[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6kkm: Crystal structure of RbcL-Raf1 complex from Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6kkm | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of RbcL-Raf1 complex from Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CHAPERONE/PHOTOSYNTHESIS / RuBisCO / Chaperone / Raf1 / RbcL / CHAPERONE-PHOTOSYNTHESIS complex | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribulose bisphosphate carboxylase complex assembly / photorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / carbon fixation / photosynthesis / monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Nostoc sp. (bacteria) Nostoc sp. (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xia, L.Y. / Jiang, Y.L. / Kong, W.W. / Chen, Y. / Zhou, C.Z. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 5items China, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2020Title: Molecular basis for the assembly of RuBisCO assisted by the chaperone Raf1. Authors: Ling-Yun Xia / Yong-Liang Jiang / Wen-Wen Kong / Hui Sun / Wei-Fang Li / Yuxing Chen / Cong-Zhao Zhou /  Abstract: The folding and assembly of RuBisCO, the most abundant enzyme in nature, needs a series of chaperones, including the RuBisCO accumulation factor Raf1, which is highly conserved in cyanobacteria and ...The folding and assembly of RuBisCO, the most abundant enzyme in nature, needs a series of chaperones, including the RuBisCO accumulation factor Raf1, which is highly conserved in cyanobacteria and plants. Here, we report the crystal structures of Raf1 from cyanobacteria Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 and its complex with RuBisCO large subunit RbcL. Structural analyses and biochemical assays reveal that each Raf1 dimer captures an RbcL dimer, with the C-terminal tail inserting into the catalytic pocket, and further mediates the assembly of RbcL dimers to form the octameric core of RuBisCO. Furthermore, the cryo-electron microscopy structures of the RbcL-Raf1-RbcS assembly intermediates enable us to see a dynamic assembly process from RbcLRaf1 to the holoenzyme RbcLRbcS. In vitro assays also indicate that Raf1 can attenuate and reverse CcmM-mediated cyanobacterial RuBisCO condensation. Combined with previous findings, we propose a putative model for the assembly of cyanobacterial RuBisCO coordinated by the chaperone Raf1. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6kkm.cif.gz 6kkm.cif.gz | 604.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6kkm.ent.gz pdb6kkm.ent.gz | 500.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6kkm.json.gz 6kkm.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kk/6kkm https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kk/6kkm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kk/6kkm ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kk/6kkm | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0959C  0960C  0961C  0962C  6kknC  6lrrC  6lrsC  1rblS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 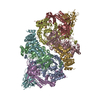
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 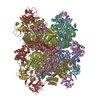
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41055.113 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria) Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria)Strain: PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576 / Gene: all5250 Production host:  References: UniProt: Q8YLP6 #2: Protein | Mass: 54913.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria) Nostoc sp. (strain PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576) (bacteria)Strain: PCC 7120 / SAG 25.82 / UTEX 2576 / Gene: cbbL, rbc, rbcA, rbcL, alr1524 Production host:  References: UniProt: P00879, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.75 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 55.32 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 289 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6 / Details: 8-10% 2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol and 0.1 M MES 6.0 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SSRF SSRF  / Beamline: BL19U1 / Wavelength: 0.97892 Å / Beamline: BL19U1 / Wavelength: 0.97892 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 S 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Oct 19, 2018 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.97892 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 3→50 Å / Num. obs: 82605 / % possible obs: 100 % / Redundancy: 13.5 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.195 / Net I/σ(I): 16 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 3→3.11 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 1.095 / Num. unique obs: 8166 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 1RBL Resolution: 3→49 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.901 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.86 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 0 / ESU R Free: 0.527 Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS U VALUES : REFINED INDIVIDUALLY
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 204.14 Å2 / Biso mean: 72.104 Å2 / Biso min: 18.05 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 3→49 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 3→3.075 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj