[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-43815: Cryo-EM structure of the active Lactococcus lactis Csm bound to t... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the active Lactococcus lactis Csm bound to target in pre-cleavage stage | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Type III-A CRISPR-Cas / Csm / Cyclic Oligoadenylate synthesis / RNA BINDING PROTEIN-RNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationexonuclease activity / endonuclease activity / defense response to virus / hydrolase activity / RNA binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis (lactic acid bacteria) Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis (lactic acid bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.79 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang B / Goswami HN / Li H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2024 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2024Title: Molecular basis for cA6 synthesis by a type III-A CRISPR-Cas enzyme and its conversion to cA4 production. Authors: Hemant N Goswami / Fozieh Ahmadizadeh / Bing Wang / Doreen Addo-Yobo / Yu Zhao / A Carl Whittington / Huan He / Michael P Terns / Hong Li /  Abstract: The type III-A (Csm) CRISPR-Cas systems are multi-subunit and multipronged prokaryotic enzymes in guarding the hosts against viral invaders. Beyond cleaving activator RNA transcripts, Csm confers ...The type III-A (Csm) CRISPR-Cas systems are multi-subunit and multipronged prokaryotic enzymes in guarding the hosts against viral invaders. Beyond cleaving activator RNA transcripts, Csm confers two additional activities: shredding single-stranded DNA and synthesizing cyclic oligoadenylates (cOAs) by the Cas10 subunit. Known Cas10 enzymes exhibit a fascinating diversity in cOA production. Three major forms-cA3, cA4 and cA6have been identified, each with the potential to trigger unique downstream effects. Whereas the mechanism for cOA-dependent activation is well characterized, the molecular basis for synthesizing different cOA isoforms remains unclear. Here, we present structural characterization of a cA6-producing Csm complex during its activation by an activator RNA. Analysis of the captured intermediates of cA6 synthesis suggests a 3'-to-5' nucleotidyl transferring process. Three primary adenine binding sites can be identified along the chain elongation path, including a unique tyrosine-threonine dyad found only in the cA6-producing Cas10. Consistently, disrupting the tyrosine-threonine dyad specifically impaired cA6 production while promoting cA4 production. These findings suggest that Cas10 utilizes a unique enzymatic mechanism for forming the phosphodiester bond and has evolved distinct strategies to regulate the cOA chain length. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_43815.map.gz emd_43815.map.gz | 157.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-43815-v30.xml emd-43815-v30.xml emd-43815.xml emd-43815.xml | 21.8 KB 21.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_43815_fsc.xml emd_43815_fsc.xml | 11.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_43815.png emd_43815.png | 80.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-43815.cif.gz emd-43815.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_43815_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43815_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43815_half_map_2.map.gz emd_43815_half_map_2.map.gz | 154.5 MB 154.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43815 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43815 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43815 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43815 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 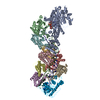 9asiMC 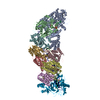 9ashC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_43815.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_43815.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
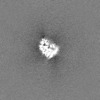
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.074 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_43815_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
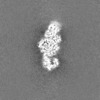
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
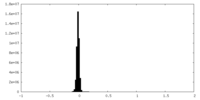
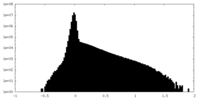
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_43815_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
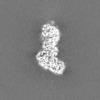
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Lactococcus lactis Csm CRISPR-Cas complex, ATP bound and Cas10 fl...
+Supramolecule #1: Lactococcus lactis Csm CRISPR-Cas complex, ATP bound and Cas10 fl...
+Macromolecule #1: CRISPR-associated protein Csm4
+Macromolecule #2: CRISPR system Cms endoribonuclease Csm3
+Macromolecule #4: CRISPR system Cms protein Csm2
+Macromolecule #6: CRISPR system Cms protein Csm5
+Macromolecule #7: CRISPR system single-strand-specific deoxyribonuclease Cas10/Csm1...
+Macromolecule #3: CRISPR RNA
+Macromolecule #5: Target RNA
+Macromolecule #8: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #9: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #10: ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: OTHER / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)