[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-44366: Cryo-EM structure of the human TRPM4 in complex with calcium at 1... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
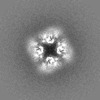
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human TRPM4 in complex with calcium at 18 degrees Celsius | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / TRP channel / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / positive regulation of regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell membrane depolarization / sodium channel complex / regulation of T cell cytokine production / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / membrane depolarization during Purkinje myocyte cell action potential / metal ion transport / negative regulation of bone mineralization / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential ...positive regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / positive regulation of regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell membrane depolarization / sodium channel complex / regulation of T cell cytokine production / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / membrane depolarization during Purkinje myocyte cell action potential / metal ion transport / negative regulation of bone mineralization / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / calcium-activated cation channel activity / sodium ion import across plasma membrane / : / dendritic cell chemotaxis / TRP channels / cellular response to ATP / sodium channel activity / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / positive regulation of vasoconstriction / protein sumoylation / negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / positive regulation of fat cell differentiation / positive regulation of heart rate / positive regulation of adipose tissue development / calcium-mediated signaling / calcium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel activity / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / protein homotetramerization / adaptive immune response / calmodulin binding / neuronal cell body / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / calcium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hu J / Lu W / Du J | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 9 items United States, 9 items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Physiological temperature drives TRPM4 ligand recognition and gating. Authors: Jinhong Hu / Sung Jin Park / Tyler Walter / Ian J Orozco / Garrett O'Dea / Xinyu Ye / Juan Du / Wei Lü /  Abstract: Temperature profoundly affects macromolecular function, particularly in proteins with temperature sensitivity. However, its impact is often overlooked in biophysical studies that are typically ...Temperature profoundly affects macromolecular function, particularly in proteins with temperature sensitivity. However, its impact is often overlooked in biophysical studies that are typically performed at non-physiological temperatures, potentially leading to inaccurate mechanistic and pharmacological insights. Here we demonstrate temperature-dependent changes in the structure and function of TRPM4, a temperature-sensitive Ca-activated ion channel. By studying TRPM4 prepared at physiological temperature using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy, we identified a 'warm' conformation that is distinct from those observed at lower temperatures. This conformation is driven by a temperature-dependent Ca-binding site in the intracellular domain, and is essential for TRPM4 function in physiological contexts. We demonstrated that ligands, exemplified by decavanadate (a positive modulator) and ATP (an inhibitor), bind to different locations of TRPM4 at physiological temperatures than at lower temperatures, and that these sites have bona fide functional relevance. We elucidated the TRPM4 gating mechanism by capturing structural snapshots of its different functional states at physiological temperatures, revealing the channel opening that is not observed at lower temperatures. Our study provides an example of temperature-dependent ligand recognition and modulation of an ion channel, underscoring the importance of studying macromolecules at physiological temperatures. It also provides a potential molecular framework for deciphering how thermosensitive TRPM channels perceive temperature changes. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44366.map.gz emd_44366.map.gz | 187.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44366-v30.xml emd-44366-v30.xml emd-44366.xml emd-44366.xml | 18.5 KB 18.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_44366.png emd_44366.png | 85.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44366.cif.gz emd-44366.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44366_additional_1.map.gz emd_44366_additional_1.map.gz emd_44366_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44366_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44366_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44366_half_map_2.map.gz | 16.5 MB 190.9 MB 190.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44366 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44366 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44366 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44366 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9b92MC  9b8wC  9b8xC  9b8yC  9b8zC  9b90C  9b91C  9b93C  9b94C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44366.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44366.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.828 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_44366_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
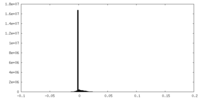
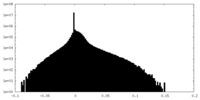
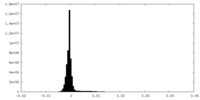
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44366_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44366_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : human TRPM4 in complex with calcium at 18 degrees Celsius
| Entire | Name: human TRPM4 in complex with calcium at 18 degrees Celsius |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: human TRPM4 in complex with calcium at 18 degrees Celsius
| Supramolecule | Name: human TRPM4 in complex with calcium at 18 degrees Celsius type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4
| Macromolecule | Name: Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 134.456484 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism: Mammalia (mammals) |
| Sequence | String: MVVPEKEQSW IPKIFKKKTC TTFIVDSTDP GGTLCQCGRP RTAHPAVAME DAFGAAVVTV WDSDAHTTEK PTDAYGELDF TGAGRKHSN FLRLSDRTDP AAVYSLVTRT WGFRAPNLVV SVLGGSGGPV LQTWLQDLLR RGLVRAAQST GAWIVTGGLH T GIGRHVGV ...String: MVVPEKEQSW IPKIFKKKTC TTFIVDSTDP GGTLCQCGRP RTAHPAVAME DAFGAAVVTV WDSDAHTTEK PTDAYGELDF TGAGRKHSN FLRLSDRTDP AAVYSLVTRT WGFRAPNLVV SVLGGSGGPV LQTWLQDLLR RGLVRAAQST GAWIVTGGLH T GIGRHVGV AVRDHQMAST GGTKVVAMGV APWGVVRNRD TLINPKGSFP ARYRWRGDPE DGVQFPLDYN YSAFFLVDDG TH GCLGGEN RFRLRLESYI SQQKTGVGGT GIDIPVLLLL IDGDEKMLTR IENATQAQLP CLLVAGSGGA ADCLAETLED TLA PGSGGA RQGEARDRIR RFFPKGDLEV LQAQVERIMT RKELLTVYSS EDGSEEFETI VLKALVKACG SSEASAYLDE LRLA VAWNR VDIAQSELFR GDIQWRSFHL EASLMDALLN DRPEFVRLLI SHGLSLGHFL TPMRLAQLYS AAPSNSLIRN LLDQA SHSA GTKAPALKGG AAELRPPDVG HVLRMLLGKM CAPRYPSGGA WDPHPGQGFG ESMYLLSDKA TSPLSLDAGL GQAPWS DLL LWALLLNRAQ MAMYFWEMGS NAVSSALGAC LLLRVMARLE PDAEEAARRK DLAFKFEGMG VDLFGECYRS SEVRAAR LL LRRCPLWGDA TCLQLAMQAD ARAFFAQDGV QSLLTQKWWG DMASTTPIWA LVLAFFCPPL IYTRLITFRK SEEEPTRE E LEFDMDSVIN GEGPVGTADP AEKTPLGVPR QSGRPGCCGG RCGGRRCLRR WFHFWGAPVT IFMGNVVSYL LFLLLFSRV LLVDFQPAPP GSLELLLYFW AFTLLCEELR QGLSGGGGSL ASGGPGPGHA SLSQRLRLYL ADSWNQCDLV ALTCFLLGVG CRLTPGLYH LGRTVLCIDF MVFTVRLLHI FTVNKQLGPK IVIVSKMMKD VFFFLFFLGV WLVAYGVATE GLLRPRDSDF P SILRRVFY RPYLQIFGQI PQEDMDVALM EHSNCSSEPG FWAHPPGAQA GTCVSQYANW LVVLLLVIFL LVANILLVNL LI AMFSYTF GKVQGNSDLY WKAQRYRLIR EFHSRPALAP PFIVISHLRL LLRQLCRRPR SPQPSSPALE HFRVYLSKEA ERK LLTWES VHKENFLLAR ARDKRESDSE RLKRTSQKVD LALKQLGHIR EYEQRLKVLE REVQQCSRVL GWVAEALSRS ALLP PGGPP PPDLPGSKD UniProtKB: Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4 |
-Macromolecule #2: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.9000000000000001 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 301000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)