / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / long-term memory / synaptic cleft / neuron development / phosphatase binding / prepulse inhibition / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / multicellular organismal response to stress / postsynaptic density, intracellular component / response to fungicide / monoatomic cation channel activity / calcium ion homeostasis / glutamate-gated receptor activity / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / cell adhesion molecule binding / cellular response to manganese ion / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jalali-Yazdi, F. / Chowdhury, S. / Yoshioka, C. / Gouaux, E. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2018 Journal: Cell / Year: 2018Title: Mechanisms for Zinc and Proton Inhibition of the GluN1/GluN2A NMDA Receptor. Authors: Farzad Jalali-Yazdi / Sandipan Chowdhury / Craig Yoshioka / Eric Gouaux /  Abstract: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) play essential roles in memory formation, neuronal plasticity, and brain development, with their dysfunction linked to a range of disorders from ischemia to ...N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) play essential roles in memory formation, neuronal plasticity, and brain development, with their dysfunction linked to a range of disorders from ischemia to schizophrenia. Zinc and pH are physiological allosteric modulators of NMDARs, with GluN2A-containing receptors inhibited by nanomolar concentrations of divalent zinc and by excursions to low pH. Despite the widespread importance of zinc and proton modulation of NMDARs, the molecular mechanism by which these ions modulate receptor activity has proven elusive. Here, we use cryoelectron microscopy to elucidate the structure of the GluN1/GluN2A NMDAR in a large ensemble of conformations under a range of physiologically relevant zinc and proton concentrations. We show how zinc binding to the amino terminal domain elicits structural changes that are transduced though the ligand-binding domain and result in constriction of the ion channel gate. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6mmu.cif.gz 6mmu.cif.gz | 550.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6mmu.ent.gz pdb6mmu.ent.gz | 451.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6mmu.json.gz 6mmu.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mm/6mmu https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mm/6mmu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mm/6mmu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mm/6mmu | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 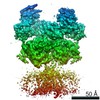 9162MC  9147C  9148C  9149C  9150C  9151C  9152C  9153C  9154C  9155C  9156C  9157C  9158C  9159C  9160C  9161C  9163C  9164C  9165C  6mm9C  6mmaC  6mmbC  6mmgC  6mmhC  6mmiC  6mmjC  6mmkC  6mmlC  6mmmC  6mmnC  6mmpC  6mmrC  6mmsC  6mmtC  6mmvC  6mmwC  6mmxC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 94189.781 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: UNP residues 1-838 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P35439 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P35439#2: Protein | | Mass: 93740.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 1-837 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q00959 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q00959#3: Protein | | Mass: 93703.305 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 1-837 / Mutation: H128S, N687Q Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q00959 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q00959#4: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #5: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Triheteromeric NMDA receptor GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2A* in the '2-Knuckle-Asymmetric' conformation, in complex with glycine and glutamate, in the presence of 1 micromolar zinc chloride, and at pH 7.4 Type: COMPLEX Details: Sample was heterologously expressed in TSA-201 cells, detergent solubilized, and affinity purified serially to obtain the triheteromeric receptor Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.5 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: TSA-201 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: TSA-201 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: This sample was monodisperse | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 291 K / Details: Sample was blotted for 3 seconds at blot force 1. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 22 sec. / Electron dose: 52 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 BASE (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 1891 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.13_2998: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 68275 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj