[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7738: Single-Molecule 3D Image of neurexin 1 alpha by Individual Partic... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7738 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Single-Molecule 3D Image of neurexin 1 alpha by Individual Particle Electron Tomography (No. 080) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Neurexin 1 alpha | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | electron tomography / negative staining / Resolution: 15.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Liu JF / Misra A / Reddy S / White MA / Ren G / Rudenko G | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2018 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2018Title: Structural Plasticity of Neurexin 1α: Implications for its Role as Synaptic Organizer. Authors: Jianfang Liu / Anurag Misra / M V V V Sekhar Reddy / Mark Andrew White / Gang Ren / Gabby Rudenko /  Abstract: α-Neurexins are synaptic organizing molecules implicated in neuropsychiatric disorders. They bind and arrange an array of different partners in the synaptic cleft. The extracellular region of ...α-Neurexins are synaptic organizing molecules implicated in neuropsychiatric disorders. They bind and arrange an array of different partners in the synaptic cleft. The extracellular region of neurexin 1α (n1α) contains six LNS domains (L1-L6) interspersed by three Egf-like repeats. N1α must encode highly evolved structure-function relationships in order to fit into the narrow confines of the synaptic cleft, and also recruit its large, membrane-bound partners. Internal molecular flexibility could provide a solution; however, it is challenging to delineate because currently no structural methods permit high-resolution structure determination of large, flexible, multi-domain protein molecules. To investigate the structural plasticity of n1α, in particular the conformation of domains that carry validated binding sites for different protein partners, we used a panel of structural techniques. Individual particle electron tomography revealed that the N-terminally and C-terminally tethered domains, L1 and L6, have a surprisingly limited range of conformational freedom with respect to the linear central core containing L2 through L5. A 2.8-Å crystal structure revealed an unexpected arrangement of the L2 and L3 domains. Small-angle X-ray scattering and electron tomography indicated that incorporation of the alternative splice insert SS6 relieves the restricted conformational freedom between L5 and L6, suggesting that SS6 may work as a molecular toggle. The architecture of n1α thus encodes a combination of rigid and flexibly tethered domains that are uniquely poised to work together to promote its organizing function in the synaptic cleft, and may permit allosterically regulated and/or concerted protein partner binding. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7738.map.gz emd_7738.map.gz | 38 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7738-v30.xml emd-7738-v30.xml emd-7738.xml emd-7738.xml | 10 KB 10 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_7738_fsc.xml emd_7738_fsc.xml | 7.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_7738.png emd_7738.png | 16.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7738 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7738 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7738 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7738 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_7738_validation.pdf.gz emd_7738_validation.pdf.gz | 78 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_7738_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_7738_full_validation.pdf.gz | 77.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_7738_validation.xml.gz emd_7738_validation.xml.gz | 494 B | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7738 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7738 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7738 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7738 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7639C  7640C  7641C  7642C  7643C  7644C  7645C  7646C  7647C  7648C  7649C  7650C  7651C  7652C  7653C  7654C  7655C  7656C  7657C  7658C  7659C  7660C  7661C  7662C  7663C  7664C  7665C  7666C  7667C  7668C  7669C  7670C 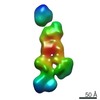 7671C  7672C  7673C  7674C  7675C  7676C  7677C  7678C  7679C 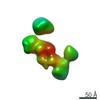 7680C  7681C  7682C  7683C  7684C  7685C  7686C  7687C  7688C  7689C  7690C  7691C  7692C  7693C  7694C  7695C  7696C  7697C  7698C  7699C  7700C  7701C  7702C  7703C  7704C  7705C  7706C  7707C  7708C  7709C  7710C  7711C  7712C  7713C 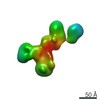 7714C  7715C  7716C  7717C  7718C  7719C 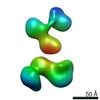 7720C  7721C  7722C  7723C  7724C  7725C  7726C  7727C  7728C  7729C  7730C  7731C  7732C  7733C  7734C  7735C  7736C 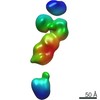 7737C  7739C  7740C  7741C  7742C  7743C  7744C  7745C  7746C  7747C  7748C  7749C  7750C  7751C  7752C  7753C  7754C  7755C  7756C  7757C  7758C  7759C  7760C  7761C  7762C  7763C  7764C  7765C  7766C  7767C  7768C  6cw1C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7738.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 42.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7738.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 42.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Neurexin 1 alpha | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.48 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : neurexin 1 alpha
| Entire | Name: neurexin 1 alpha |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: neurexin 1 alpha
| Supramolecule | Name: neurexin 1 alpha / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 0.137 kDa/nm |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  unidentified baculovirus unidentified baculovirus |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | electron tomography |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 / Details: 25 mM Tris pH 8, 100 mM NaCl, 3 mM CaCl2 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: uranyl formate Details: The grid was stained for 15 s by sequential submersion in two drops of uranyl formate (UF). |
| Grid | Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.039 kPa |
| Details | The purified neurexin 1 alpha proteins were stored in 25 mM Tris pH 8, 100 mM NaCl in flash-frozen aliquots. |
| Sectioning | Other: NO SECTIONING |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | ZEISS LIBRA120PLUS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: In-column Omega Filter |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Number real images: 81 / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 15.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source: LAB6 |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.2 mm / Nominal magnification: 80000 |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | X-ray speckles in images were removed before alignment and 3D reconstruction. |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 15.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF Details: The 3D reconstruction was performed by Individual-Particle Electron Tomography (IPET). Number images used: 65 |
| CTF correction | Software: (Name: TOMOCTF,  IMOD) IMOD)Details: Micrographs were aligned together by IMOD. The CTF was corrected by TOMOCTF. |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


