+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8727 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The cryo-ET structure of frozen-hydrated honey bee Z-disk | ||||||||||||
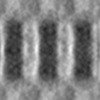
 Map data Map data | frozen-hydrated honey bee Z-disk- filtered to 60 Angstrom | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
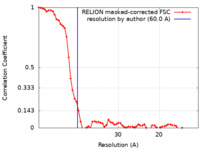
| Method | subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 60.0 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Taylor KA / Hu Z | ||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Muscle Res Cell Motil / Year: 2017 Journal: J Muscle Res Cell Motil / Year: 2017Title: Structure of isolated Z-disks from honeybee flight muscle. Authors: Mara Rusu / Zhongjun Hu / Kenneth A Taylor / John Trinick /   Abstract: The Z-disk is a complex structure comprising some 40 proteins that are involved in the transmission of force developed during muscle contraction and in important signalling pathways that govern ...The Z-disk is a complex structure comprising some 40 proteins that are involved in the transmission of force developed during muscle contraction and in important signalling pathways that govern muscle homeostasis. In the Z-disk the ends of antiparallel thin filaments from adjacent sarcomeres are crosslinked by α-actinin. The structure of the Z-disk lattice varies greatly throughout the animal kingdom. In vertebrates the thin filaments form a tetragonal lattice, whereas invertebrate flight muscle has a hexagonal lattice. The width of the Z-disk varies considerably and correlates with the number of α-actinin bridges. A detailed description at a high resolution of the Z-disk lattice is needed in order to better understand muscle function and disease. The molecular architecture of the Z-disk lattice in honeybee (Apis mellifera) is known from plastic embedded thin sections to a resolution of 7 nm, which is not sufficient to dock component protein crystal structures. It has been shown that sectioning is a damaging process that leads to the loss of finer details present in biological specimens. However, the Apis Z-disk is a thin structure (120 nm) suitable for cryo EM. We have isolated intact honeybee Z-disks from indirect flight muscle, thus obviating the need of plastic sectioning. We have employed cryo electron tomography and image processing to investigate the arrangement of proteins within the hexagonal lattice of the Apis Z-disk. The resolution obtained, ~6 nm, was probably limited by damage caused by the harshness of the conditions used to extract the myofibrils and isolate the Z-disks. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8727.map.gz emd_8727.map.gz | 24.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8727-v30.xml emd-8727-v30.xml emd-8727.xml emd-8727.xml | 19.7 KB 19.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_8727_fsc.xml emd_8727_fsc.xml | 6.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_8727.png emd_8727.png | 255.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_8727_additional.map.gz emd_8727_additional.map.gz emd_8727_additional_1.map.gz emd_8727_additional_1.map.gz | 2.1 GB 2.1 GB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8727 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8727 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8727 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8727 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10095 (Title: Structure of the Z-disk isolated from the indirect flight muscle of the honey bee EMPIAR-10095 (Title: Structure of the Z-disk isolated from the indirect flight muscle of the honey beeData size: 3.0 / Data #1: tomo9.mrc [class averages]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8727.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8727.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | frozen-hydrated honey bee Z-disk- filtered to 60 Angstrom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 7.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: frozen-hydrated honey bee Z-disk - raw tomogram. The...
| File | emd_8727_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | frozen-hydrated honey bee Z-disk - raw tomogram. The contour level here is non-sense. The map is raw tomogram, which is used to make the subvolume. Layer line data is not actually layer line, instead, it is a coordiates file for extracting subvolume | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: frozen-hydrated honey bee Z-disk - raw tomogram. The...
| File | emd_8727_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | frozen-hydrated honey bee Z-disk - raw tomogram. The contour level here is non-sense. The map is raw tomogram, which is used to make the subvolume. Layer line data is not actually layer line, instead, it is a coordiates file for extracting subvolume | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Z-disc
| Entire | Name: Z-disc |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Z-disc
| Supramolecule | Name: Z-disc / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Z-disc directly isolated from Apis mellifera (honey bee) indirect flight muscle |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVGMGQKDSY VGDEAQSKRG ILTLKYPIEH GIITNWDDME KIWHHTFYNE LRVAPEEHPV LLTEAPLNPK ANREKMTQIM FETFNSPAMY VAIQAVLSLY ASGRTTGIVL DSGDGVSHTV PIYEGYALPH AILRLDLAGR DLTDYLMKIL TERGYSFTTT AEREIVRDIK ...String: MVGMGQKDSY VGDEAQSKRG ILTLKYPIEH GIITNWDDME KIWHHTFYNE LRVAPEEHPV LLTEAPLNPK ANREKMTQIM FETFNSPAMY VAIQAVLSLY ASGRTTGIVL DSGDGVSHTV PIYEGYALPH AILRLDLAGR DLTDYLMKIL TERGYSFTTT AEREIVRDIK EKLCYVALDF EQEMATAAAS TSLEKSYELP DGQVITIGNE RFRCPEALFQ PSFLGMESCG IHETVYNSIM KCDVDIRKDL YANNVLSGGT TMYPGIADRM QKEITALAPS TIKIKIIAPP ERKYSVWIGG SILASLSTFQ QMWISKQEYD ESGPGIVHRK CF |
-Macromolecule #2: alpha-actinin
| Macromolecule | Name: alpha-actinin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MEEYERLASD LLEWIRRTMP WLASRQTDNS LAGCQKKLEE YRTYRRKHKP PRVEQKAKLE TNFNTLQTKL RLSNRPAYMP TEGKMVSDIN KAWKGLELAE KSFEEWLLSE MMRLERLEHL AQKFKHKADA HEEWTAGKEE MLTSQHFRQC KLNELKALKK KHEAFESDLA ...String: MEEYERLASD LLEWIRRTMP WLASRQTDNS LAGCQKKLEE YRTYRRKHKP PRVEQKAKLE TNFNTLQTKL RLSNRPAYMP TEGKMVSDIN KAWKGLELAE KSFEEWLLSE MMRLERLEHL AQKFKHKADA HEEWTAGKEE MLTSQHFRQC KLNELKALKK KHEAFESDLA AHQDRVEQIA AIAQELNTLE YHDSASVNAR CQRICDQWDR LGTLTQRRRQ ALDEAERILE KIDVLHLEFA KRAAPFNNWL DGTREDLVDM FIVHTMEEIQ GLMDAHAAFK ATLGEADKEY NAIVGLVREV ESIVKQFQIP GGLENPYTTL TALDLTKKWS DVRQLVPQRD GTLQAELRKQ QNNELLRRQF AEKANAVGPW IERQLDAVTA IGLGLQGTLE DQLHRLKEYE QAVYQYKVHL EELEKIHQAV QEGMIFENRY TQYTMETLRV GWEQLLTSIN RNINEVENQI LTRDSKGITQ EQLNEFRSSF NHFDKNRTGR LAPDEFKSCL VSLGYSIGKD RQGDIDFQRI LAIVDPNNSG YVHFDAFLDF MTRESTDTDT AEQVIDSFRI LAGDKPYILA DELRRELPPD QAEYCIQRMP PYKGPNAIPG ALDYRSFSTA LYGESDL |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | tissue |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 Component:
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R3.5/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 20 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER Details: Carbon coated grids were made hydrophilic by glow discharging for 40 seconds at a high tension of 10 kV in a Cressington 208 Carbon Coater. | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: After the Z-disk suspension was added to the grid it was left to settle for 10-15 seconds followed by washing with low salt buffer (25 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl). The washing step is crucial for ...Details: After the Z-disk suspension was added to the grid it was left to settle for 10-15 seconds followed by washing with low salt buffer (25 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl). The washing step is crucial for the removal of salts present in the extraction buffer, ensuring that plunge frozen grids were free of contamination. Plunge freezing was carried out using Quantifoil grids (Agar Scientific) in a Vitrobot Mark IV (FEI) at 4-5 degrees C, 90-100% humidity using a blotting force of 3-5 for 4-6 seconds.. | |||||||||
| Details | Indirect flight muscle was harvested from the thorax of Apis mellifera obtained from a local bee keeper. Myofibrils in suspension were prepared according to previously published methods (Bullard et al., 1973; Saide and Ullrick, 1974) with the following modifications. The IFM were collected in ice cold sucrose containing buffer (0.3 M sucrose, 0.1 M KCl, 0.01 M potassium phosphate pH 7, 1 mM MgCl2, 2 mM EGTA, 0.02 M NaN3 and EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Tablets followed by homogenization using a Wheaton tissue grinder. Soluble proteins and sucrose were washed away by centrifugation in 0.1 M KCl, 0.01 M potassium phosphate pH 7 buffer. Myofibrils in suspension were stored in 75% glycerol at -80 degrees C. Intact Z-disks were isolated by incubating myofibrils on ice in a high ionic strength extraction solution containing 0.7 M KCl, 0.6 M KI, 0.08 M NaHCO3 pH 8 for 60 minutes. Following extraction Z-disks were either negatively stained or plunge frozen for further electron microscopic investigation. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Details | Tilt series were recorded using the Saxton acquisition scheme (Saxton et al., 1984). Tilt angles ranged from -69.87 to +67.66 degrees starting at 0 degrees, 96 total images, with an initial step of 2 degrees. The average electron dose/micrograph was ~0.7 electrons/Angstrom2. A total of 12 tilt series, designated tomo1 - tomo12, were collected but only one proved to be useful, tomo9. The others had poor resolution due to either low intrinsic order, excessive extraction of actin or other structural Z-disk proteins, or due to excessive radiation damage. |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Average electron dose: 1.0 e/Å2 / Details: Electron dose may not be accurate. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 22500 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 22500 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | For actin, filaments of 28 subunits having the helical symmetry of 28/13 were constructed and maps computed using the software pdb2mrc. These maps were then placed manually within the Z-disk thin filaments and fit quantitatively using chimera. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)