+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
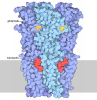
| Title | octopus sensory receptor CRT1 bound to Lumichrome | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | complex / membrane protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationextracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Octopus bimaculoides (California two-spot octopus) Octopus bimaculoides (California two-spot octopus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.28 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jiang H / Hibbs RE | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2025 Journal: Cell / Year: 2025Title: Environmental microbiomes drive chemotactile sensation in octopus. Authors: Rebecka J Sepela / Hao Jiang / Yern-Hyerk Shin / Tessa L Hautala / Jon Clardy / Ryan E Hibbs / Nicholas W Bellono /  Abstract: Microbial communities coat nearly every surface in the environment and have co-existed with animals throughout evolution. Whether animals exploit omnipresent microbial cues to navigate their ...Microbial communities coat nearly every surface in the environment and have co-existed with animals throughout evolution. Whether animals exploit omnipresent microbial cues to navigate their surroundings is not well understood. Octopuses use "taste-by-touch" chemotactile receptors (CRs) to explore the seafloor, but how they distinguish meaningful surfaces from the rocks and crevices they encounter is unknown. Here, we report that secreted signals from microbiomes of ecologically relevant surfaces activate CRs to guide octopus behavior. Distinct molecules isolated from individual bacterial strains located on prey or eggs bind single CRs in subtly different structural conformations to elicit specific mechanisms of receptor activation, ion permeation and signal transduction, and maternal care and predation behavior. Thus, microbiomes on ecological surfaces act at the level of primary sensory receptors to inform behavior. Our study demonstrates that uncovering interkingdom interactions is essential to understanding how animal sensory systems evolved in a microbe-rich world. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_47556.map.gz emd_47556.map.gz | 60.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-47556-v30.xml emd-47556-v30.xml emd-47556.xml emd-47556.xml | 15.4 KB 15.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_47556_fsc.xml emd_47556_fsc.xml | 10.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_47556.png emd_47556.png | 95.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-47556.cif.gz emd-47556.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_47556_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47556_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47556_half_map_2.map.gz emd_47556_half_map_2.map.gz | 116.1 MB 116.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47556 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47556 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47556 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47556 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_47556_validation.pdf.gz emd_47556_validation.pdf.gz | 839.2 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_47556_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_47556_full_validation.pdf.gz | 838.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_47556_validation.xml.gz emd_47556_validation.xml.gz | 19 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_47556_validation.cif.gz emd_47556_validation.cif.gz | 24.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47556 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47556 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47556 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47556 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9e6dMC  9e6bC  9e6cC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_47556.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_47556.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.072 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_47556_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_47556_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : octopus sensory receptor CRT1 bound to lumichrome
| Entire | Name: octopus sensory receptor CRT1 bound to lumichrome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: octopus sensory receptor CRT1 bound to lumichrome
| Supramolecule | Name: octopus sensory receptor CRT1 bound to lumichrome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Octopus bimaculoides (California two-spot octopus) Octopus bimaculoides (California two-spot octopus) |
-Macromolecule #1: Chemotactile receptor CRT1
| Macromolecule | Name: Chemotactile receptor CRT1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Octopus bimaculoides (California two-spot octopus) Octopus bimaculoides (California two-spot octopus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.334262 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MIFVIYLVFI LISSIPIVKS TPTYGDERLL REKLLTNYSK SIRPVINLTK VVDVTALLYL QTLYDLDFVN NFIMARYYLG LIWIDEKLT WNPLDYNNIT SIYLPKDKIW TPPIKMCNSM DKSEENDGVG ELMLTYTGWI NMWSFRLLHT YCQINAYTYP F DEHTCEIY ...String: MIFVIYLVFI LISSIPIVKS TPTYGDERLL REKLLTNYSK SIRPVINLTK VVDVTALLYL QTLYDLDFVN NFIMARYYLG LIWIDEKLT WNPLDYNNIT SIYLPKDKIW TPPIKMCNSM DKSEENDGVG ELMLTYTGWI NMWSFRLLHT YCQINAYTYP F DEHTCEIY LCVALHTINH TRIKELIYED SKFTQNYKWD INVSGKVNGT DELFSYAFAP MYLRRKLTVG IIAMLIPTVM MT ILTIFVF LLPPESGEKV SLATTIFLSN VLYLVQIDKT TPTNTKYPSL LMLYLMLLSM LSGIATLGSV VISKLYVIQS PSL RKSNPS DQNMNKSHTN KVADISTISK VQSDLPIREK PNEKRIYCIS DYIRLDDIFL KLSIATSVII SMIFTCLLFI PLES SAWSH PQFEK UniProtKB: Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand-binding domain-containing protein |
-Macromolecule #2: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 25 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #3: LUMICHROME
| Macromolecule | Name: LUMICHROME / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: LUM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 242.233 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-LUM: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOCONTINUUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.4000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






































