+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 | ||||||||||||
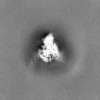
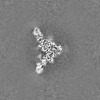
 Map data Map data | unsharpened map of EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | EBOV glycoprotein / nanobody / VIRAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated killing of host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum / viral budding from plasma membrane / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell cytoplasm / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / membrane raft / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane ...symbiont-mediated killing of host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum / viral budding from plasma membrane / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell cytoplasm / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / membrane raft / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / lipid binding / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / extracellular region / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.36 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bu F / Ye G / Liu B / Li F | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2024 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2024Title: Discovery of Nanosota-EB1 and -EB2 as Novel Nanobody Inhibitors Against Ebola Virus Infection. Authors: Fan Bu / Gang Ye / Kimberly Morsheimer / Alise Mendoza / Hailey Turner-Hubbard / Morgan Herbst / Benjamin Spiller / Brian E Wadzinski / Brett Eaton / Manu Anantpadma / Ge Yang / Bin Liu / ...Authors: Fan Bu / Gang Ye / Kimberly Morsheimer / Alise Mendoza / Hailey Turner-Hubbard / Morgan Herbst / Benjamin Spiller / Brian E Wadzinski / Brett Eaton / Manu Anantpadma / Ge Yang / Bin Liu / Robert Davey / Fang Li /  Abstract: The Ebola filovirus (EBOV) poses a serious threat to global health and national security. Nanobodies, a type of single-domain antibody, have demonstrated promising therapeutic potential. We ...The Ebola filovirus (EBOV) poses a serious threat to global health and national security. Nanobodies, a type of single-domain antibody, have demonstrated promising therapeutic potential. We identified two anti-EBOV nanobodies, Nanosota-EB1 and Nanosota-EB2, which specifically target the EBOV glycoprotein (GP). Cryo-EM and biochemical data revealed that Nanosota-EB1 binds to the glycan cap of GP1, preventing its protease cleavage, while Nanosota-EB2 binds to critical membrane-fusion elements in GP2, stabilizing it in the pre-fusion state. Nanosota-EB2 is a potent neutralizer of EBOV infection in vitro and offers excellent protection in a mouse model of EBOV challenge, while Nanosota-EB1 provides moderate neutralization and protection. Nanosota-EB1 and Nanosota-EB2 are the first nanobodies shown to inhibit authentic EBOV. Combined with our newly developed structure-guided in vitro evolution approach, they lay the foundation for nanobody-based therapies against EBOV and other viruses within the ebolavirus genus. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44872.map.gz emd_44872.map.gz | 63 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44872-v30.xml emd-44872-v30.xml emd-44872.xml emd-44872.xml | 19.3 KB 19.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
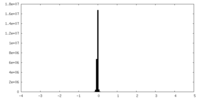
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44872_fsc.xml emd_44872_fsc.xml | 10.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44872.png emd_44872.png | 52.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44872.cif.gz emd-44872.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44872_additional_1.map.gz emd_44872_additional_1.map.gz emd_44872_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44872_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44872_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44872_half_map_2.map.gz | 118.2 MB 115.9 MB 115.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44872 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44872 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44872 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44872 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9bsuMC  9bsvC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44872.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44872.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | unsharpened map of EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: sharpened map of EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex
| File | emd_44872_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
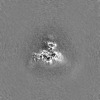
| Annotation | sharpened map of EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
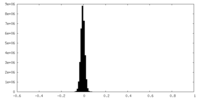
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half map A of EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex
| File | emd_44872_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map_A of EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half map B of EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex
| File | emd_44872_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map_B of EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex
| Entire | Name: EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: EBOV GP/Nanosota-EB1 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: EBOV GP
| Supramolecule | Name: EBOV GP / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Nanosota-EB1
| Supramolecule | Name: Nanosota-EB1 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Envelope glycoprotein
| Macromolecule | Name: Envelope glycoprotein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 77.812781 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGVTGILQLP RDRFKRTSFF LWVIILFQRT FSIPLGVIHN STLQVSDVDK LVCRDKLSST NQLRSVGLNL EGNGVATDVP SATKRWGFR SGVPPKVVNY EAGEWAENCY NLEIKKPDGS ECLPAAPDGI RGFPRCRYVH KVSGTGPCAG DFAFHKEGAF F LYDRLAST ...String: MGVTGILQLP RDRFKRTSFF LWVIILFQRT FSIPLGVIHN STLQVSDVDK LVCRDKLSST NQLRSVGLNL EGNGVATDVP SATKRWGFR SGVPPKVVNY EAGEWAENCY NLEIKKPDGS ECLPAAPDGI RGFPRCRYVH KVSGTGPCAG DFAFHKEGAF F LYDRLAST VIYRGTTFAE GVVAFLILPQ AKKDFFSSHP LREPVNATED PSSGYYSTTI RYQATGFGTN ETEYLFEVDN LT YVQLESR FTPQFLLQLN ETIYTSGKRS NTTGKLIWKV NPEIDTTIGE WAFWETKKNL TRKIRSEELS FTVVSNGAKN ISG QSPART SSDPGTNTTT EDHKIMASEN SSAMVQVHSQ GREAAVSHLT TLATISTSPQ SLTTKPGPDN STHNTPVYKL DISE ATQVE QHHRRTDNDS TASDTPSATT AAGPPKAENT NTSKSTDFLD PATTTSPQNH SETAGNNNTH HQDTGEESAS SGKLG LITN TIAGVAGLIT GGRRTRREAI VNAQPKCNPN LHYWTTQDEG AAIGLAWIPY FGPAAEGIYI EGLMHNQDGL ICGLRQ LAN ETTQALQLFL RATTELRTFS ILNRKAIDFL LQRWGGTCHI LGPDCCIEPH DWTKNITDKI DQIIHDFVDK TLPDQGD ND NWWTGWRQWI PAGIGVTGVI IAVIALFCIC KFVFGSGYIP EAPRDGQAYV RKDGEWVLLS TFLG UniProtKB: Envelope glycoprotein |
-Macromolecule #2: Nanosota-EB1
| Macromolecule | Name: Nanosota-EB1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.592182 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: QVQLQESGGG QVQAGGSLRL SCAASGSTSV IYAMGWYRQA PGKQRELVAA ITRGVGSTNY ADSVKGRFTI SRDNAKNTMY LQMNSLKPE DTAVYYCNAR LLVAPPPYEY DYWGQGTQVT VSSGGQHHHH HHGAYPYDVP DYAS |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)