[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-4udf: STRUCTURAL BASIS OF HUMAN PARECHOVIRUS NEUTRALIZATION BY HUMAN MO... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4udf | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | STRUCTURAL BASIS OF HUMAN PARECHOVIRUS NEUTRALIZATION BY HUMAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / HUMAN PARECHOVIRUS 1 / HUMAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY / HPEV1-AM28 FAB | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell nucleolus / host cell Golgi membrane / picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / ribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / channel activity / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell ...host cell nucleolus / host cell Golgi membrane / picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / ribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / channel activity / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / RNA helicase activity / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / symbiont-mediated activation of host autophagy / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / viral RNA genome replication / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / DNA-templated transcription / virion attachment to host cell / structural molecule activity / proteolysis / RNA binding / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Human parechovirus 1 Human parechovirus 1 HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 20 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shakeel, S. / Westerhuis, B.M. / Ora, A. / Koen, G. / Bakker, A.Q. / Claassen, Y. / Beaumont, T. / Wolthers, K.C. / Butcher, S.J. | ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2015 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2015Title: Structural Basis of Human Parechovirus Neutralization by Human Monoclonal Antibodies. Authors: Shabih Shakeel / Brenda M Westerhuis / Ari Ora / Gerrit Koen / Arjen Q Bakker / Yvonne Claassen / Koen Wagner / Tim Beaumont / Katja C Wolthers / Sarah J Butcher /   Abstract: Since it was first recognized in 2004 that human parechoviruses (HPeV) are a significant cause of central nervous system and neonatal sepsis, their clinical importance, primarily in children, has ...Since it was first recognized in 2004 that human parechoviruses (HPeV) are a significant cause of central nervous system and neonatal sepsis, their clinical importance, primarily in children, has started to emerge. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment is the only treatment available in such life-threatening cases and has given moderate success. Direct inhibition of parechovirus infection using monoclonal antibodies is a potential treatment. We have developed two neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against HPeV1 and HPeV2, namely, AM18 and AM28, which also cross-neutralize other viruses. Here, we present the mapping of their epitopes using peptide scanning, surface plasmon resonance, fluorescence-based thermal shift assays, electron cryomicroscopy, and image reconstruction. We determined by peptide scanning and surface plasmon resonance that AM18 recognizes a linear epitope motif including the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid on the C terminus of capsid protein VP1. This epitope is normally used by the virus to attach to host cell surface integrins during entry and is found in 3 other viruses that AM18 neutralizes. Therefore, AM18 is likely to cause virus neutralization by aggregation and by blocking integrin binding to the capsid. Further, we show by electron cryomicroscopy, three-dimensional reconstruction, and pseudoatomic model fitting that ordered RNA interacts with HPeV1 VP1 and VP3. AM28 recognizes quaternary epitopes on the capsid composed of VP0 and VP3 loops from neighboring pentamers, thereby increasing the RNA accessibility temperature for the virus-AM28 complex compared to the virus alone. Thus, inhibition of RNA uncoating probably contributes to neutralization by AM28. IMPORTANCE: Human parechoviruses can cause mild infections to severe diseases in young children, such as neonatal sepsis, encephalitis, and cardiomyopathy. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment is the ...IMPORTANCE: Human parechoviruses can cause mild infections to severe diseases in young children, such as neonatal sepsis, encephalitis, and cardiomyopathy. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment is the only treatment available in such life-threatening cases. In order to develop more targeted treatment, we have searched for human monoclonal antibodies that would neutralize human parechoviruses 1 and 2, associated with mild infections such as gastroenteritis and severe infections of the central nervous system, and thus allow safe treatment. In the current study, we show how two such promising antibodies interact with the virus, modeling the atomic interactions between the virus and the antibody to propose how neutralization occurs. Both antibodies can cause aggregation; in addition, one antibody interferes with the virus recognizing its target cell, while the other, recognizing only the whole virus, inhibits the genome uncoating and replication in the cell. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4udf.cif.gz 4udf.cif.gz | 8.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4udf.ent.gz pdb4udf.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4udf.json.gz 4udf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ud/4udf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ud/4udf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ud/4udf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ud/4udf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 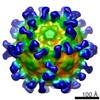 2761MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 20555.203 Da / Num. of mol.: 60 / Fragment: UNP residues 360-542 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: FAB FRAGMENTS OF HUMAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY, AM28 WERE ATTACHED TO THE VIRUS Source: (natural)  Human parechovirus 1 (strain Harris) / Strain: Harris / References: UniProt: Q66578 Human parechovirus 1 (strain Harris) / Strain: Harris / References: UniProt: Q66578#2: Protein | Mass: 25594.449 Da / Num. of mol.: 60 / Fragment: UNP residues 61-289 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: FAB FRAGMENTS OF HUMAN MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY, AM28 WERE ATTACHED TO THE VIRUS Source: (natural)  Human parechovirus 1 (strain Harris) / Strain: Harris / References: UniProt: Q66578 Human parechovirus 1 (strain Harris) / Strain: Harris / References: UniProt: Q66578#3: Antibody | Mass: 12168.451 Da / Num. of mol.: 60 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human)#4: Antibody | Mass: 13032.227 Da / Num. of mol.: 60 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human)Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: AM28 FAB FRAGMENT IN COMPLEX WITH HUMAN PARECHOVIRUS 1 Type: VIRUS |
|---|---|
| Details of virus | Host category: VERTEBRATES / Isolate: STRAIN / Type: VIRION |
| Natural host | Organism: Homo sapiens |
| Buffer solution | Name: 10mM TRIS HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1mM MgCl2 (1X TNM Buffer) / pH: 7.5 Details: 10mM TRIS HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1mM MgCl2 (1X TNM Buffer) |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: HOLEY CARBON |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Details: LIQUID ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 / Date: Feb 1, 2013 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 69000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4060 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1650 nm / Cs: 2 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GENERIC GATAN |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 65 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: Auto3DEM / Category: 3D reconstruction |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: WHOLE MICROGRAPH |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: I (icosahedral) |
| 3D reconstruction | Method: POLAR FOURIER TRANSFORM / Resolution: 20 Å / Num. of particles: 270 / Nominal pixel size: 2.17 Å Magnification calibration: SYMMETRY RELATED VP0 HELICES FITTING IN EM DENSITY Details: SUBMISSION BASED ON EXPERIMENTAL DATA FROM EMDB EMD-2761 Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient Details: METHOD--MOLECULAR DYNAMIC SIMULATION AND NORMAL MODE ANALYSIS REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--HOMOLOGY MODEL |
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 20 Å |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj



