+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Artificial membrane protein TMHC4_R (ROCKET) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Synthetic construct / membrane protein / artificial protein | |||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
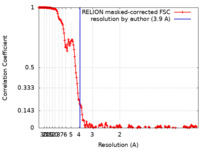
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Abramsson ML / Anden O / Howard RJ / Lindahl E / Landreh M | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, 2 items Sweden, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2025 Journal: Elife / Year: 2025Title: Engineering cardiolipin binding to an artificial membrane protein reveals determinants for lipid-mediated stabilization. Authors: Mia L Abramsson / Robin A Corey / Jan L Skerle / Louise J Persson / Olivia Anden / Abraham O Oluwole / Rebecca J Howard / Erik Lindahl / Carol V Robinson / Kvido Strisovsky / Erik G Marklund ...Authors: Mia L Abramsson / Robin A Corey / Jan L Skerle / Louise J Persson / Olivia Anden / Abraham O Oluwole / Rebecca J Howard / Erik Lindahl / Carol V Robinson / Kvido Strisovsky / Erik G Marklund / David Drew / Phillip J Stansfeld / Michael Landreh /    Abstract: Integral membrane proteins carry out essential functions in the cell, and their activities are often modulated by specific protein-lipid interactions in the membrane. Here, we elucidate the intricate ...Integral membrane proteins carry out essential functions in the cell, and their activities are often modulated by specific protein-lipid interactions in the membrane. Here, we elucidate the intricate role of cardiolipin (CDL), a regulatory lipid, as a stabilizer of membrane proteins and their complexes. Using the in silico-designed model protein TMHC4_R (ROCKET) as a scaffold, we employ a combination of molecular dynamics simulations and native mass spectrometry to explore the protein features that facilitate preferential lipid interactions and mediate stabilization. We find that the spatial arrangement of positively charged residues as well as local conformational flexibility are factors that distinguish stabilizing from non-stabilizing CDL interactions. However, we also find that even in this controlled, artificial system, a clear-cut distinction between binding and stabilization is difficult to attain, revealing that overlapping lipid contacts can partially compensate for the effects of binding site mutations. Extending our insights to naturally occurring proteins, we identify a stabilizing CDL site within the rhomboid intramembrane protease GlpG and uncover its regulatory influence on enzyme substrate preference. In this work, we establish a framework for engineering functional lipid interactions, paving the way for the design of proteins with membrane-specific properties or functions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_50106.map.gz emd_50106.map.gz | 31.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-50106-v30.xml emd-50106-v30.xml emd-50106.xml emd-50106.xml | 15.6 KB 15.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_50106_fsc.xml emd_50106_fsc.xml | 18.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
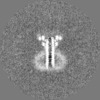
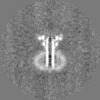
| Images |  emd_50106.png emd_50106.png | 78.3 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_50106_msk_1.map emd_50106_msk_1.map | 512 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-50106.cif.gz emd-50106.cif.gz | 5.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_50106_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50106_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50106_half_map_2.map.gz emd_50106_half_map_2.map.gz | 403.8 MB 403.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50106 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50106 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50106 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50106 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_50106.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_50106.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
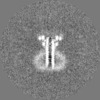
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.5076 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
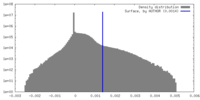
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_50106_msk_1.map emd_50106_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
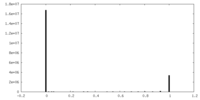
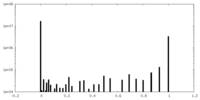
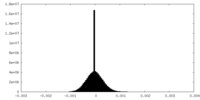
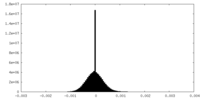
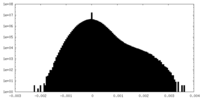
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_50106_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
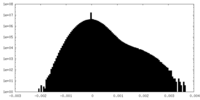
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_50106_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Artificial membrane protein TMHC4_R (ROCKET)
| Entire | Name: Artificial membrane protein TMHC4_R (ROCKET) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Artificial membrane protein TMHC4_R (ROCKET)
| Supramolecule | Name: Artificial membrane protein TMHC4_R (ROCKET) / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 100.40 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: TMHC4_R (ROCKET)
| Macromolecule | Name: TMHC4_R (ROCKET) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSKDTEDSRK IWRTIMLLLV FAILLSAIIW YQITTNPDTS QIATLLSMQL LLIALMLVVI ALLLSRQTEQ VAESIRRDVS ALAYVMLGLL LSLLNRLSLA AEAYKKAIEL DPNDALAWLL LGSVLEKLKR LDEAAEAYKK AIELKPNDAS AWKELGKVLE KLGRLDEAAE ...String: MSKDTEDSRK IWRTIMLLLV FAILLSAIIW YQITTNPDTS QIATLLSMQL LLIALMLVVI ALLLSRQTEQ VAESIRRDVS ALAYVMLGLL LSLLNRLSLA AEAYKKAIEL DPNDALAWLL LGSVLEKLKR LDEAAEAYKK AIELKPNDAS AWKELGKVLE KLGRLDEAAE AYKKAIELDP EDAEAWKELG KVLEKLGRLD EAAEAYKKAI ELDPNDLEHH HHHH |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | 3D array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



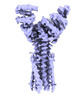

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)