[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
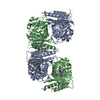
Yorodumi- EMDB-70119: Pr/Pr homodimer of Stigmatella aurantiaca bacteriophytochrome 2 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Pr/Pr homodimer of Stigmatella aurantiaca bacteriophytochrome 2 | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Full map | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Photoreceptor / Bacteriophytochrome / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Stigmatella aurantiaca (bacteria) Stigmatella aurantiaca (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.0 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Karki P / Stojkovic EA / Schmidt M | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Struct Dyn / Year: 2025 Journal: Struct Dyn / Year: 2025Title: Structures of myxobacterial phytochrome revealed by cryo-EM using the Spotiton technique and with x-ray crystallography. Authors: Prabin Karki / David Menendez / William Budell / Shishir Dangi / Carolina Hernandez / Joshua Mendez / Srinivasan Muniyappan / Shibom Basu / Peter Schwander / Tek N Malla / Emina A Stojković / Marius Schmidt /   Abstract: Phytochromes are red-light photoreceptors first identified in plants, with homologs found in bacteria and fungi, that regulate a variety of critical physiological processes. They undergo a reversible ...Phytochromes are red-light photoreceptors first identified in plants, with homologs found in bacteria and fungi, that regulate a variety of critical physiological processes. They undergo a reversible photocycle between two distinct states: a red-light-absorbing Pr form and a far-red light-absorbing Pfr form. This Pr/Pfr photoconversion controls the activity of a C-terminal enzymatic domain, typically a histidine kinase (HK). However, the molecular mechanisms underlying light-induced regulation of HK activity in bacteria remain poorly understood, as only a few structures of unmodified bacterial phytochromes with HK activity are known. Recently, cryo-EM structures of a wild-type bacterial phytochrome with HK activity are solved that reveal homodimers in both the Pr and Pfr states, as well as a heterodimer with individual monomers in distinct Pr and Pfr states. Cryo-EM structures of a truncated version of the same phytochrome-lacking the HK domain-also show a homodimer in the Pfr state and a Pr/Pfr heterodimer. Here, we describe in detail how structural information is obtained from cryo-EM data on a full-length intact bacteriophytochrome, and how the cryo-EM structure can contribute to the understanding of the function of the phytochrome. In addition, we compare the cryo-EM structure to an unusual x-ray structure that is obtained from a fragmented full-length phytochrome crystallized in the Pr-state. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_70119.map.gz emd_70119.map.gz | 36.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-70119-v30.xml emd-70119-v30.xml emd-70119.xml emd-70119.xml | 15.4 KB 15.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_70119_fsc.xml emd_70119_fsc.xml | 7.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_70119.png emd_70119.png | 32.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-70119.cif.gz emd-70119.cif.gz | 5.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_70119_half_map_1.map.gz emd_70119_half_map_1.map.gz emd_70119_half_map_2.map.gz emd_70119_half_map_2.map.gz | 35.7 MB 35.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70119 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70119 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70119 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70119 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_70119.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 38.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_70119.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 38.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Full map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.658 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_70119_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_70119_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Stigmatella aurantiaca bacteriophytochrome
| Entire | Name: Stigmatella aurantiaca bacteriophytochrome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Stigmatella aurantiaca bacteriophytochrome
| Supramolecule | Name: Stigmatella aurantiaca bacteriophytochrome / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Stigmatella aurantiaca (bacteria) Stigmatella aurantiaca (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 81 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Bacteriophytochrome
| Macromolecule | Name: Bacteriophytochrome / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Stigmatella aurantiaca (bacteria) Stigmatella aurantiaca (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: ELSQCDREPI HLLGGIQAYG VLLAFRGPDR RLEVVSANTQ ALLGRPPEAL LGKTAAQVLP AELWAQWELL SARGALRVAL PSGPYRALLH ESDGLTVLEL EPAELQPDME ETALELVRRL VSPLAGAKGT RELLQTAANT VRALTGFDRV MVYRFDADWH GEVLAESKRE ...String: ELSQCDREPI HLLGGIQAYG VLLAFRGPDR RLEVVSANTQ ALLGRPPEAL LGKTAAQVLP AELWAQWELL SARGALRVAL PSGPYRALLH ESDGLTVLEL EPAELQPDME ETALELVRRL VSPLAGAKGT RELLQTAANT VRALTGFDRV MVYRFDADWH GEVLAESKRE GMDGFLGMHF PATDIPVQAR ALYTRNPLRL IANARARPVP LVPSVVPELG RPLDLSGSAL RSVSPIHLEY LRNMGVEASF SLSLLKDGAL WGLIACHHLA PLHLSYERRR ACEVLTQLLA LQLSSEERAA EAAEDSHRAA LLGPLATSLG AGGTLEEALA KDGARVLELT GATGAALLLG GEPLLVGRTP SMDEVEALAA WLAPQPFQTS FHTERLGSLY PPLAARADVA AGLLAVRLAP ASSRLALWFR PEAVRTISWA GNPRKPAEPE PGHARLHPRG SFQAWEETVR ETSPAWKRAD LAAAEGFRSA LIGVVLRQAA ELERLSEALS RSNAELDAFG HTVAHDLKEP LRGIQQYAGF VMEDYHGALG PEGRGHMESL MWLAQRSGDM LDGLFEYSRA GRVDLAWGEV NMQEVVDEVL ATLSTRFQAE KLTVRMPRRL PTVRCDGIRI AQVWANLLVN AAKYQEGPER WVEAGFHGPG EPRPGAAGRY ASAYVFYVKD PGIGIAPPFH EAIFEMFRRL HSAKAYGGGT GVGLAIARRL VQLHGGALWV DSAPKQGATF YFTLGRGPG |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 45.47 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





































