[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-2l14: Structure of CBP nuclear coactivator binding domain in complex wi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 2l14 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of CBP nuclear coactivator binding domain in complex with p53 TAD | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN BINDING / p53 / CBP / p300 / TAD | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationActivation of the TFAP2 (AP-2) family of transcription factors / Regulation of FOXO transcriptional activity by acetylation / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / Attenuation phase / LRR FLII-interacting protein 1 (LRRFIP1) activates type I IFN production / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of myeloid cells / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling ...Activation of the TFAP2 (AP-2) family of transcription factors / Regulation of FOXO transcriptional activity by acetylation / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / Attenuation phase / LRR FLII-interacting protein 1 (LRRFIP1) activates type I IFN production / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of myeloid cells / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling / Regulation of gene expression by Hypoxia-inducible Factor / cAMP response element binding protein binding / Notch-HLH transcription pathway / Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of MITF-M expression and activity / germ-line stem cell population maintenance / negative regulation of viral process / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / peptide lactyltransferase (CoA-dependent) activity / outer kinetochore / histone H3K18 acetyltransferase activity / N-terminal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / negative regulation of interferon-beta production / histone H3K27 acetyltransferase activity / negative regulation of helicase activity / Loss of function of TP53 in cancer due to loss of tetramerization ability / MRF binding / Regulation of TP53 Expression / signal transduction by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of G1 to G0 transition / negative regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate / Transcriptional activation of cell cycle inhibitor p21 / regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / ATP-dependent DNA/DNA annealing activity / Activation of NOXA and translocation to mitochondria / regulation of cell cycle G2/M phase transition / oligodendrocyte apoptotic process / negative regulation of miRNA processing / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hypoxia / positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process / oxidative stress-induced premature senescence / regulation of tissue remodeling / positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability / regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process / mRNA transcription / bone marrow development / circadian behavior / positive regulation of programmed necrotic cell death / T cell proliferation involved in immune response / regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process / histone deacetylase regulator activity / RUNX3 regulates CDKN1A transcription / germ cell nucleus / homolactic fermentation / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Death Receptors and Ligands / TP53 regulates transcription of additional cell cycle genes whose exact role in the p53 pathway remain uncertain / Activation of PUMA and translocation to mitochondria / face morphogenesis / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Association with Co-factors / regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of glial cell proliferation / negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation / mitochondrial DNA repair / cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus / T cell lineage commitment / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / thymocyte apoptotic process / ER overload response / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Caspase Activators and Caspases / cardiac septum morphogenesis / entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod / B cell lineage commitment / acetyltransferase activity / negative regulation of mitophagy / negative regulation of DNA replication / Zygotic genome activation (ZGA) / Association of TriC/CCT with target proteins during biosynthesis / PI5P Regulates TP53 Acetylation / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in Cytochrome C Release / necroptotic process / positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / negative regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / histone acetyltransferase activity / SUMOylation of transcription factors / TP53 regulates transcription of several additional cell death genes whose specific roles in p53-dependent apoptosis remain uncertain / TFIIB-class transcription factor binding / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / cellular response to actinomycin D / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / rRNA transcription / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / cellular response to UV-C / viral process / histone acetyltransferase complex / general transcription initiation factor binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | SOLUTION NMR / simulated annealing, molecular dynamics | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lee, C. / Martinez-Yamout, M.A. / Dyson, H.J. / Wright, P.E. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 2010 Journal: Biochemistry / Year: 2010Title: Structure of the p53 transactivation domain in complex with the nuclear receptor coactivator binding domain of CREB binding protein. Authors: Lee, C.W. / Martinez-Yamout, M.A. / Dyson, H.J. / Wright, P.E. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  2l14.cif.gz 2l14.cif.gz | 655.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb2l14.ent.gz pdb2l14.ent.gz | 553.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  2l14.json.gz 2l14.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/2l14 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/2l14 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/2l14 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/2l14 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 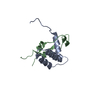
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||
| NMR ensembles |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 6568.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: CBP nuclear coactivator binding domain Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5574.096 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: p53 TAD Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Plasmid: pET21 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Plasmid: pET21 / Production host:  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: SOLUTION NMR | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMR experiment |
|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Details | Contents: 0.5 mM [U-99% 15N] CBP nuclear coactivator binding domain, 0.5 mM [U-99% 15N] p53 TAD, 0.5 mM [U-99% 13C; U-99% 15N] CBP nuclear coactivator binding domain, 0.5 mM [U-99% 13C; U-99% 15N] ...Contents: 0.5 mM [U-99% 15N] CBP nuclear coactivator binding domain, 0.5 mM [U-99% 15N] p53 TAD, 0.5 mM [U-99% 13C; U-99% 15N] CBP nuclear coactivator binding domain, 0.5 mM [U-99% 13C; U-99% 15N] p53 TAD, 90% H2O/10% D2O Solvent system: 90% H2O/10% D2O | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Sample conditions | Ionic strength: 0.05 / pH: 6.5 / Pressure: ambient / Temperature: 298 K |
-NMR measurement
| NMR spectrometer |
|
|---|
- Processing
Processing
| NMR software | Name:  Amber / Version: 9 Amber / Version: 9 Developer: Case, Darden, Cheatham, III, Simmerling, Wang, Duke, Luo, ... and Kollm Classification: refinement |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Method: simulated annealing, molecular dynamics / Software ordinal: 1 |
| NMR representative | Selection criteria: lowest energy |
| NMR ensemble | Conformer selection criteria: structures with the lowest energy Conformers calculated total number: 100 / Conformers submitted total number: 20 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






















