+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of K2P13.1 (THIK1) S136P in lipid nanodisc | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ion channel / K2P channel / transport protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of excitatory synapse pruning / Tandem pore domain halothane-inhibited K+ channel (THIK) / regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / Phase 4 - resting membrane potential / potassium ion leak channel activity / regulation of resting membrane potential / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / monoatomic ion channel complex / potassium channel activity / potassium ion transmembrane transport ...regulation of excitatory synapse pruning / Tandem pore domain halothane-inhibited K+ channel (THIK) / regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / Phase 4 - resting membrane potential / potassium ion leak channel activity / regulation of resting membrane potential / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / monoatomic ion channel complex / potassium channel activity / potassium ion transmembrane transport / protein heterodimerization activity / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.36 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Roy-Chowdhury S / Adberemane-Ali F / Minor DL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Structure of the human K13.1 channel reveals a hydrophilic pore restriction and lipid cofactor site. Authors: Shatabdi Roy-Chowdhury / Seil Jang / Fayal Abderemane-Ali / Fiona Naughton / Michael Grabe / Daniel L Minor /  Abstract: Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) lipids modulate the neuronal and microglial leak potassium channel K13.1 (THIK1) and other voltage-gated ion channel (VGIC) superfamily members through poorly ...Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) lipids modulate the neuronal and microglial leak potassium channel K13.1 (THIK1) and other voltage-gated ion channel (VGIC) superfamily members through poorly understood mechanisms. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of human THIK1 and mutants, revealing a unique two-chamber aqueous inner cavity obstructed by a hydrophilic barrier important for gating, the flow restrictor, and a P1-M4 intersubunit interface lipid at a site, the PUFA site, corresponding to the K small-molecule modulator pocket. This overlap, together with functional studies, indicates that PUFA site lipids are THIK1 cofactors. Comparison with a PUFA-responsive VGIC, K7.1, reveals a shared modulatory role for the pore domain intersubunit interface, providing a framework for understanding PUFA action on the VGIC superfamily. Our findings reveal the distinct THIK1 architecture, highlight the importance of the P1-M4 interface for K control by natural and synthetic ligands and should aid in the development of THIK subfamily modulators for neuroinflammation and autism. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_45077.map.gz emd_45077.map.gz | 45.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-45077-v30.xml emd-45077-v30.xml emd-45077.xml emd-45077.xml | 20.9 KB 20.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_45077.png emd_45077.png | 56.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-45077.cif.gz emd-45077.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_45077_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45077_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45077_half_map_2.map.gz emd_45077_half_map_2.map.gz | 84.5 MB 84.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45077 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45077 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45077 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45077 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9c09MC 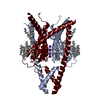 9bsnC  9bwsC  9byiC  9c07C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_45077.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_45077.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_45077_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_45077_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Homodimer of human K2P13.1 (THIK1) with S136P activating mutation
| Entire | Name: Homodimer of human K2P13.1 (THIK1) with S136P activating mutation |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Homodimer of human K2P13.1 (THIK1) with S136P activating mutation
| Supramolecule | Name: Homodimer of human K2P13.1 (THIK1) with S136P activating mutation type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 80 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium channel subfamily K member 13
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium channel subfamily K member 13 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.383613 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAGRGFSWGP GHLNEDNARF LLLAALIVLY LLGGAAVFSA LELAHERQAK QRWEERLAQF SRGHQLSRDE LRGFLRHYEE ATRAGIRVD NVRPRWDFTG AFYFVGTVVS TIGFGMTTPA TVGGKIFLIF YGLVGCPSTI LFFNLFLERL ITIIAYIMKS C HQRQLRRR ...String: MAGRGFSWGP GHLNEDNARF LLLAALIVLY LLGGAAVFSA LELAHERQAK QRWEERLAQF SRGHQLSRDE LRGFLRHYEE ATRAGIRVD NVRPRWDFTG AFYFVGTVVS TIGFGMTTPA TVGGKIFLIF YGLVGCPSTI LFFNLFLERL ITIIAYIMKS C HQRQLRRR GALPQESLKD AGQCEVDSLA GWKPSVYYVM LILCTASILI SCCASAMYTP IEGWSYFDSL YFCFVAFSTI GF GDLVSSQ NAHYESQGLY RFANFVFILM GVCCIYSLFN VISILIKQSL NWILRKMDSG CCPQCQRGLL RSRRNVVMPG SVR NRCNIS IETDGVAESD TDGRRLSGEM ISMK UniProtKB: Potassium channel subfamily K member 13 |
-Macromolecule #2: DODECANE
| Macromolecule | Name: DODECANE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: D12 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 170.335 Da |
| Chemical component information | 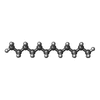 ChemComp-D12: |
-Macromolecule #3: DECANE
| Macromolecule | Name: DECANE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: D10 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 142.282 Da |
| Chemical component information | 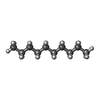 ChemComp-D10: |
-Macromolecule #4: N-OCTANE
| Macromolecule | Name: N-OCTANE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: OCT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 114.229 Da |
| Chemical component information | 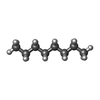 ChemComp-OCT: |
-Macromolecule #5: LINOLEIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: LINOLEIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: EIC |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 280.445 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-EIC: |
-Macromolecule #6: HEXANE
| Macromolecule | Name: HEXANE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: HEX |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 86.175 Da |
| Chemical component information | 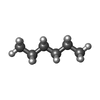 ChemComp-HEX: |
-Macromolecule #7: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 Component:
| |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




































