+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
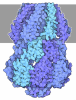
| Title | Amyloid DNA Bridging by Hfq C-terminal region | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Amyloid / Nucleoid Associated Protein NAP / DNA bridging / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing / positive regulation of translation, ncRNA-mediated / bacterial nucleoid / regulation of translation, ncRNA-mediated / bent DNA binding / regulation of RNA stability / RNA folding chaperone / tRNA processing / tRNA binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription ...sRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing / positive regulation of translation, ncRNA-mediated / bacterial nucleoid / regulation of translation, ncRNA-mediated / bent DNA binding / regulation of RNA stability / RNA folding chaperone / tRNA processing / tRNA binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA binding / RNA binding / ATP binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 19.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gragera M / Arluison V | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2025 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2025Title: Amyloid-like DNA bridging: a new mode of DNA shaping. Authors: Frank Wien / Marcos Gragera / Tatsuhito Matsuo / Gautier Moroy / María Teresa Bueno-Carrasco / Rocío Arranz / Antoine Cossa / Anne Martel / Heloisa N Bordallo / Svemir Rudić / Marisela ...Authors: Frank Wien / Marcos Gragera / Tatsuhito Matsuo / Gautier Moroy / María Teresa Bueno-Carrasco / Rocío Arranz / Antoine Cossa / Anne Martel / Heloisa N Bordallo / Svemir Rudić / Marisela Velez / Johan R C van der Maarel / Judith Peters / Véronique Arluison /       Abstract: All organisms depend on specific proteins to compact and organize their genomes. In eukaryotes, histones fulfil this role, while bacterial chromosomes are shaped by nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs) ...All organisms depend on specific proteins to compact and organize their genomes. In eukaryotes, histones fulfil this role, while bacterial chromosomes are shaped by nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs). Among its pleiotropic functions, the NAP Hfq plays a pivotal role in bacterial genome organization. In this study, we characterized the structure of the C-terminal extension of Hfq, which mediates chromosomal compaction, in its DNA-bound state. Using an integrative approach that combined transmission electron microscopy, neutron scattering, site-directed mutagenesis, and molecular modeling, we identified an amyloid module formed by the C-terminal region of Hfq. This module uniquely bridges and compacts six DNA molecules, marking the first documented instance of an amyloid structure with DNA-bridging properties. Our findings redefine the functional landscape of amyloids, linking them to genome architecture and gene regulation. This result suggests that amyloid-DNA interactions may represent a conserved mechanism across biological systems, with profound implications for understanding genome organization and the regulation of gene expression in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_52187.map.gz emd_52187.map.gz | 363.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-52187-v30.xml emd-52187-v30.xml emd-52187.xml emd-52187.xml | 15.9 KB 15.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_52187_fsc.xml emd_52187_fsc.xml | 26.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_52187.png emd_52187.png | 32.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-52187.cif.gz emd-52187.cif.gz | 4.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_52187_half_map_1.map.gz emd_52187_half_map_1.map.gz emd_52187_half_map_2.map.gz emd_52187_half_map_2.map.gz | 690.5 MB 690.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52187 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52187 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52187 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52187 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_52187.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 744.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_52187.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 744.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.37 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_52187_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_52187_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Hfq C-terminal amyloid domain bound to dsDNA(dA:dT)59
| Entire | Name: Hfq C-terminal amyloid domain bound to dsDNA(dA:dT)59 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Hfq C-terminal amyloid domain bound to dsDNA(dA:dT)59
| Supramolecule | Name: Hfq C-terminal amyloid domain bound to dsDNA(dA:dT)59 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Hfq C-terminal region, 38 aa, SRPVSHHSNNAGGGTSSNYHHGSSAQNTSAQQDSEETE DNA (dA:dT)59 Chemical synthesis |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Hfq C-terminal
| Macromolecule | Name: Hfq C-terminal / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: DNA:protein complex / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SRPVSHHSNN AGGGTSSNYH HGSSAQNTSA QQDSEETE UniProtKB: RNA-binding protein Hfq |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (dA:dT)59
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (dA:dT)59 / type: dna / ID: 2 Details: Double stranded (ds) DNA sequence: (dA:dT)59. The choice of this 59-basepair homo-polymeric DNA sequence was made because Hfq has highest affinity for A-rich sequences. Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Sequence | String: AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 5 / Details: water |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Details: 25 mA |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| Details | The sample consisted in the amyloid structure formed by Hfq CTR region (38 amino acid residues) bound to a double stranded (ds) DNA sequence: (dA:dT)59 prepared in water at 20 mg/mL and then diluted. The molar ratio DNA:CTR was 4:1 (DNA concentration expressed in base-pair). Samples were analyzed after 4 weeks to allow complex full self-assembly. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS TALOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





































