[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-2n0k: Chemical shift assignments and structure of the alpha-crystallin ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 2n0k | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Chemical shift assignments and structure of the alpha-crystallin domain from human, HSPB5 | ||||||
 Components Components | Alpha-crystallin B chain | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | METAL BINDING PROTEIN / crystallin / human / ACD / Protein | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule polymerization or depolymerization / negative regulation of intracellular transport / apoptotic process involved in morphogenesis / regulation of programmed cell death / cardiac myofibril / tubulin complex assembly / structural constituent of eye lens / negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation / M band / lens development in camera-type eye ...microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / negative regulation of intracellular transport / apoptotic process involved in morphogenesis / regulation of programmed cell death / cardiac myofibril / tubulin complex assembly / structural constituent of eye lens / negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation / M band / lens development in camera-type eye / muscle organ development / actin filament bundle / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / HSF1-dependent transactivation / stress-activated MAPK cascade / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / muscle contraction / synaptic membrane / response to hydrogen peroxide / cellular response to gamma radiation / negative regulation of cell growth / Z disc / unfolded protein binding / response to estradiol / amyloid-beta binding / protein folding / response to heat / protein refolding / microtubule binding / dendritic spine / perikaryon / response to hypoxia / lysosome / protein stabilization / negative regulation of gene expression / axon / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / negative regulation of apoptotic process / protein-containing complex binding / structural molecule activity / cell surface / protein homodimerization activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | SOLUTION NMR / simulated annealing | ||||||
| Model details | closest to the average, model1 | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Rajagopal, P. / Klevit, R.E. / Shi, L. / Baker, D. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2015 Journal: Elife / Year: 2015Title: A conserved histidine modulates HSPB5 structure to trigger chaperone activity in response to stress-related acidosis. Authors: Rajagopal, P. / Tse, E. / Borst, A.J. / Delbecq, S.P. / Shi, L. / Southworth, D.R. / Klevit, R.E. #1: Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2009 Title: alphaB-crystallin: a hybrid solid-state/solution-state NMR investigation reveals structural aspects of the heterogeneous oligomer. Authors: Jehle, S. / van Rossum, B. / Stout, J.R. / Noguchi, S.M. / Falber, K. / Rehbein, K. / Oschkinat, H. / Klevit, R.E. / Rajagopal, P. #2:  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2010 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2010Title: Solid-state NMR and SAXS studies provide a structural basis for the activation of alphaB-crystallin oligomers. Authors: Stefan Jehle / Ponni Rajagopal / Benjamin Bardiaux / Stefan Markovic / Ronald Kühne / Joseph R Stout / Victoria A Higman / Rachel E Klevit / Barth-Jan van Rossum / Hartmut Oschkinat /  Abstract: The small heat shock protein alphaB-crystallin (alphaB) contributes to cellular protection against stress. For decades, high-resolution structural studies on oligomeric alphaB have been confounded by ...The small heat shock protein alphaB-crystallin (alphaB) contributes to cellular protection against stress. For decades, high-resolution structural studies on oligomeric alphaB have been confounded by its polydisperse nature. Here, we present a structural basis of oligomer assembly and activation of the chaperone using solid-state NMR and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). The basic building block is a curved dimer, with an angle of approximately 121 degrees between the planes of the beta-sandwich formed by alpha-crystallin domains. The highly conserved IXI motif covers a substrate binding site at pH 7.5. We observe a pH-dependent modulation of the interaction of the IXI motif with beta4 and beta8, consistent with a pH-dependent regulation of the chaperone function. N-terminal region residues Ser59-Trp60-Phe61 are involved in intermolecular interaction with beta3. Intermolecular restraints from NMR and volumetric restraints from SAXS were combined to calculate a model of a 24-subunit alphaB oligomer with tetrahedral symmetry. #3:  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2011 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2011Title: N-terminal domain of alphaB-crystallin provides a conformational switch for multimerization and structural heterogeneity. Authors: Stefan Jehle / Breanna S Vollmar / Benjamin Bardiaux / Katja K Dove / Ponni Rajagopal / Tamir Gonen / Hartmut Oschkinat / Rachel E Klevit /  Abstract: The small heat shock protein (sHSP) αB-crystallin (αB) plays a key role in the cellular protection system against stress. For decades, high-resolution structural studies on heterogeneous sHSPs have ...The small heat shock protein (sHSP) αB-crystallin (αB) plays a key role in the cellular protection system against stress. For decades, high-resolution structural studies on heterogeneous sHSPs have been confounded by the polydisperse nature of αB oligomers. We present an atomic-level model of full-length αB as a symmetric 24-subunit multimer based on solid-state NMR, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), and EM data. The model builds on our recently reported structure of the homodimeric α-crystallin domain (ACD) and C-terminal IXI motif in the context of the multimer. A hierarchy of interactions contributes to build multimers of varying sizes: Interactions between two ACDs define a dimer, three dimers connected by their C-terminal regions define a hexameric unit, and variable interactions involving the N-terminal region define higher-order multimers. Within a multimer, N-terminal regions exist in multiple environments, contributing to the heterogeneity observed by NMR. Analysis of SAXS data allows determination of a heterogeneity parameter for this type of system. A mechanism of multimerization into higher-order asymmetric oligomers via the addition of up to six dimeric units to a 24-mer is proposed. The proposed asymmetric multimers explain the homogeneous appearance of αB in negative-stain EM images and the known dynamic exchange of αB subunits. The model of αB provides a structural basis for understanding known disease-associated missense mutations and makes predictions concerning substrate binding and the reported fibrilogenesis of αB. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
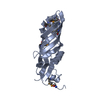
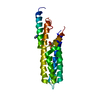
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  2n0k.cif.gz 2n0k.cif.gz | 515.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb2n0k.ent.gz pdb2n0k.ent.gz | 431.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  2n0k.json.gz 2n0k.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n0/2n0k https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n0/2n0k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n0/2n0k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n0/2n0k | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data | |
|---|---|
| Other databases |
|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||
| NMR ensembles |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 10200.497 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: unp residues 64-152 / Mutation: N146D Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CRYA2, CRYAB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CRYA2, CRYAB / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: SOLUTION NMR | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMR experiment |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR details | Text: Solution structure was determined with NOEs and RDCs. |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Details |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sample conditions |
|
-NMR measurement
| NMR spectrometer |
|
|---|
- Processing
Processing
| NMR software |
|
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj

 HSQC
HSQC