+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Consensus map of hFASN/NADPH State 7 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Consensus map of hFASN/NADPH State 7 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Megasynthase / Lipogenesis / BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.45 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Schultz K / Marmorstein R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: Snapshots of acyl carrier protein shuttling in human fatty acid synthase. Authors: Kollin Schultz / Pedro Costa-Pinheiro / Lauren Gardner / Laura V Pinheiro / Julio Ramirez-Solis / Sarah M Gardner / Kathryn E Wellen / Ronen Marmorstein /  Abstract: The mammalian fatty acid synthase (FASN) enzyme is a dynamic multienzyme that belongs to the megasynthase family. In mammals, a single gene encodes six catalytically active domains and a flexibly ...The mammalian fatty acid synthase (FASN) enzyme is a dynamic multienzyme that belongs to the megasynthase family. In mammals, a single gene encodes six catalytically active domains and a flexibly tethered acyl carrier protein (ACP) domain that shuttles intermediates between active sites for fatty acid biosynthesis. FASN is an essential enzyme in mammalian development through the role that fatty acids have in membrane formation, energy storage, cell signalling and protein modifications. Thus, FASN is a promising target for treatment of a large variety of diseases including cancer, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, and viral and parasite infections. The multi-faceted mechanism of FASN and the dynamic nature of the protein, in particular of the ACP, have made it challenging to understand at the molecular level. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of human FASN in a multitude of conformational states with NADPH and NADP plus acetoacetyl-CoA present, including structures with the ACP stalled at the dehydratase (DH) and enoyl-reductase (ER) domains. We show that FASN activity in vitro and de novo lipogenesis in cells is inhibited by mutations at the ACP-DH and ACP-ER interfaces. Together, these studies provide new molecular insights into the dynamic nature of FASN and the ACP shuttling mechanism, with implications for developing improved FASN-targeted therapeutics. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_43454.map.gz emd_43454.map.gz | 89.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-43454-v30.xml emd-43454-v30.xml emd-43454.xml emd-43454.xml | 17.8 KB 17.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_43454_fsc.xml emd_43454_fsc.xml | 11.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_43454.png emd_43454.png | 79.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_43454_msk_1.map emd_43454_msk_1.map | 178 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-43454.cif.gz emd-43454.cif.gz | 4.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_43454_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43454_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43454_half_map_2.map.gz emd_43454_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.5 MB 165.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43454 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43454 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43454 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43454 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_43454_validation.pdf.gz emd_43454_validation.pdf.gz | 916.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_43454_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_43454_full_validation.pdf.gz | 916.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_43454_validation.xml.gz emd_43454_validation.xml.gz | 20.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_43454_validation.cif.gz emd_43454_validation.cif.gz | 26.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-43454 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-43454 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-43454 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-43454 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8vf7C  8vg4C  8vleC  8vloC  8vlpC  8vm0C  8vm5C  8vm6C  8vm7C  8vmcC  8vmdC C: citing same article ( |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_43454.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_43454.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Consensus map of hFASN/NADPH State 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
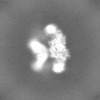
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.069 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
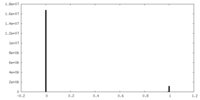
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_43454_msk_1.map emd_43454_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
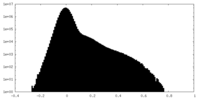
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_43454_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_43454_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : human Fatty Acid Synthase
| Entire | Name: human Fatty Acid Synthase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: human Fatty Acid Synthase
| Supramolecule | Name: human Fatty Acid Synthase / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Details: Consensus map of human FASN with NADPH in State 7 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 554 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 3.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R0.6/1 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Slit width: 30 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 19126 / Average electron dose: 52.4 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






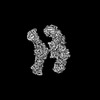






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)