+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of glycopeptide fibril | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | helical fibril / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xia WC / Liu C | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Am Chem Soc / Year: 2025 Journal: J Am Chem Soc / Year: 2025Title: Design and Structural Elucidation of Glycopeptide Fibrils: Emulating Glycosaminoglycan Functions for Biomedical Applications. Authors: Wencheng Xia / Zhongxin Xu / Hui Dong / Shengnan Zhang / Changdong He / Dan Li / Bo Sun / Bin Dai / Suwei Dong / Cong Liu /  Abstract: Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are essential polysaccharides crucial for various cellular functions, such as cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation. However, their complex structure and ...Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are essential polysaccharides crucial for various cellular functions, such as cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation. However, their complex structure and variability from natural sources pose challenges for functional studies and therapeutic applications. In this study, we engineered a glycopeptide that assembles into fibrils, emulating the functional attributes of GAGs. Utilizing cryo-EM, we elucidated the atomic structure of the designed glycopeptide fibril, which is composed of three identical protofilaments intertwined into a left-handed helix and held together by a variety of intermolecular interactions. Remarkably, the functional sugar units, glucuronic acids, are orderly positioned on the fibril surface, making them readily accessible to the solvent. This distinctive spatial configuration allows the designed glycopeptide fibril to effectively mimic key GAG functionalities, including the promotion of cell proliferation, cell migration, and osteogenic differentiation. Our findings offer a structural framework for designing glycan functionalities on glycopeptide fibrils and open avenues for developing glycopeptide-based materials with versatile biological activities. This work further enhances the potential of these materials for applications in therapeutic and regenerative medicine. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_62213.map.gz emd_62213.map.gz | 3.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-62213-v30.xml emd-62213-v30.xml emd-62213.xml emd-62213.xml | 14.4 KB 14.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_62213_fsc.xml emd_62213_fsc.xml | 6.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_62213.png emd_62213.png | 46.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-62213.cif.gz emd-62213.cif.gz | 4.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_62213_half_map_1.map.gz emd_62213_half_map_1.map.gz emd_62213_half_map_2.map.gz emd_62213_half_map_2.map.gz | 16.9 MB 16.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62213 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62213 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62213 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62213 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_62213_validation.pdf.gz emd_62213_validation.pdf.gz | 605.2 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_62213_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_62213_full_validation.pdf.gz | 604.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_62213_validation.xml.gz emd_62213_validation.xml.gz | 12 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_62213_validation.cif.gz emd_62213_validation.cif.gz | 16.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-62213 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-62213 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-62213 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-62213 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_62213.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_62213.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_62213_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_62213_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of glycopeptide fibril
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of glycopeptide fibril |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of glycopeptide fibril
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of glycopeptide fibril / type: cell / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
-Macromolecule #1: TYR-TYR-CYS-TYR-TYR
| Macromolecule | Name: TYR-TYR-CYS-TYR-TYR / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 12 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 773.853 Da |
| Sequence | String: YYCYY |
-Macromolecule #2: beta-D-glucopyranuronic acid
| Macromolecule | Name: beta-D-glucopyranuronic acid / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: BDP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 194.139 Da |
| Chemical component information | 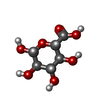 ChemComp-BDP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 55.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





































