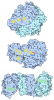
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1ofg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | GLUCOSE-FRUCTOSE OXIDOREDUCTASE | ||||||
 Components Components | GLUCOSE-FRUCTOSE OXIDOREDUCTASE | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | OXIDOREDUCTASE / NADP BINDING / OSMOTIC PROTECTION / PERIPLASM | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglucose-fructose oxidoreductase / sorbitol biosynthetic process / glucose-fructose oxidoreductase activity / periplasmic space / nucleotide binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Zymomonas mobilis (bacteria) Zymomonas mobilis (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  MIR / Resolution: 2.7 Å MIR / Resolution: 2.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kingston, R.L. / Scopes, R.K. / Baker, E.N. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 1996 Journal: Structure / Year: 1996Title: The structure of glucose-fructose oxidoreductase from Zymomonas mobilis: an osmoprotective periplasmic enzyme containing non-dissociable NADP. Authors: Kingston, R.L. / Scopes, R.K. / Baker, E.N. #1:  Journal: J.Bacteriol. / Year: 1994 Journal: J.Bacteriol. / Year: 1994Title: Sorbitol Promotes Growth of Zymomonas Mobilis in Environments with High Concentrations of Sugar: Evidence for a Physiological Function of Glucose-Fructose Oxidoreductase in Osmoprotection Authors: Loos, H. / Kramer, R. / Sahm, H. / Sprenger, G.A. #2:  Journal: J.Bacteriol. / Year: 1992 Journal: J.Bacteriol. / Year: 1992Title: Cloning, Sequence Analysis, and Expression of the Structural Gene Encoding Glucose-Fructose Oxidoreductase from Zymomonas Mobilis Authors: Kanagasundaram, V. / Scopes, R.K. #3:  Journal: J.Bacteriol. / Year: 1986 Journal: J.Bacteriol. / Year: 1986Title: Glucose-Fructose Oxidoreductase, a New Enzyme Isolated from Zymomonas Mobilis that is Responsible for Sorbitol Production Authors: Zachariou, M. / Scopes, R.K. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1ofg.cif.gz 1ofg.cif.gz | 450.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1ofg.ent.gz pdb1ofg.ent.gz | 371.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1ofg.json.gz 1ofg.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/of/1ofg https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/of/1ofg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/of/1ofg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/of/1ofg | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 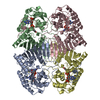
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 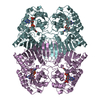
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS oper:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | NON-CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC SYMMETRY CONSTRAINTS WERE APPLIED THROUGHOUT THE REFINEMENT. THUS THE SIX MODELLED SUBUNITS (A, B, C, D, E, F) ARE ALL IDENTICAL. CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS CALCULATED DURING MAP AVERAGING PROCEDURES SUGGEST THERE MAY BE SMALL DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SUBUNITS. THESE HAVE NOT BEEN MODELLED DUE TO THE LIMITED RESOLUTION OF THE DATA. |
- Components
Components
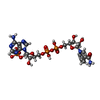
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42213.957 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Zymomonas mobilis (bacteria) / Cellular location: PERIPLASM Zymomonas mobilis (bacteria) / Cellular location: PERIPLASMReferences: UniProt: Q07982, glucose-fructose oxidoreductase #2: Chemical | ChemComp-NDP / #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 4 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 4 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.7 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 54 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal grow | pH: 5.5 / Details: pH 5.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 277 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU / Wavelength: 1.5418 ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU / Wavelength: 1.5418 |
| Detector | Type: RIGAKU / Detector: IMAGE PLATE / Date: Apr 1, 1996 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: GRAPHITE(002) / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.5418 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.7→50 Å / Num. obs: 71500 / % possible obs: 91 % / Observed criterion σ(I): 0 / Redundancy: 4.8 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 44 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.09 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.7→2.87 Å / Redundancy: 2 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.265 / % possible all: 60 |
| Reflection | *PLUS Num. measured all: 353200 |
| Reflection shell | *PLUS % possible obs: 60 % / Num. unique obs: 7701 / Num. measured obs: 15509 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MIR / Resolution: 2.7→50 Å / σ(F): 0 / Stereochemistry target values: ENGH AND HUBER (1991) MIR / Resolution: 2.7→50 Å / σ(F): 0 / Stereochemistry target values: ENGH AND HUBER (1991)Details: THE OCCUPANCIES OF SOLVENT MOLECULES WITH HIGH TEMPERATURE FACTORS WERE REDUCED TO 0.5 IN THE COURSE OF STRUCTURE REFINEMENT. THERE ARE CLEAR INDICATIONS OF ALTERNATE CONFORMATIONS FOR THE ...Details: THE OCCUPANCIES OF SOLVENT MOLECULES WITH HIGH TEMPERATURE FACTORS WERE REDUCED TO 0.5 IN THE COURSE OF STRUCTURE REFINEMENT. THERE ARE CLEAR INDICATIONS OF ALTERNATE CONFORMATIONS FOR THE FOLLOWING RESIDUES (NOT YET MODELLED): GLN 256, MET 314
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.7→50 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Software | *PLUS Name: TNT / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS Rfactor obs: 0.203 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj