+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | TTLL11 bound to microtubule | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TTLL11 / polyglutamylase / tubulin / microtubule / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtubulin-glutamic acid ligase activity / protein-glutamic acid ligase activity, initiating / protein-glutamic acid ligase activity, elongating / microtubule severing / Ligases; Forming carbon-nitrogen bonds; Acid-amino-acid ligases (peptide synthases) / odontoblast differentiation / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / Cilium Assembly / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin ...tubulin-glutamic acid ligase activity / protein-glutamic acid ligase activity, initiating / protein-glutamic acid ligase activity, elongating / microtubule severing / Ligases; Forming carbon-nitrogen bonds; Acid-amino-acid ligases (peptide synthases) / odontoblast differentiation / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / Cilium Assembly / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / haloalkane dehalogenase / haloalkane dehalogenase activity / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Intraflagellar transport / Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC / Gap junction assembly / Kinesins / GTPase activating protein binding / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / regulation of synapse organization / nuclear envelope lumen / Recycling pathway of L1 / MHC class I protein binding / RHOH GTPase cycle / microtubule-based process / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / Hedgehog 'off' state / intercellular bridge / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / cytoplasmic microtubule / spindle assembly / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Mitotic Prometaphase / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / cellular response to interleukin-4 / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / tubulin binding / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / protein modification process / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / PKR-mediated signaling / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / response to toxic substance / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / mitotic cell cycle / double-stranded RNA binding / microtubule cytoskeleton / cell body / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Potential therapeutics for SARS / microtubule / cytoskeleton / cilium / ciliary basal body / membrane raft / protein domain specific binding / cell division / GTPase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / structural molecule activity / protein-containing complex / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.28 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Barinka C / Campbell J / Desfosses A / Gutsche I | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Czech Republic, 1 items Czech Republic, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025Title: Mechanistic insights into TTLL11 polyglutamylase-mediated primary tubulin chain elongation. Authors: Jana Campbell / Miroslava Vosahlikova / Samar Ismail / Margareta Volnikova / Lucia Motlova / Julia Kudlacova / Kseniya Ustinova / Ivan Snajdr / Zora Novakova / Miroslav Basta / Irina Gutsche ...Authors: Jana Campbell / Miroslava Vosahlikova / Samar Ismail / Margareta Volnikova / Lucia Motlova / Julia Kudlacova / Kseniya Ustinova / Ivan Snajdr / Zora Novakova / Miroslav Basta / Irina Gutsche / Marie-Jo Moutin / Ambroise Desfosses / Cyril Barinka /    Abstract: Microtubules (MTs) undergo diverse posttranslational modifications that regulate their structural and functional properties. Among these, polyglutamylation-a dominant and conserved modification ...Microtubules (MTs) undergo diverse posttranslational modifications that regulate their structural and functional properties. Among these, polyglutamylation-a dominant and conserved modification targeting unstructured tubulin C-terminal tails-plays a pivotal role in defining the tubulin code. Here, we describe a mechanism by which tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 11 (TTLL11) expands and diversifies the code. Cryo-electron microscopy revealed a unique bipartite MT recognition strategy wherein TTLL11 binding and catalytic domains engage adjacent MT protofilaments. Biochemical and cellular assays identified previously uncharacterized polyglutamylation patterns, showing that TTLL11 directly extends the primary polypeptide chains of α- and β-tubulin in vitro, challenging the prevailing paradigms emphasizing lateral branching. Moreover, cell-based and in vivo data suggest a cross-talk between polyglutamylation and the detyrosination/tyrosination cycle likely linked to the TTLL11-mediated elongation of the primary α-tubulin chain. These findings unveil an unrecognized layer of complexity within the tubulin code and offer mechanistic insights into the molecular basis of functional specialization of MT cytoskeleton. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_52338.map.gz emd_52338.map.gz | 376.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-52338-v30.xml emd-52338-v30.xml emd-52338.xml emd-52338.xml | 21.5 KB 21.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_52338_fsc.xml emd_52338_fsc.xml | 15.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_52338.png emd_52338.png | 281.4 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_52338_msk_1.map emd_52338_msk_1.map | 421.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-52338.cif.gz emd-52338.cif.gz | 8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_52338_half_map_1.map.gz emd_52338_half_map_1.map.gz emd_52338_half_map_2.map.gz emd_52338_half_map_2.map.gz | 391.8 MB 391.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52338 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52338 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52338 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52338 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9hq4MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_52338.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_52338.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.349 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_52338_msk_1.map emd_52338_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_52338_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_52338_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of TTLL11 and two tubulin dimers
| Entire | Name: Complex of TTLL11 and two tubulin dimers |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of TTLL11 and two tubulin dimers
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of TTLL11 and two tubulin dimers / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Tubulin alpha-1B chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1B chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Native tubulin isolated from HEK 293T cells, unaligned regions are intrinsicly disordered Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50.204445 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE ...String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE FSIYPAPQVS TAVVEPYNSI LTTHTTLEHS DCAFMVDNEA IYDICRRNLD IERPTYTNLN RLISQIVSSI TA SLRFDGA LNVDLTEFQT NLVPYPRIHF PLATYAPVIS AEKAYHEQLS VAEITNACFE PANQMVKCDP RHGKYMACCL LYR GDVVPK DVNAAIATIK TKRSIQFVDW CPTGFKVGIN YQPPTVVPGG DLAKVQRAVC MLSNTTAIAE AWARLDHKFD LMYA KRAFV HWYVGEGMEE GEFSEAREDM AALEKDYEEV GVDSVEGEGE EEGEEY UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha-1B chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: The C-terminal part of tubulin is intrinsicaly disordered thus not visible in the structure. Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 49.717629 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGTYHGDS DLQLDRISVY YNEATGGKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKEAESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS ...String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGTYHGDS DLQLDRISVY YNEATGGKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKEAESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS VVPSPKVSDT VVEPYNATLS VHQLVENTDE TYCIDNEALY DICFRTLKLT TPTYGDLNHL VSATMSGVTT CL RFPGQLN ADLRKLAVNM VPFPRLHFFM PGFAPLTSRG SQQYRALTVP ELTQQVFDAK NMMAACDPRH GRYLTVAAVF RGR MSMKEV DEQMLNVQNK NSSYFVEWIP NNVKTAVCDI PPRGLKMAVT FIGNSTAIQE LFKRISEQFT AMFRRKAFLH WYTG EGMDE MEFTEAESNM NDLVSEYQQY QDATAEEEED FGEEAEEEA UniProtKB: Tubulin beta chain |
-Macromolecule #3: Tubulin polyglutamylase TTLL11
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin polyglutamylase TTLL11 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 Details: The original protein contains N-terminal Halo tag on a flexible linker so it is not visible in the map or included in the model. TTLL11 containes several instriscally disordered regions that ...Details: The original protein contains N-terminal Halo tag on a flexible linker so it is not visible in the map or included in the model. TTLL11 containes several instriscally disordered regions that are left out from the model. Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Ligases; Forming carbon-nitrogen bonds; Acid-amino-acid ligases (peptide synthases) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 111.410188 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MASAWSHPQF EKGGGSGGGS GGSAWSHPQF EKGGSGGSDY KDDDDKGSGS GEIGTGFPFD PHYVEVLGER MHYVDVGPRD GTPVLFLHG NPTSSYVWRN IIPHVAPTHR CIAPDLIGMG KSDKPDLGYF FDDHVRFMDA FIEALGLEEV VLVIHDWGSA L GFHWAKRN ...String: MASAWSHPQF EKGGGSGGGS GGSAWSHPQF EKGGSGGSDY KDDDDKGSGS GEIGTGFPFD PHYVEVLGER MHYVDVGPRD GTPVLFLHG NPTSSYVWRN IIPHVAPTHR CIAPDLIGMG KSDKPDLGYF FDDHVRFMDA FIEALGLEEV VLVIHDWGSA L GFHWAKRN PERVKGIAFM EFIRPIPTWD EWPEFARETF QAFRTTDVGR KLIIDQNVFI EGTLPMGVVR PLTEVEMDHY RE PFLNPVD REPLWRFPNE LPIAGEPANI VALVEEYMDW LHQSPVPKLL FWGTPGVLIP PAEAARLAKS LPNCKAVDIG PGL NLLQED NPDLIGSEIA RWLSTLEISG EPTTEDLYFQ SDNAIASEFC RYPAQWRPLE SSRHNQTSLY KKAGSENLYF QSGG GENGS QRPVTVDSSK ARTSLDALKI SIRQLKWKEF PFGRRLPCDI YWHGVSFHDN DIFSGQVNKF PGMTEMVRKI TLSRA VRTM QNLFPEEYNF YPRSWILPDE FQLFVAQVQM VKDDDPSWKP TFIVKPDGGC QGDGIYLIKD PSDIRLAGTL QSRPAV VQE YICKPLLIDK LKFDIRLYVL LKSLDPLEIY IAKDGLSRFC TEPYQEPTPK NLHRIFMHLT NYSLNIHSGN FIHSDSA ST GSKRTFSSIL CRLSSKGVDI KKVWSDIISV VIKTVIALTP ELKVFYQSDI PTGRPGPTCF QILGFDILLM KNLKPILL G VNANPSMRIE HEHELSPGVF ENVPSLVDEE VKVAVIRDTL RLMDPLKKKR ENQSQQLEKP FAGKEDALDG ELTSAPDCN ANPEAHLPSI CLKQVFPKYA KQFNYLRLVD RMANLFIRFL GIKGTMKLGP TGFRTFIRSC KLSSSSLSMA AVDILYIDIT RRWNSMTLD QRDSGMCLQA FVEAFFFLAQ RKFKMLPLHE QVASLIDLCE YHLSLLDEKR LVCGRGVPSG GRPPHRGPPQ E PSPSAQPA GDNPPPRTSC ANKLSHPRHT LS UniProtKB: Haloalkane dehalogenase, Tubulin polyglutamylase TTLL11 |
-Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: G2P |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 521.208 Da |
| Chemical component information | 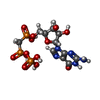 ChemComp-G2P: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: TAXOL
| Macromolecule | Name: TAXOL / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: TA1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 853.906 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-TA1: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7 Details: 40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0, 1 mM TCEP, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 % glycerol |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Instrument: LEICA EM GP |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)














































