+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the human truncated BOS complex in GDN | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | membrane protein biogenesis / membrane protein complex / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of nodal signaling pathway / multi-pass transmembrane protein insertion into ER membrane / multi-pass translocon complex / determination of left/right asymmetry in lateral mesoderm / protein localization to nuclear inner membrane / regulation of protein complex stability / regulation of signal transduction / regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / ribosome binding / carbohydrate binding ...negative regulation of nodal signaling pathway / multi-pass transmembrane protein insertion into ER membrane / multi-pass translocon complex / determination of left/right asymmetry in lateral mesoderm / protein localization to nuclear inner membrane / regulation of protein complex stability / regulation of signal transduction / regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / ribosome binding / carbohydrate binding / nuclear membrane / protein stabilization / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.65 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nguyen VN / Tomaleri GP / Voorhees RM | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Role of a holo-insertase complex in the biogenesis of biophysically diverse ER membrane proteins. Authors: Katharine R Page / Vy N Nguyen / Tino Pleiner / Giovani Pinton Tomaleri / Maxine L Wang / Alina Guna / Masami Hazu / Ting-Yu Wang / Tsui-Fen Chou / Rebecca M Voorhees /  Abstract: Mammalian membrane proteins perform essential physiologic functions that rely on their accurate insertion and folding at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Using forward and arrayed genetic screens, we ...Mammalian membrane proteins perform essential physiologic functions that rely on their accurate insertion and folding at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Using forward and arrayed genetic screens, we systematically studied the biogenesis of a panel of membrane proteins, including several G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). We observed a central role for the insertase, the ER membrane protein complex (EMC), and developed a dual-guide approach to identify genetic modifiers of the EMC. We found that the back of Sec61 (BOS) complex, a component of the multipass translocon, was a physical and genetic interactor of the EMC. Functional and structural analysis of the EMC⋅BOS holocomplex showed that characteristics of a GPCR's soluble domain determine its biogenesis pathway. In contrast to prevailing models, no single insertase handles all substrates. We instead propose a unifying model for coordination between the EMC, the multipass translocon, and Sec61 for the biogenesis of diverse membrane proteins in human cells. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_45294.map.gz emd_45294.map.gz | 175.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-45294-v30.xml emd-45294-v30.xml emd-45294.xml emd-45294.xml | 24.6 KB 24.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_45294.png emd_45294.png | 46.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-45294.cif.gz emd-45294.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_45294_additional_1.map.gz emd_45294_additional_1.map.gz emd_45294_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45294_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45294_half_map_2.map.gz emd_45294_half_map_2.map.gz | 170.2 MB 318.7 MB 318.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45294 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45294 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45294 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45294 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9c7uMC  9c7vC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_45294.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_45294.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
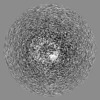
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.832 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
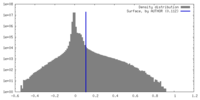
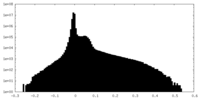
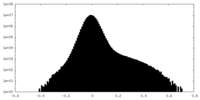
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Original unsharpened map of truncated BOS complex
| File | emd_45294_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Original unsharpened map of truncated BOS complex | ||||||||||||
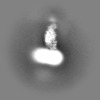
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
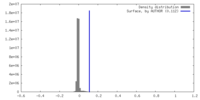
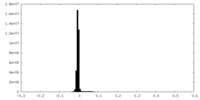
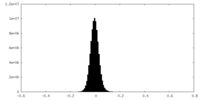
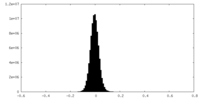
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_45294_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
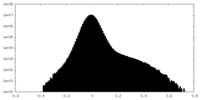
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_45294_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human truncated BOS complex
| Entire | Name: Human truncated BOS complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human truncated BOS complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Human truncated BOS complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 Details: Human BOS complex of truncated NOMO (delta Ig 1-9), TMEM147, and NCLN |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Nicalin
| Macromolecule | Name: Nicalin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 63.047145 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MLEEAGEVLE NMLKASCLPL GFIVFLPAVL LLVAPPLPAA DAAHEFTVYR MQQYDLQGQP YGTRNAVLNT EARTMAAEVL SRRCVLMRL LDFSYEQYQK ALRQSAGAVV IILPRAMAAV PQDVVRQFME IEPEMLAMET AVPVYFAVED EALLSIYKQT Q AASASQGS ...String: MLEEAGEVLE NMLKASCLPL GFIVFLPAVL LLVAPPLPAA DAAHEFTVYR MQQYDLQGQP YGTRNAVLNT EARTMAAEVL SRRCVLMRL LDFSYEQYQK ALRQSAGAVV IILPRAMAAV PQDVVRQFME IEPEMLAMET AVPVYFAVED EALLSIYKQT Q AASASQGS ASAAEVLLRT ATANGFQMVT SGVQSKAVSD WLIASVEGRL TGLGGEDLPT IVIVAHYDAF GVAPWLSLGA DS NGSGVSV LLELARLFSR LYTYKRTHAA YNLLFFASGG GKFNYQGTKR WLEDNLDHTD SSLLQDNVAF VLCLDTVGRG SSL HLHVSK PPREGTLQHA FLRELETVAA HQFPEVRFSM VHKRINLAED VLAWEHERFA IRRLPAFTLS HLESHRDGQR SSIM DVRSR VDSKTLTRNT RIIAEALTRV IYNLTEKGTP PDMPVFTEQM QIQQEQLDSV MDWLTNQPRA AQLVDKDSTF LSTLE HHLS RYLKDVKQHH VKADKRDPEF VFYDQLKQVM NAYRVKPAVF DLLLAVGIAA YLGMAYVAVQ HFSLLYKTVQ RLLVKA KTQ UniProtKB: BOS complex subunit NCLN |
-Macromolecule #2: BOS complex subunit NOMO2
| Macromolecule | Name: BOS complex subunit NOMO2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42.388957 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MLVGQGAGLL GPAVVTAAVV LLLSGVGPAH GSEDIVYALA GVSFEIKAED DQPLPGVLLS LSGGLFRSNL LTQDNGILTF SNLSPGQYY FKPMMKEFRF EPSSQMIEVQ EGQNLKITIT GYRTAYSCYG TVSSLNGEPE QGVAMEAVGQ NDCSIYGEDT V TDEEGKFR ...String: MLVGQGAGLL GPAVVTAAVV LLLSGVGPAH GSEDIVYALA GVSFEIKAED DQPLPGVLLS LSGGLFRSNL LTQDNGILTF SNLSPGQYY FKPMMKEFRF EPSSQMIEVQ EGQNLKITIT GYRTAYSCYG TVSSLNGEPE QGVAMEAVGQ NDCSIYGEDT V TDEEGKFR LRGLLPGCVY HVQLKAEGND HIERALPHHR VIEVGNNDID DVNIIVFRQI NQFDLSGNVI TSSEYLPTLW VK LYKSENL DNPIQTVSLG QSLFFHFPPL LRDGENYVVL LDSTLPRSQY DYILPQVSFT AVGYHKHITL IFNPTRKLPE QDI AQGSYI ALPLTLLVLL AGYNHDKLIP LLLQLTSRLQ GVGALGQAAS DNSGPEDAKR QAKKQKTRRT UniProtKB: BOS complex subunit NOMO2, BOS complex subunit NOMO2 |
-Macromolecule #3: Transmembrane protein 147
| Macromolecule | Name: Transmembrane protein 147 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.279848 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MTLFHFGNCF ALAYFPYFIT YKCSGLSEYN AFWKCVQAGV TYLFVQLCKM LFLATFFPTW EGGIYDFIGE FMKASVDVAD LIGLNLVMS RNAGKGEYKI MVAALGWATA ELIMSRCIPL WVGARGIEFD WKYIQMSIDS NISLVHYIVA SAQVWMITRY D LYHTFRPA ...String: MTLFHFGNCF ALAYFPYFIT YKCSGLSEYN AFWKCVQAGV TYLFVQLCKM LFLATFFPTW EGGIYDFIGE FMKASVDVAD LIGLNLVMS RNAGKGEYKI MVAALGWATA ELIMSRCIPL WVGARGIEFD WKYIQMSIDS NISLVHYIVA SAQVWMITRY D LYHTFRPA VLLLMFLSVY KAFVMETFVH LCSLGSWAAL LARAVVTGLL ALSTLALYVA VVNVHS UniProtKB: BOS complex subunit TMEM147 |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 279 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | Sample solubilized and purified in GDN. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 15929 / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-9c7u: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)