[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-6652: Ensemble cryo-EM uncovers inchworm-like translocation of a viral ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6652 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Ensemble cryo-EM uncovers inchworm-like translocation of a viral IRES through the ribosome | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Saccharomyces cerevisiae 80S ribosome bound to eEF2-GDP-sordarin and TSV IRES, Structure IV. For classification, 2D masking around the E site was used, including the 5' domain of PKI. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | cryo-EM / translocation / IRES / ribosome / eEF2 | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPeptide chain elongation / Synthesis of diphthamide-EEF2 / positive regulation of translational elongation / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, LSU-rRNA,5S) / regulation of amino acid metabolic process / negative regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / translational readthrough / positive regulation of translational fidelity / : / RMTs methylate histone arginines ...Peptide chain elongation / Synthesis of diphthamide-EEF2 / positive regulation of translational elongation / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, LSU-rRNA,5S) / regulation of amino acid metabolic process / negative regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / translational readthrough / positive regulation of translational fidelity / : / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Protein methylation / mTORC1-mediated signalling / Protein hydroxylation / ribosome-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / pre-mRNA 5'-splice site binding / GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit assembly / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay / nonfunctional rRNA decay / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Translation initiation complex formation / response to cycloheximide / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / cleavage in ITS2 between 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / preribosome, small subunit precursor / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / mRNA destabilization / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / preribosome, large subunit precursor / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / negative regulation of translational frameshifting / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / translational elongation / endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 3'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / Ub-specific processing proteases / 90S preribosome / translation elongation factor activity / ribosomal subunit export from nucleus / translational termination / regulation of translational fidelity / protein-RNA complex assembly / maturation of LSU-rRNA / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / translation regulator activity / Neutrophil degranulation / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity / rescue of stalled cytosolic ribosome / cellular response to amino acid starvation / protein kinase C binding / ribosome assembly / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / macroautophagy / maturation of SSU-rRNA / translational initiation / small-subunit processome / maintenance of translational fidelity / modification-dependent protein catabolic process / protein tag activity / cytoplasmic stress granule / rRNA processing / protein-folding chaperone binding / ribosome biogenesis / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / cytoplasmic translation / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / protein ubiquitination / ribosome / translation / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / ribonucleoprotein complex / negative regulation of gene expression / response to antibiotic / GTPase activity / mRNA binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / GTP binding / nucleolus / mitochondrion Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Taura syndrome virus Taura syndrome virus | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Abeyrathne PD / Koh CS / Grant T / Grigorieff N / Korostelev AA | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2016 Journal: Elife / Year: 2016Title: Ensemble cryo-EM uncovers inchworm-like translocation of a viral IRES through the ribosome. Authors: Priyanka D Abeyrathne / Cha San Koh / Timothy Grant / Nikolaus Grigorieff / Andrei A Korostelev /  Abstract: Internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) mediate cap-independent translation of viral mRNAs. Using electron cryo-microscopy of a single specimen, we present five ribosome structures formed with the ...Internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) mediate cap-independent translation of viral mRNAs. Using electron cryo-microscopy of a single specimen, we present five ribosome structures formed with the Taura syndrome virus IRES and translocase eEF2•GTP bound with sordarin. The structures suggest a trajectory of IRES translocation, required for translation initiation, and provide an unprecedented view of eEF2 dynamics. The IRES rearranges from extended to bent to extended conformations. This inchworm-like movement is coupled with ribosomal inter-subunit rotation and 40S head swivel. eEF2, attached to the 60S subunit, slides along the rotating 40S subunit to enter the A site. Its diphthamide-bearing tip at domain IV separates the tRNA-mRNA-like pseudoknot I (PKI) of the IRES from the decoding center. This unlocks 40S domains, facilitating head swivel and biasing IRES translocation via hitherto-elusive intermediates with PKI captured between the A and P sites. The structures suggest missing links in our understanding of tRNA translocation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6652.map.gz emd_6652.map.gz | 21.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6652-v30.xml emd-6652-v30.xml emd-6652.xml emd-6652.xml | 11.6 KB 11.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  400_6652.gif 400_6652.gif 80_6652.gif 80_6652.gif | 84.9 KB 4.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6652 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6652 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6652 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6652 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5jutMC 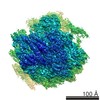 6643C 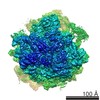 6644C  6645C  6646C  6647C  6648C  6649C  6650C  6651C  6653C  5juoC  5jupC  5jusC  5juuC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6652.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 62.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6652.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 62.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Saccharomyces cerevisiae 80S ribosome bound to eEF2-GDP-sordarin and TSV IRES, Structure IV. For classification, 2D masking around the E site was used, including the 5' domain of PKI. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.64 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Saccharomyces cerevisiae 80S ribosome bound to TSV IRES and eEF2 ...
| Entire | Name: Saccharomyces cerevisiae 80S ribosome bound to TSV IRES and eEF2 translation initiation complex, Structure IV, Map 2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Saccharomyces cerevisiae 80S ribosome bound to TSV IRES and eEF2 ...
| Supramolecule | Name: Saccharomyces cerevisiae 80S ribosome bound to TSV IRES and eEF2 translation initiation complex, Structure IV, Map 2 type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.2 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: Ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI / Ribosome-details: ribosome-eukaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.2 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Internal Ribosome Entry Site
| Macromolecule | Name: Internal Ribosome Entry Site / type: rna / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: IRES / Classification: OTHER / Structure: SINGLE STRANDED / Synthetic?: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Taura syndrome virus Taura syndrome virus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 80 KDa |
-Macromolecule #2: eukaryotic elongation factor 2
| Macromolecule | Name: eukaryotic elongation factor 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: eEF2 / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: Quantifoil Cu 200 mesh |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 85 % / Chamber temperature: 103 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 120,000 times magnification. Legacy - Electron beam tilt params: 0 |
| Details | 10 electrons/physical pixel/second |
| Date | Nov 11, 2015 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Sampling interval: 5 µm / Number real images: 2662 / Average electron dose: 70 e/Å2 Details: Images recorded as movies in super-resolution mode. Bits/pixel: 8 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 30487 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7 µm / Nominal magnification: 18000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | FREALIGN |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: each particle |
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: Unblur, CTFFIND4, FREALIGN Details: The highest resolution included in the refinement was 7 Angstrom. Number images used: 1105737 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)