[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
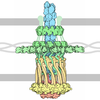
Yorodumi- PDB-3jc8: Architectural model of the type IVa pilus machine in a piliated state -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3jc8 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Architectural model of the type IVa pilus machine in a piliated state | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / motor / pilus / ring / membrane channel | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtype IV pilus assembly / type IV pilus-dependent motility / pilus assembly / protein secretion by the type II secretion system / protein secretion / cell outer membrane / cell division / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding ...type IV pilus assembly / type IV pilus-dependent motility / pilus assembly / protein secretion by the type II secretion system / protein secretion / cell outer membrane / cell division / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / electron tomography / cryo EM | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chang, Y.-W. / Rettberg, L.A. / Jensen, G.J. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2016 Journal: Science / Year: 2016Title: Architecture of the type IVa pilus machine. Authors: Yi-Wei Chang / Lee A Rettberg / Anke Treuner-Lange / Janet Iwasa / Lotte Søgaard-Andersen / Grant J Jensen /   Abstract: Type IVa pili are filamentous cell surface structures observed in many bacteria. They pull cells forward by extending, adhering to surfaces, and then retracting. We used cryo-electron tomography of ...Type IVa pili are filamentous cell surface structures observed in many bacteria. They pull cells forward by extending, adhering to surfaces, and then retracting. We used cryo-electron tomography of intact Myxococcus xanthus cells to visualize type IVa pili and the protein machine that assembles and retracts them (the type IVa pilus machine, or T4PM) in situ, in both the piliated and nonpiliated states, at a resolution of 3 to 4 nanometers. We found that T4PM comprises an outer membrane pore, four interconnected ring structures in the periplasm and cytoplasm, a cytoplasmic disc and dome, and a periplasmic stem. By systematically imaging mutants lacking defined T4PM proteins or with individual proteins fused to tags, we mapped the locations of all 10 T4PM core components and the minor pilins, thereby providing insights into pilus assembly, structure, and function. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3jc8.cif.gz 3jc8.cif.gz | 3.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3jc8.ent.gz pdb3jc8.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3jc8.json.gz 3jc8.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jc/3jc8 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jc/3jc8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jc/3jc8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jc/3jc8 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3247MC  3248C  3249C  3250C  3251C  3252C  3253C  3254C  3255C  3256C  3257C  3258C  3259C  3260C  3261C  3262C  3263C  3264C  3jc9C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 9 types, 115 molecules AaAbAcAdAeAfAgAhAiAjAkAlAmAnAoApAqArAsAtAuAvAwAxAyAzA1A2A3A4...
| #1: Protein | Mass: 17210.494 Da / Num. of mol.: 35 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria)#2: Protein | Mass: 62618.117 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q1D098 Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q1D098#3: Protein | Mass: 45191.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q1D0A0 Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q1D0A0#4: Protein | Mass: 24889.914 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q306N5 Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q306N5#5: Protein | Mass: 22911.150 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q306N4 Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q306N4#6: Protein | Mass: 42267.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q1D0B0 Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q1D0B0#7: Protein | Mass: 96199.984 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q9ZFG1 Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q9ZFG1#8: Protein | Mass: 18154.627 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q306N3 Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q306N3#9: Protein | Mass: 44704.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q1D813 Myxococcus xanthus DK 1622 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q1D813 |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: electron tomography |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Type IVa pilus machine in vivo / Type: COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: Plunged into liquid ethane (FEI VITROBOT MARK III). |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 / Date: Aug 26, 2013 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 27500 X / Cs: 2.2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder type: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN / Temperature: 77 K / Tilt angle max: -60 ° / Tilt angle min: 60 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 150 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF / Energyfilter upper: 20 eV / Energyfilter lower: 0 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: Simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique / Nominal pixel size: 7.8 Å / Actual pixel size: 7.8 Å / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj