+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Xenorhabdus nematophilus XptA2, wild type State 2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Xenorhabdus nematophilus XptA2, wild type State 2 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TcA / Pore Forming Toxin / TOXIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / TcdA1, receptor binding domain / TcA receptor binding domain / TcA receptor binding domain / ABC toxin, N-terminal domain / ABC toxin N-terminal region / Insecticidal toxin complex/plasmid virulence protein / Tc toxin complex TcA, C-terminal TcB-binding domain / Neuraminidase-like domain / Salmonella virulence plasmid 28.1kDa A protein ...: / TcdA1, receptor binding domain / TcA receptor binding domain / TcA receptor binding domain / ABC toxin, N-terminal domain / ABC toxin N-terminal region / Insecticidal toxin complex/plasmid virulence protein / Tc toxin complex TcA, C-terminal TcB-binding domain / Neuraminidase-like domain / Salmonella virulence plasmid 28.1kDa A protein / Tc toxin complex TcA C-terminal TcB-binding domain / Neuraminidase-like domain Similarity search - Domain/homology | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Xenorhabdus nematophila (bacteria) Xenorhabdus nematophila (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Aller SG / Martin CL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: BioTech (Basel) / Year: 2025 Journal: BioTech (Basel) / Year: 2025Title: Evaluating TcAs for Use in Biotechnology Applications. Authors: Cole L Martin / John H Hill / Brian D Wright / Solana R Fernandez / Aubrey L Miller / Karina J Yoon / Suzanne E Lapi / Stephen G Aller /  Abstract: ABC toxin complexes (Tcs) are tripartite complexes that come together to form nano-syringe-like translocation systems. ABC Tcs are often compared with (Bt) toxins, and as such, they have been highly ...ABC toxin complexes (Tcs) are tripartite complexes that come together to form nano-syringe-like translocation systems. ABC Tcs are often compared with (Bt) toxins, and as such, they have been highly studied as a potential novel pesticide to combat growing insect resistance. Moreover, it is possible to substitute the cytotoxic hypervariable region with alternative peptides, which promise potential use as a novel peptide delivery system. These toxins possess the unique ability to form active chimeric holotoxins across species and display the capability to translocate a variety of payloads across membrane bilayers. Additionally, mutagenesis on the linker region and the receptor binding domains (RBDs) show that mutations do not inherently cause a loss of functionality for translocation. For these reasons, Tcs have emerged as an ideal candidate for targeted protein engineering. However, elucidation of the specific function of each RBD in relation to target receptor recognition currently limits the use of a rational design approach with any ABC Tc. Additionally, there is a distinct lack of targeting and biodistribution data for many Tcs among mammals and mammalian cell lines. Here, we outline two separate strategies for modifying the targeting capabilities of the A subunit (TcA) from , Xn-XptA2. We identify novel structural differences that make Xn-XptA2 different than other characterized TcAs and display the modular capabilities of substituting RBDs from alternative TcAs into the Xn-XptA2 scaffold. Finally, we show the first, to our knowledge, biodistribution data of any TcA in mice. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_48372.map.gz emd_48372.map.gz | 150 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-48372-v30.xml emd-48372-v30.xml emd-48372.xml emd-48372.xml | 20.5 KB 20.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_48372.png emd_48372.png | 40.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-48372.cif.gz emd-48372.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_48372_half_map_1.map.gz emd_48372_half_map_1.map.gz emd_48372_half_map_2.map.gz emd_48372_half_map_2.map.gz | 144.1 MB 145 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48372 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48372 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48372 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48372 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 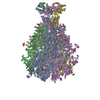 9mlhMC  9mlgC  9mliC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_48372.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 158 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_48372.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 158 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Xenorhabdus nematophilus XptA2, wild type State 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.268 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half Map A
| File | emd_48372_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half Map B
| File | emd_48372_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : A subunit of ABC Toxin Complex
| Entire | Name: A subunit of ABC Toxin Complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: A subunit of ABC Toxin Complex
| Supramolecule | Name: A subunit of ABC Toxin Complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Xenorhabdus nematophila (bacteria) Xenorhabdus nematophila (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.4 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: XptA2 protein
| Macromolecule | Name: XptA2 protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Xenorhabdus nematophila (bacteria) Xenorhabdus nematophila (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 284.392188 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MYSTAVLLNK ISPTRDGQTM TLADLQYLSF SELRKIFDDQ LSWGEARHLY HETIEQKKNN RLLEARIFTR ANPQLSGAIR LGIERDSVS RSYDEMFGAR SSSFVKPGSV ASMFSPAGYL TELYREAKDL HFSSSAYHLD NRRPDLADLT LSQSNMDTEI S TLTLSNEL ...String: MYSTAVLLNK ISPTRDGQTM TLADLQYLSF SELRKIFDDQ LSWGEARHLY HETIEQKKNN RLLEARIFTR ANPQLSGAIR LGIERDSVS RSYDEMFGAR SSSFVKPGSV ASMFSPAGYL TELYREAKDL HFSSSAYHLD NRRPDLADLT LSQSNMDTEI S TLTLSNEL LLEHITRKTG GDSDALMESL STYRQAIDTP YHQPYETIRQ VIMTHDSTLS ALSRNPEVMG QAEGASLLAI LA NISPELY NILTEEITEK NADALFAQNF SENITPENFA SQSWIAKYYG LELSEVQKYL GMLQNGYSDS TSAYVDNIST GLV VNNESK LEAYKITRVK TDDYDKNINY FDLMYEGNNQ FFIRANFKVS REFGATLRKN AGPSGIVGSL SGPLIANTNF KSNY LSNIS DSEYKNGVKI YAYRYTSSTS ATNQGGGIFT FESYPLTIFA LKLNKAIRLC LTSGLSPNEL QTIVRSDNAQ GIIND SVLT KVFYTLFYSH RYALSFDDAQ VLNGSVINQY ADDDSVSHFN RLFNTPPLKG KIFEADGNTV SIDPDEEQST FARSAL MRG LGVNSGELYQ LGKLAGVLDA QNTITLSVFV ISSLYRLTLL ARVHQLTVNE LCMLYGLSPF NGKTTASLSS GELPRLV IW LYQVTQWLTE AEITTEAIWL LCTPEFSGNI SPEISNLLNN LRPSISEDMA QSHNRELQAE ILAPFIAATL HLASPDMA R YILLWTDNLR PGGLDIAGFM TLVLKESLNA NETTQLVQFC HVMAQLSLSV QTLRLSEAEL SVLVISGFAV LGAKNQPAG QHNIDTLFSL YRFHQWINGL GNPGSDTLDM LRQQTLTADR LASVMGLDIS MVTQAMVSAG VNQLQCWQDI NTVLQWIDVA SALHTMPSV IRTLVNIRYV TALNKAESNL PSWDEWQTLA ENMEAGLSTQ QAQTLADYTA ERLSSVLCNW FLANIQPEGV S LHSRDDLY SYFLIDNQVS SAIKTTRLAE AIAGIQLYIN RALNRIEPNA RADVSTRQFF TDWTVNNRYS TWGGVSRLVY YP ENYIDPT QRIGQTRMMD ELLENISQSK LSRDTVEDAF KTYLTRFETV ADLKVVSAYH DNVNSNTGLT WFVGQTRENL PEY YWRNVD ISRMQAGELA ANAWKEWTKI DTAVNPYKDA IRPVIFRERL HLIWVEKEEV AKNGTDPVET YDRFTLKLAF LRHD GSWSA PWSYDITTQV EAVTDKKPDT ERLALAASGF QGEDTLLVFV YKTGKSYSDF GGSNKNVAGM TIYGDGSFKK MENTA LSRY SQLKNTFDII HTQGNDLVRK ASYRFAQDFE VPASLNMGSA IGDDSLTVME NGNIPQITSK YSSDNLAITL HNAAFT VRY DGSGNVIRNK QISAMKLTGV DGKSQYGNAF IIANTVKHYG GYSDLGGPIT VYNKTKNYIA SVQGHLMNAD YTRRLIL TP VENNYYARLF EFPFSPNTIL NTVFTVGSNK TSDFKKCSYA VDGNNSQGFQ IFSSYQSSGW LDIDTGINNT DIKITVMA G SKTHTFTASD HIASLPANSF DAMPYTFKPL EIDASSLAFT NNIAPLDIVF ETKAKDGRVL GKIKQTLSVK RVNYNPEDI LFLRETHSGA QYMQLGVYRI RLNTLLASQL VSRANTGIDT ILTMETQRLP EPPLGEGFFA NFVLPKYDPA EHGDERWFKI HIGNVGGNT GRQPYYSGML SDTSETSMTL FVPYAEGYYM HEGVRLGVGY QKITYDNTWE SAFFYFDETK QQFVLINDAD H DSGMTQQG IVKNIKKYKG FLNVSIATGY SAPMDFNSAS ALYYWELFYY TPMMCFQRLL QEKQFDEATQ WINYVYNPAG YI VNGEIAP WIWNCRPLEE TTSWNANPLD AIDPDAVAQN DPMHYKIATF MRLLDQLILR GDMAYRELTR DALNEAKMWY VRT LELLGD EPEDYGSQQW AAPSLSGAAS QTVQAAYQQD LTMLGRGGVS KNLRTANSLV GLFLPEYNPA LTDYWQTLRL RLFN LRHNL SIDGQPLSLA IYAEPTDPKA LLTSMVQASQ GGSAVLPGTL SLYRFPVMLE RTRNLVAQLT QFGTSLLSMA EHDDA DELT TLLLQQGMEL ATQSIRIQQR TVDEVDADIA VLAESRRSAQ NRLEKYQQLY DEDINHGEQR AMSLLDAAAG QSLAGQ VLS IAEGVADLVP NVFGLACGGS RWGAALRASA SVMSLSATAS QYSADKISRS EAYRRRRQEW EIQRDNADGE VKQMDAQ LE SLKIRREAAQ MQVEYQETQQ AHTQAQLELL QRKFTNKALY SWMRGKLSAI YYQFFDLTQS FCLMAQEALR RELTDNGV T FIRGGAWNGT TAGLMAGETL LLNLAEMEKV WLERDERALE VTRTVSLAQF YQALSSDNFN LTEKLTQFLR EGKGNVGAS GNELKLSNRQ IEASVRLSDL KIFSDYPESL GNTRQLKQVS VTLPALVGPY EDIRAVLNYG GSIVMPRGCS AIALSHGVND SGQFMLDFN DSRYLPFEGI SVNDSGSLTL SFPDATDRQK ALLESLSDII LHIRYTIRS UniProtKB: XptA2 protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 75.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




































