[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-42628: Structure of the insect gustatory receptor Gr9 from Bombyx mori -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the insect gustatory receptor Gr9 from Bombyx mori | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Gustatory receptor / Ion channel / Sugar-binding / Fructose / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationionotropic taste receptor activity / detection of chemical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sweet taste / male courtship behavior / chemosensory behavior / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / axon / neuronal cell body / dendrite / signal transduction / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
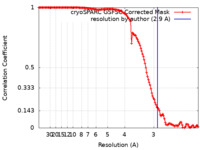
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gomes JV / Butterwick JA | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: The molecular basis of sugar detection by an insect taste receptor. Authors: João Victor Gomes / Shivinder Singh-Bhagania / Matthew Cenci / Carlos Chacon Cordon / Manjodh Singh / Joel A Butterwick /  Abstract: Animals crave sugars because of their energy potential and the pleasurable sensation of tasting sweetness. Yet all sugars are not metabolically equivalent, requiring mechanisms to detect and ...Animals crave sugars because of their energy potential and the pleasurable sensation of tasting sweetness. Yet all sugars are not metabolically equivalent, requiring mechanisms to detect and differentiate between chemically similar sweet substances. Insects use a family of ionotropic gustatory receptors to discriminate sugars, each of which is selectively activated by specific sweet molecules. Here, to gain insight into the molecular basis of sugar selectivity, we determined structures of Gr9, a gustatory receptor from the silkworm Bombyx mori (BmGr9), in the absence and presence of its sole activating ligand, D-fructose. These structures, along with structure-guided mutagenesis and functional assays, illustrate how D-fructose is enveloped by a ligand-binding pocket that precisely matches the overall shape and pattern of chemical groups in D-fructose. However, our computational docking and experimental binding assays revealed that other sugars also bind BmGr9, yet they are unable to activate the receptor. We determined the structure of BmGr9 in complex with one such non-activating sugar, L-sorbose. Although both sugars bind a similar position, only D-fructose is capable of engaging a bridge of two conserved aromatic residues that connects the pocket to the pore helix, inducing a conformational change that allows the ion-conducting pore to open. Thus, chemical specificity does not depend solely on the selectivity of the ligand-binding pocket, but it is an emergent property arising from a combination of receptor-ligand interactions and allosteric coupling. Our results support a model whereby coarse receptor tuning is derived from the size and chemical characteristics of the pocket, whereas fine-tuning of receptor activation is achieved through the selective engagement of an allosteric pathway that regulates ion conduction. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_42628.map.gz emd_42628.map.gz | 203.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-42628-v30.xml emd-42628-v30.xml emd-42628.xml emd-42628.xml | 16.2 KB 16.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_42628_fsc.xml emd_42628_fsc.xml | 12.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_42628.png emd_42628.png | 170.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-42628.cif.gz emd-42628.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_42628_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42628_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42628_half_map_2.map.gz emd_42628_half_map_2.map.gz | 200.1 MB 200.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42628 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42628 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42628 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42628 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_42628_validation.pdf.gz emd_42628_validation.pdf.gz | 804.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_42628_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_42628_full_validation.pdf.gz | 804.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_42628_validation.xml.gz emd_42628_validation.xml.gz | 21.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_42628_validation.cif.gz emd_42628_validation.cif.gz | 27.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42628 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42628 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42628 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42628 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8uvtMC  8uvuC  8vv3C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_42628.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_42628.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.068 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_42628_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
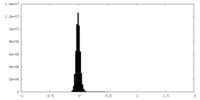
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_42628_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
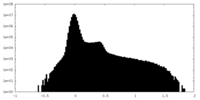
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Homotetramer of Gr9 in the absence of ligand
| Entire | Name: Homotetramer of Gr9 in the absence of ligand |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Homotetramer of Gr9 in the absence of ligand
| Supramolecule | Name: Homotetramer of Gr9 in the absence of ligand / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Gustatory receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Gustatory receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50.67707 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GPGRAPPSPD LRADEPKTPC LVGGAHAFIL KISSFCGLAP LRFEPRSQEY AVTISKGKCF YSYILVTFLV ICTIYGLVAE IGVGVEKSV RMSSRMSQVV SACDILVVAV TAGVGVYGAP ARMRTMLSYM ENIVAVDREL GRHHSAATER KLCALLLLIL L SFTILLVD ...String: GPGRAPPSPD LRADEPKTPC LVGGAHAFIL KISSFCGLAP LRFEPRSQEY AVTISKGKCF YSYILVTFLV ICTIYGLVAE IGVGVEKSV RMSSRMSQVV SACDILVVAV TAGVGVYGAP ARMRTMLSYM ENIVAVDREL GRHHSAATER KLCALLLLIL L SFTILLVD DFCFYAMQAG KTGRQWEIVT NYAGFYFLWY IVMVLELQFA FTALSLRARL KLFNEALNVT ASQVCKPVKK PK NSQLSVY ATSVRPVSCK RENVIVETIR VRDKDDAFVM MKTADGVPCL QVPPCEAVGR LSRMRCTLCE VTRHIADGYG LPL VIILMS TLLHLIVTPY FLIMEIIVST HRLHFLVLQF LWCTTHLIRM LVVVEPCHYT IREGKRTEDI LCRLMTLAPH GGVL SSRLE VLSRLLMLQN ISYSPLGMCT LDRPLMVTVL GAVTTYLVIL IQFQRYDS UniProtKB: Gustatory receptor |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)