+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | structure of human KCNQ1-KCNE1-CaM complex with PIP2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ion channels / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvestibular nucleus development / negative regulation of protein targeting to membrane / secretory granule organization / gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior ...vestibular nucleus development / negative regulation of protein targeting to membrane / secretory granule organization / gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / regulation of gastric acid secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / iodide transport / Phase 3 - rapid repolarisation / regulation of potassium ion transport / membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane repolarization during action potential / telethonin binding / Phase 2 - plateau phase / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / intracellular chloride ion homeostasis / negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion export across plasma membrane / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / renal sodium ion absorption / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of membrane repolarization / auditory receptor cell development / protein phosphatase 1 binding / membrane repolarization / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion homeostasis / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / Voltage gated Potassium channels / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / non-motile cilium assembly / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / cardiac muscle cell contraction / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / epithelial cell maturation / intestinal absorption / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / inner ear morphogenesis / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / renal absorption / autophagosome membrane docking / ciliary base / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / regulation of heart contraction / presynaptic endocytosis / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / inner ear development / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / monoatomic ion channel complex / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / action potential / cochlea development / Calcineurin activates NFAT / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / social behavior / Smooth Muscle Contraction Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.36 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hou PP / Zhang J / Wan SY / Cheng XY / Zhong L / Hu B | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2025 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2025Title: Secondary structure transitions and dual PIP2 binding define cardiac KCNQ1-KCNE1 channel gating. Authors: Ling Zhong / Xiaoqing Lin / Xinyu Cheng / Shuangyan Wan / Yaoguang Hua / Weiwei Nan / Bin Hu / Xiangjun Peng / Zihan Zhou / Qiansen Zhang / Huaiyu Yang / Frank Noé / Zhenzhen Yan / Dexiang ...Authors: Ling Zhong / Xiaoqing Lin / Xinyu Cheng / Shuangyan Wan / Yaoguang Hua / Weiwei Nan / Bin Hu / Xiangjun Peng / Zihan Zhou / Qiansen Zhang / Huaiyu Yang / Frank Noé / Zhenzhen Yan / Dexiang Jiang / Hangyu Zhang / Fengjiao Liu / Chenxin Xiao / Zhuo Zhou / Yimin Mou / Haijie Yu / Lijuan Ma / Chen Huang / Vincent Kam Wai Wong / Sookja Kim Chung / Bing Shen / Zhi-Hong Jiang / Erwin Neher / Wandi Zhu / Jin Zhang / Panpan Hou /    Abstract: The KCNQ1 + KCNE1 potassium channel complex produces the slow delayed rectifier current (I) critical for cardiac repolarization. Loss-of-function mutations in KCNQ1 and KCNE1 cause long QT ...The KCNQ1 + KCNE1 potassium channel complex produces the slow delayed rectifier current (I) critical for cardiac repolarization. Loss-of-function mutations in KCNQ1 and KCNE1 cause long QT syndrome (LQTS) types 1 and 5 (LQT1/LQT5), accounting for over one-third of clinical LQTS cases. Despite prior structural work on KCNQ1 and KCNQ1 + KCNE3, the structural basis of KCNQ1 + KCNE1 remains unresolved. Using cryo-electron microscopy and electrophysiology, we determined high-resolution (2.5-3.4 Å) structures of human KCNQ1, and KCNQ1 + KCNE1 in both closed and open states. KCNE1 occupies a pivotal position at the interface of three KCNQ1 subunits, inducing six helix-to-loop transitions in KCNQ1 transmembrane segments. Three of them occur at both ends of the S4-S5 linker, maintaining a loop conformation during I gating, while the other three, in S6 and helix A, undergo dynamic helix-loop transitions during I gating. These structural rearrangements: (1) stabilize the closed pore and the conformation of the intermediate state voltage-sensing domain, thereby determining channel gating, ion permeation, and single-channel conductance; (2) enable a dual-PIP2 modulation mechanism, where one PIP2 occupies the canonical site, while the second PIP2 bridges the S4-S5 linker, KCNE1, and the adjacent S6', stabilizing channel opening; (3) create a fenestration capable of binding compounds specific for KCNQ1 + KCNE1 (e.g., AC-1). Together, these findings reveal a previously unrecognized large-scale secondary structural transition during ion channel gating that fine-tunes I function and provides a foundation for developing targeted LQTS therapy. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_64038.map.gz emd_64038.map.gz | 230 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-64038-v30.xml emd-64038-v30.xml emd-64038.xml emd-64038.xml | 19.5 KB 19.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_64038.png emd_64038.png | 90.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-64038.cif.gz emd-64038.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_64038_half_map_1.map.gz emd_64038_half_map_1.map.gz emd_64038_half_map_2.map.gz emd_64038_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.1 MB 226.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-64038 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-64038 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-64038 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-64038 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9uc8MC  9u7fC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_64038.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_64038.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.96 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_64038_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_64038_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of human KCNQ1-KCNE1-CaM complex
| Entire | Name: Structure of human KCNQ1-KCNE1-CaM complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of human KCNQ1-KCNE1-CaM complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of human KCNQ1-KCNE1-CaM complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 74.800492 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAAASSPPRA ERKRWGWGRL PGARRGSAGL AKKCPFSLEL AEGGPAGGAL YAPIAPGAPG PAPPASPAAP AAPPVASDLG PRPPVSLDP RVSIYSTRRP VLARTHVQGR VYNFLERPTG WKCFVYHFAV FLIVLVCLIF SVLSTIEQYA ALATGTLFWM E IVLVVFFG ...String: MAAASSPPRA ERKRWGWGRL PGARRGSAGL AKKCPFSLEL AEGGPAGGAL YAPIAPGAPG PAPPASPAAP AAPPVASDLG PRPPVSLDP RVSIYSTRRP VLARTHVQGR VYNFLERPTG WKCFVYHFAV FLIVLVCLIF SVLSTIEQYA ALATGTLFWM E IVLVVFFG TEYVVRLWSA GCRSKYVGLW GRLRFARKPI SIIDLIVVVA SMVVLCVGSK GQVFATSAIR GIRFLQILRM LH VDRQGGT WRLLGSVVFI HRQELITTLY IGFLGLIFSS YFVYLAEKDA VNESGRVEFG SYADALWWGV VTVTTIGYGD KVP QTWVGK TIASCFSVFA ISFFALPAGI LGSGFALKVQ QKQRQKHFNR QIPAAASLIQ TAWRCYAAEN PDSSTWKIYI RKAP RSHTL LSPSPKPKKS VVVKKKKFKL DKDNGVTPGE KMLTVPHITC DPPEERRLDH FSVDGYDSSV RKSPTLLEVS MPHFM RTNS FAEDLDLEGE TLLTPITHIS QLREHHRATI KVIRRMQYFV AKKKFQQARK PYDVRDVIEQ YSQGHLNLMV RIKELQ RRL DQSIGKPSLF ISVSEKSKDR GSNTIGARLN RVEDKVTQLD QRLALITDML HQLLSLHGGS TPGSGGPPRE GGAHITQ PC GSGGSVDPEL FLPSNTLPTY EQLTVPRRGP DEGS UniProtKB: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.404093 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: DGKLEALYVL MVLGFFGFFT LGIMLSYIRS UniProtKB: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: [(2R)-2-octanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(o...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2R)-2-octanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(oxidanyl)-4,5-diphosphonooxy-cyclohexyl]oxy-phosphoryl]oxy-propyl] octanoate type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: PIO |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 746.566 Da |
| Chemical component information | 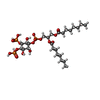 ChemComp-PIO: |
-Macromolecule #5: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI SPIRIT |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.73 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Spirit / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




































