登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-7529タイトル GluN1-GluN@B NMDA receptors with exon 5 GluN1-GluN2B NMDA receptor with exon 5 複合体 : GluN1-GluN2B NMDA receptor ion channel複合体 : Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1タンパク質・ペプチド : Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1複合体 : Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2Bタンパク質・ペプチド : Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2Bリガンド : 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Rattus norvegicus (ドブネズミ)手法 / / 解像度 : 4.6 Å Furukawa H / Grant T 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Mental Health (NIH/NIMH) MH085926 National Institutes of Health/National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIH/NIGMS) GM105730 Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI)
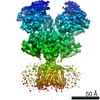
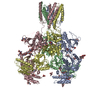
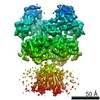
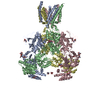
ジャーナル : Neuron / 年 : 2018タイトル : Structural Mechanism of Functional Modulation by Gene Splicing in NMDA Receptors.著者 : Michael C Regan / Timothy Grant / Miranda J McDaniel / Erkan Karakas / Jing Zhang / Stephen F Traynelis / Nikolaus Grigorieff / Hiro Furukawa / 要旨 : Alternative gene splicing gives rise to N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor ion channels with defined functional properties and unique contributions to calcium signaling in a given chemical ... Alternative gene splicing gives rise to N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor ion channels with defined functional properties and unique contributions to calcium signaling in a given chemical environment in the mammalian brain. Splice variants possessing the exon-5-encoded motif at the amino-terminal domain (ATD) of the GluN1 subunit are known to display robustly altered deactivation rates and pH sensitivity, but the underlying mechanism for this functional modification is largely unknown. Here, we show through cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) that the presence of the exon 5 motif in GluN1 alters the local architecture of heterotetrameric GluN1-GluN2 NMDA receptors and creates contacts with the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of the GluN1 and GluN2 subunits, which are absent in NMDA receptors lacking the exon 5 motif. The unique interactions established by the exon 5 motif are essential to the stability of the ATD/LBD and LBD/LBD interfaces that are critically involved in controlling proton sensitivity and deactivation. 履歴 登録 2018年3月7日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2018年5月16日 - マップ公開 2018年10月3日 - 更新 2025年5月14日 - 現状 2025年5月14日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報
 データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 3件
米国, 3件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Neuron / 年: 2018
ジャーナル: Neuron / 年: 2018
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_7529.map.gz
emd_7529.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-7529-v30.xml
emd-7529-v30.xml emd-7529.xml
emd-7529.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_7529.png
emd_7529.png emd-7529.cif.gz
emd-7529.cif.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7529
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7529 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7529
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7529 emd_7529_validation.pdf.gz
emd_7529_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_7529_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_7529_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_7529_validation.xml.gz
emd_7529_validation.xml.gz emd_7529_validation.cif.gz
emd_7529_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7529
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7529 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7529
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7529 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
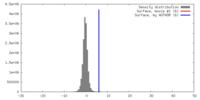
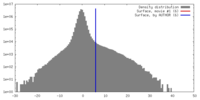
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_7529.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_7529.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素


 Spodoptera frugiperda multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (ウイルス)
Spodoptera frugiperda multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (ウイルス)
 Spodoptera frugiperda multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (ウイルス)
Spodoptera frugiperda multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (ウイルス)
 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)