+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | 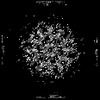 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Subtomogram average of capsid (CA) from immature Enveloped Delivery Vehicles (EDVs) containing Cas9 | ||||||||||||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | |||||||||||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | Cas9 delivery / Gene editing / EDV / VIRUS LIKE PARTICLE | ||||||||||||||||||
| 生物種 |   lentivirus derived Envelope Delivery Vehicle (EDV) (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) / lentivirus derived Envelope Delivery Vehicle (EDV) (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) /   lentivirus derived envelope delivery vehicle (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) lentivirus derived envelope delivery vehicle (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 手法 | サブトモグラム平均法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 9.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Peukes J / Ngo W / Nogales E / Doudna J | ||||||||||||||||||
| 資金援助 | European Union,  ドイツ, ドイツ,  カナダ, カナダ,  米国, 5件 米国, 5件
| ||||||||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2025 ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2025タイトル: Mechanism-guided engineering of a minimal biological particle for genome editing. 著者: Wayne Ngo / Julia Peukes / Alisha Baldwin / Zhiwei Wayne Xue / Sidney Hwang / Robert R Stickels / Zhi Lin / Ansuman T Satpathy / James A Wells / Randy Schekman / Eva Nogales / Jennifer A Doudna /  要旨: The widespread application of genome editing to treat and cure disease requires the delivery of genome editors into the nucleus of target cells. Enveloped delivery vehicles (EDVs) are engineered ...The widespread application of genome editing to treat and cure disease requires the delivery of genome editors into the nucleus of target cells. Enveloped delivery vehicles (EDVs) are engineered virally derived particles capable of packaging and delivering CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins (RNPs). However, the presence of lentiviral genome encapsulation and replication proteins in EDVs has obscured the underlying delivery mechanism and precluded particle optimization. Here, we show that Cas9 RNP nuclear delivery is independent of the native lentiviral capsid structure. Instead, EDV-mediated genome editing activity corresponds directly to the number of nuclear localization sequences on the Cas9 enzyme. EDV structural analysis using cryo-electron tomography and small molecule inhibitors guided the removal of ~80% of viral residues, creating a minimal EDV (miniEDV) that retains full RNP delivery capability. MiniEDVs are 25% smaller yet package equivalent amounts of Cas9 RNPs relative to the original EDVs and demonstrated increased editing in cell lines and therapeutically relevant primary human T cells. These results show that virally derived particles can be streamlined to create efficacious genome editing delivery vehicles with simpler production and manufacturing. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_47745.map.gz emd_47745.map.gz | 5.5 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-47745-v30.xml emd-47745-v30.xml emd-47745.xml emd-47745.xml | 15.5 KB 15.5 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_47745.png emd_47745.png | 187.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-47745.cif.gz emd-47745.cif.gz | 5 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_47745_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47745_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47745_half_map_2.map.gz emd_47745_half_map_2.map.gz | 5.5 MB 5.5 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47745 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47745 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47745 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47745 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_47745_validation.pdf.gz emd_47745_validation.pdf.gz | 905.8 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_47745_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_47745_full_validation.pdf.gz | 905.3 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_47745_validation.xml.gz emd_47745_validation.xml.gz | 8.4 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_47745_validation.cif.gz emd_47745_validation.cif.gz | 9.8 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47745 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47745 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47745 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47745 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_47745.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 6 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_47745.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 6 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 3.34 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-ハーフマップ: #1
| ファイル | emd_47745_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #2
| ファイル | emd_47745_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : lentivirus derived envelope delivery vehicle
| 全体 | 名称:   lentivirus derived envelope delivery vehicle (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) lentivirus derived envelope delivery vehicle (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: lentivirus derived envelope delivery vehicle
| 超分子 | 名称: lentivirus derived envelope delivery vehicle / タイプ: virus / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / NCBI-ID: 11676 / 生物種: lentivirus derived envelope delivery vehicle / ウイルスタイプ: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE / ウイルス・単離状態: OTHER / ウイルス・エンベロープ: Yes / ウイルス・中空状態: No |
|---|
-超分子 #2: capsid (immature Gag)
| 超分子 | 名称: capsid (immature Gag) / タイプ: complex / ID: 2 / 親要素: 1 詳細: The capsid map was generated by subtomogram averaging of the capsid protein density from immature Gag in tomograms of Cas9 containing EDVs that were generated by expressing constructs derived ...詳細: The capsid map was generated by subtomogram averaging of the capsid protein density from immature Gag in tomograms of Cas9 containing EDVs that were generated by expressing constructs derived from lentiviral vectors. |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:   lentivirus derived Envelope Delivery Vehicle (EDV) (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) lentivirus derived Envelope Delivery Vehicle (EDV) (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | サブトモグラム平均法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| グリッド | モデル: Quantifoil R2/2 / 支持フィルム - 材質: CARBON |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| 詳細 | Purified virus like particles also referred to as Enveloped Delivery Vehicles (EDVs) containing Cas9. |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 特殊光学系 | 詳細: Tilt series were acquired using a dose-symmetric tilt scheme using the tilt series controller in serialEM. |
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 2.92 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 4.5 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 2.0 µm |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
- 画像解析
画像解析
| 最終 再構成 | 解像度のタイプ: BY AUTHOR / 解像度: 9.5 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / ソフトウェア - 名称: subTOM / 使用したサブトモグラム数: 42366 |
|---|---|
| 抽出 | トモグラム数: 38 / 使用した粒子像数: 465070 |
| 最終 角度割当 | タイプ: OTHER 詳細: The first 2 euler angles were assigned based on the orientation relative to the membrane. The final in plane rotation was randomized. |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




































