[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-42478: Trehalose Synthase (TreS) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in comple... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Trehalose Synthase (TreS) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in complex with 6-TreAz compound | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TreS / Trehalose Synthase / Mycobacterium tuberculosis / 6-TreAz / CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmaltose alpha-D-glucosyltransferase / maltose alpha-D-glucosyltransferase activity / capsule polysaccharide biosynthetic process / alpha-amylase / glycogen biosynthetic process / alpha-amylase activity / polysaccharide catabolic process / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pathirage R / Ronning DR | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: ACS Infect Dis / Year: 2024 Journal: ACS Infect Dis / Year: 2024Title: Targeting Persistence through Inhibition of the Trehalose Catalytic Shift. Authors: Karishma Kalera / Rachel Liu / Juhyeon Lim / Rasangi Pathirage / Daniel H Swanson / Ulysses G Johnson / Alicyn I Stothard / Jae Jin Lee / Anne W Poston / Peter J Woodruff / Donald R Ronning ...Authors: Karishma Kalera / Rachel Liu / Juhyeon Lim / Rasangi Pathirage / Daniel H Swanson / Ulysses G Johnson / Alicyn I Stothard / Jae Jin Lee / Anne W Poston / Peter J Woodruff / Donald R Ronning / Hyungjin Eoh / Benjamin M Swarts /  Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB), caused by (Mtb), is the leading cause of death worldwide by infectious disease. Treatment of Mtb infection requires a six-month course of multiple antibiotics, an extremely ...Tuberculosis (TB), caused by (Mtb), is the leading cause of death worldwide by infectious disease. Treatment of Mtb infection requires a six-month course of multiple antibiotics, an extremely challenging regimen necessitated by Mtb's ability to form drug-tolerant persister cells. Mtb persister formation is dependent on the trehalose catalytic shift, a stress-responsive metabolic remodeling mechanism in which the disaccharide trehalose is liberated from cell surface glycolipids and repurposed as an internal carbon source to meet energy and redox demands. Here, using a biofilm-persister model, metabolomics, and cryo-electron microscopy (EM), we found that azidodeoxy- and aminodeoxy-d-trehalose analogues block the Mtb trehalose catalytic shift through inhibition of trehalose synthase TreS (Rv0126), which catalyzes the isomerization of trehalose to maltose. Out of a focused eight-member compound panel constructed by chemoenzymatic synthesis, the natural product 2-trehalosamine exhibited the highest potency and significantly potentiated first- and second-line TB drugs in broth culture and macrophage infection assays. We also report the first structure of TreS bound to a substrate analogue inhibitor, obtained via cryo-EM, which revealed conformational changes likely essential for catalysis and inhibitor binding that can potentially be exploited for future therapeutic development. Our results demonstrate that inhibition of the trehalose catalytic shift is a viable strategy to target Mtb persisters and advance trehalose analogues as tools and potential adjunctive therapeutics for investigating and targeting mycobacterial persistence. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
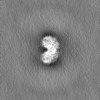
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_42478.map.gz emd_42478.map.gz | 203.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-42478-v30.xml emd-42478-v30.xml emd-42478.xml emd-42478.xml | 15.6 KB 15.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_42478.png emd_42478.png | 100.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-42478.cif.gz emd-42478.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_42478_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42478_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42478_half_map_2.map.gz emd_42478_half_map_2.map.gz | 200.3 MB 200.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42478 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42478 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42478 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42478 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_42478_validation.pdf.gz emd_42478_validation.pdf.gz | 981.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_42478_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_42478_full_validation.pdf.gz | 981.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_42478_validation.xml.gz emd_42478_validation.xml.gz | 15.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_42478_validation.cif.gz emd_42478_validation.cif.gz | 18.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42478 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42478 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42478 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-42478 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8uqvMC  8uzhC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
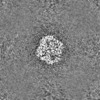
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_42478.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_42478.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.13 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_42478_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
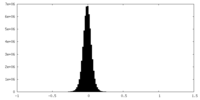
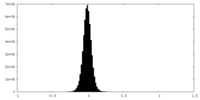
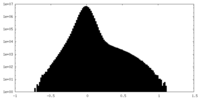
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_42478_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
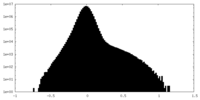
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : 6-TreAz bound Trehalose synthase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
| Entire | Name: 6-TreAz bound Trehalose synthase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: 6-TreAz bound Trehalose synthase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
| Supramolecule | Name: 6-TreAz bound Trehalose synthase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Trehalose synthase/amylase TreS
| Macromolecule | Name: Trehalose synthase/amylase TreS / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.792586 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: PVQGSHVEGG VVEHPDAKDF GSAAALPADP TWFKHAVFYE VLVRAFFDAS ADGSGDLRGL IDRLDYLQWL GIDCIWLPPF YDSPLRDGG YDIRDFYKVL PEFGTVDDFV ALVDAAHRRG IRIITDLVMN HTSESHPWFQ ESRRDPDGPY GDYYVWSDTS E RYTDARII ...String: PVQGSHVEGG VVEHPDAKDF GSAAALPADP TWFKHAVFYE VLVRAFFDAS ADGSGDLRGL IDRLDYLQWL GIDCIWLPPF YDSPLRDGG YDIRDFYKVL PEFGTVDDFV ALVDAAHRRG IRIITDLVMN HTSESHPWFQ ESRRDPDGPY GDYYVWSDTS E RYTDARII FVDTEESNWS FDPVRRQFYW HRFFSHQPDL NYDNPAVQEA MIDVIRFWLG LGIDGFRLAA VPYLFEREGT NC ENLPETH AFLKRVRKVV DDEFPGRVLL AEANQWPGDV VEYFGDPNTG GDECHMAFHF PLMPRIFMAV RRESRFPISE IIA QTPPIP DMAQWGIFLR NHDELTLEMV TDEERDYMYA EYAKDPRMKA NVGIRRRLAP LLDNDRNQIE LFTALLLSLP GSPV LYYGD EIGMGDVIWL GDRDGVRIPM QWTPDRNAGF STANPGRLYL PPSQDPVYGY QAVNVEAQRD TSTSLLNFTR TMLAV RRRH PAFAVGAFQE LGGSNPSVLA YVRQVAGDDG DTVLCVNNLS RFPQPIELDL QQWTNYTPVE LTGHVEFPRI GQVPYL LTL PGHGFYWFQL TT UniProtKB: Trehalose synthase/amylase TreS |
-Macromolecule #2: alpha-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: alpha-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: GLC |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 180.156 Da |
| Chemical component information | 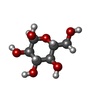 ChemComp-GLC: |
-Macromolecule #3: 6-azido-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 6-azido-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: XVC |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 205.169 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 80 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Details: 50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 300 mM NaCl and 0.3 mM TCEP |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 1.99734 sec. / Average electron dose: 1.06 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 195445 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)