[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
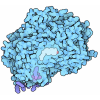
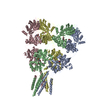
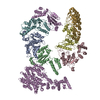
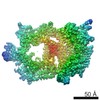
Yorodumi- PDB-5grs: Complex structure of the fission yeast SREBP-SCAP binding domains -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5grs | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Complex structure of the fission yeast SREBP-SCAP binding domains | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN TRANSPORT / protein complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of ergosterol biosynthetic process / positive regulation of ergosterol biosynthetic process / SREBP-SCAP complex / regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / sterol binding / SREBP signaling pathway / DNA-binding transcription activator activity / cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / steroid metabolic process / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific ...regulation of ergosterol biosynthetic process / positive regulation of ergosterol biosynthetic process / SREBP-SCAP complex / regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / sterol binding / SREBP signaling pathway / DNA-binding transcription activator activity / cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / steroid metabolic process / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / cellular response to hypoxia / protein dimerization activity / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / Golgi membrane / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / chromatin / endoplasmic reticulum / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gong, X. / Qian, H.W. / Wu, J.P. / Yan, N. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 2items China, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2016 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2016Title: Complex structure of the fission yeast SREBP-SCAP binding domains reveals an oligomeric organization. Authors: Xin Gong / Hongwu Qian / Wei Shao / Jingxian Li / Jianping Wu / Jun-Jie Liu / Wenqi Li / Hong-Wei Wang / Peter Espenshade / Nieng Yan /   Abstract: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) transcription factors are master regulators of cellular lipid homeostasis in mammals and oxygen-responsive regulators of hypoxic adaptation in fungi. ...Sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) transcription factors are master regulators of cellular lipid homeostasis in mammals and oxygen-responsive regulators of hypoxic adaptation in fungi. SREBP C-terminus binds to the WD40 domain of SREBP cleavage-activating protein (SCAP), which confers sterol regulation by controlling the ER-to-Golgi transport of the SREBP-SCAP complex and access to the activating proteases in the Golgi. Here, we biochemically and structurally show that the carboxyl terminal domains (CTD) of Sre1 and Scp1, the fission yeast SREBP and SCAP, form a functional 4:4 oligomer and Sre1-CTD forms a dimer of dimers. The crystal structure of Sre1-CTD at 3.5 Å and cryo-EM structure of the complex at 5.4 Å together with in vitro biochemical evidence elucidate three distinct regions in Sre1-CTD required for Scp1 binding, Sre1-CTD dimerization and tetrameric formation. Finally, these structurally identified domains are validated in a cellular context, demonstrating that the proper 4:4 oligomeric complex formation is required for Sre1 activation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5grs.cif.gz 5grs.cif.gz | 620.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5grs.ent.gz pdb5grs.ent.gz | 512.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5grs.json.gz 5grs.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  5grs_validation.pdf.gz 5grs_validation.pdf.gz | 965.9 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  5grs_full_validation.pdf.gz 5grs_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  5grs_validation.xml.gz 5grs_validation.xml.gz | 79.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  5grs_validation.cif.gz 5grs_validation.cif.gz | 116.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gr/5grs https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gr/5grs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gr/5grs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gr/5grs | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9537MC  5gpdC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 44956.750 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: UNP residues 567-961 / Mutation: C671S, C873S, C901S, C920S, C941S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: scp1, SPBC3B9.15c / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11868.574 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: UNP residues 986-1085 / Mutation: C1010S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: scp1, SPBC3B9.15c / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 30318.842 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: UNP residues 628-896 / Mutation: C644S, C672S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: sre1, SPBC19C2.09 / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex structure of the fission yeast SREBP-SCAP binding domains Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 20 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 157243 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj