+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
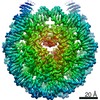
| Title | SNF2H bound to nucleosome - Class E1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | SNF2H bound to nucleosome - Class E1 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | chromatin / remodelers / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationstructural constituent of chromatin / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / protein heterodimerization activity / DNA binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) / | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Malik D / Deshmukh AA / Bilokapic S / Halic M | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025Title: Mechanisms of chromatin remodeling by an Snf2-type ATPase. Authors: Deepshikha Malik / Ashish Deshmukh / Silvija Bilokapic / Mario Halic /  Abstract: Chromatin remodeling enzymes play a crucial role in the organization of chromatin, enabling both stability and plasticity of genome regulation. These enzymes use a Snf2-type ATPase motor to move ...Chromatin remodeling enzymes play a crucial role in the organization of chromatin, enabling both stability and plasticity of genome regulation. These enzymes use a Snf2-type ATPase motor to move nucleosomes, but how they translocate DNA around the histone octamer is unclear. Here we use cryo-EM to visualize the continuous motion of nucleosomal DNA induced by human chromatin remodeler SNF2H, an ISWI family member. Our work reveals conformational changes in SNF2H, DNA and histones during nucleosome sliding and provides the structural basis for DNA translocation. ATP hydrolysis induces conformational changes in SNF2H that pull the DNA tracking strand, distorting DNA and histones at SHL2. This is followed by SNF2H rotation on the nucleosome, which first pulls the DNA guide strand and creates one-base pair bulge at SHL2, and then releases the pulled DNA. Given the high conservation of the catalytic motors among ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers, the mechanisms we describe likely apply to other families. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_47427.map.gz emd_47427.map.gz | 418 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-47427-v30.xml emd-47427-v30.xml emd-47427.xml emd-47427.xml | 19.5 KB 19.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_47427.png emd_47427.png | 47.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-47427.cif.gz emd-47427.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_47427_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47427_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47427_half_map_2.map.gz emd_47427_half_map_2.map.gz | 172.6 MB 172.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47427 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47427 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47427 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47427 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_47427_validation.pdf.gz emd_47427_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_47427_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_47427_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_47427_validation.xml.gz emd_47427_validation.xml.gz | 15.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_47427_validation.cif.gz emd_47427_validation.cif.gz | 17.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47427 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47427 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47427 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47427 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9e1yC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_47427.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 468.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_47427.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 468.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | SNF2H bound to nucleosome - Class E1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half Map B
| File | emd_47427_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half Map A
| File | emd_47427_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : SNF2H bound to nucleosome - Class E2
| Entire | Name: SNF2H bound to nucleosome - Class E2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: SNF2H bound to nucleosome - Class E2
| Supramolecule | Name: SNF2H bound to nucleosome - Class E2 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MARTKQTARK STGGKAPRKQ LATKAARKSA PATGGVKKPH RYRPGTVALR EIRRYQKSTE LLIRKLPFQR LVREIAQDFK TDLRFQSSAV MALQEASEAY LVGLFEDTNL CAIHAKRVTI MPKDIQLARR IRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKGGKG LGKGGAKRHR KVLRDNIQGI TKPAIRRLAR RGGVKRISGL IYEETRGVLK VFLENVIRDA VTYTEHAKRK TVTAMDVVYA LKRQGRTLYG FGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKQGGK TRAKAKTRSS RAGLQFPVGR VHRLLRKGNY AERVGAGAPV YLAAVLEYLT AEILELAGNA ARDNKKTRII PRHLQLAVRN DEELNKLLGG VTIAQGGVLP NIQSVLLPKK TESAKSAKSK |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B 1.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B 1.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPEPAKSAPA PKKGSKKAVT KTQKKDGKKR RKTRKESYAI YVYKVLKQVH PDTGISSKAM SIMNSFVNDV FERIAGEASR LAHYNKRSTI TSREIQTAVR LLLPGELAKH AVSEGTKAVT KYTSAK |
-Macromolecule #7: SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of ch...
| Macromolecule | Name: SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Sequence | String: MSSAAEPPPP PPPESAPSKP AASIASGGSN SSNKGGPEGV AAQAVASAAS AGPADAEMEE IFDDASPGKQ KEIQEPDPTY EEKMQTDRAN RFEYLLKQTE LFAHFIQPAA QKTPTSPLKM KPGRPRIKKD EKQNLLSVGD YRHRRTEQEE DEELLTESSK ATNVCTRFED ...String: MSSAAEPPPP PPPESAPSKP AASIASGGSN SSNKGGPEGV AAQAVASAAS AGPADAEMEE IFDDASPGKQ KEIQEPDPTY EEKMQTDRAN RFEYLLKQTE LFAHFIQPAA QKTPTSPLKM KPGRPRIKKD EKQNLLSVGD YRHRRTEQEE DEELLTESSK ATNVCTRFED SPSYVKWGKL RDYQVRGLNW LISLYENGIN GILADEMGLG KTLQTISLLG YMKHYRNIPG PHMVLVPKST LHNWMSEFKR WVPTLRSVCL IGDKEQRAAF VRDVLLPGEW DVCVTSYEML IKEKSVFKKF NWRYLVIDEA HRIKNEKSKL SEIVREFKTT NRLLLTGTPL QNNLHELWSL LNFLLPDVFN SADDFDSWFD TNNCLGDQKL VERLHMVLRP FLLRRIKADV EKSLPPKKEV KIYVGLSKMQ REWYTRILMK DIDILNSAGK MDKMRLLNIL MQLRKCCNHP YLFDGAEPGP PYTTDMHLVT NSGKMVVLDK LLPKLKEQGS RVLIFSQMTR VLDILEDYCM WRNYEYCRLD GQTPHDERQD SINAYNEPNS TKFVFMLSTR AGGLGINLAT ADVVILYDSD WNPQVDLQAM DRAHRIGQTK TVRVFRFITD NTVEERIVER AEMKLRLDSI VIQQGRLVDQ NLNKIGKDEM LQMIRHGATH VFASKESEIT DEDIDGILER GAKKTAEMNE KLSKMGESSL RNFTMDTESS VYNFEGEDYR EKQKIAFTEW IEPPKRERKA NYAVDAYFRE ALRVSEPKAP KAPRPPKQPN VQDFQFFPPR LFELLEKEIL FYRKTIGYKV PRNPELPNAA QAQKEEQLKI DEAESLNDEE LEEKEKLLTQ GFTNWNKRDF NQFIKANEKW GRDDIENIAR EVEGKTPEEV IEYSAVFWER CNELQDIEKI MAQIERGEAR IQRRISIKKA LDTKIGRYKA PFHQLRISYG TNKGKNYTEE EDRFLICMLH KLGFDKENVY DELRQCIRNS PQFRFDWFLK SRTAMELQRR CNTLITLIER ENMELEEKEK AEKKKRGPKP STQKRKMDGA PDGRGRKKKL KL |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA(149-mer)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA(149-mer) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA(150-mer)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA(150-mer) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC) (DG)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 45 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 285.65 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 160.0 K / Max: 175.0 K |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 61.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 7000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)