+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | In situ human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state | |||||||||||||||||||||
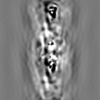
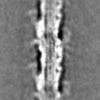
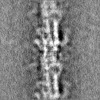
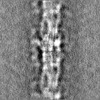
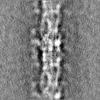
 Map data Map data | Human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | myosin / cMyBP-C / titin / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
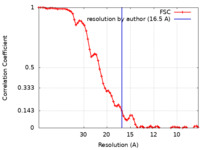
| Method | subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 16.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen L / Liu J / Rastegarpouyani H / Janssen PML / Pinto JR / Taylor KA | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 6 items United States, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: Structure of mavacamten-free human cardiac thick filaments within the sarcomere by cryoelectron tomography. Authors: Liang Chen / Jun Liu / Hosna Rastegarpouyani / Paul M L Janssen / Jose R Pinto / Kenneth A Taylor /  Abstract: Heart muscle has the unique property that it can never rest; all cardiomyocytes contract with each heartbeat which requires a complex control mechanism to regulate cardiac output to physiological ...Heart muscle has the unique property that it can never rest; all cardiomyocytes contract with each heartbeat which requires a complex control mechanism to regulate cardiac output to physiological requirements. Changes in calcium concentration regulate the thin filament activation. A separate but linked mechanism regulates the thick filament activation, which frees sufficient myosin heads to bind the thin filament, thereby producing the required force. Thick filaments contain additional nonmyosin proteins, myosin-binding protein C and titin, the latter being the protein that transmits applied tension to the thick filament. How these three proteins interact to control thick filament activation is poorly understood. Here, we show using 3-D image reconstruction of frozen-hydrated human cardiac muscle myofibrils lacking exogenous drugs that the thick filament is structured to provide three levels of myosin activation corresponding to the three crowns of myosin heads in each 429Å repeat. In one crown, the myosin heads are almost completely activated and disordered. In another crown, many myosin heads are inactive, ordered into a structure called the interacting heads motif. At the third crown, the myosin heads are ordered into the interacting heads motif, but the stability of that motif is affected by myosin-binding protein C. We think that this hierarchy of control explains many of the effects of length-dependent activation as well as stretch activation in cardiac muscle control. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_40468.map.gz emd_40468.map.gz | 22.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-40468-v30.xml emd-40468-v30.xml emd-40468.xml emd-40468.xml | 32.8 KB 32.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
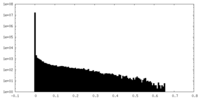
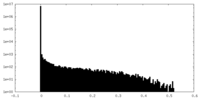
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_40468_fsc.xml emd_40468_fsc.xml | 6.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_40468.png emd_40468.png | 55.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-40468.cif.gz emd-40468.cif.gz | 4.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_40468_additional_1.map.gz emd_40468_additional_1.map.gz emd_40468_additional_2.map.gz emd_40468_additional_2.map.gz emd_40468_additional_3.map.gz emd_40468_additional_3.map.gz emd_40468_additional_4.map.gz emd_40468_additional_4.map.gz emd_40468_additional_5.map.gz emd_40468_additional_5.map.gz emd_40468_additional_6.map.gz emd_40468_additional_6.map.gz emd_40468_additional_7.map.gz emd_40468_additional_7.map.gz emd_40468_additional_8.map.gz emd_40468_additional_8.map.gz emd_40468_additional_9.map.gz emd_40468_additional_9.map.gz emd_40468_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40468_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40468_half_map_2.map.gz emd_40468_half_map_2.map.gz | 362.6 KB 313.3 KB 311.2 KB 50.4 MB 50 MB 53 MB 25 MB 11.8 MB 16.4 MB 25.1 MB 25.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40468 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40468 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40468 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40468 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_40468_validation.pdf.gz emd_40468_validation.pdf.gz | 931 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_40468_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_40468_full_validation.pdf.gz | 930.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_40468_validation.xml.gz emd_40468_validation.xml.gz | 13.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_40468_validation.cif.gz emd_40468_validation.cif.gz | 17.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40468 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40468 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40468 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40468 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_40468.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_40468.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
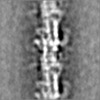
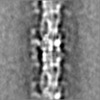
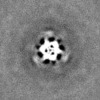
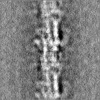
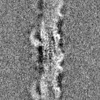
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.2368 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
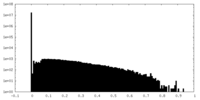
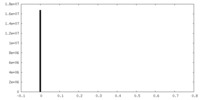
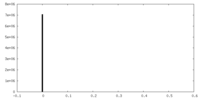
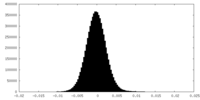
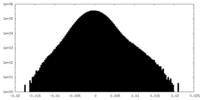
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
+Additional map: Curved layer composed of five human cardiac myosin II tail of IHM-C.
+Additional map: Curved layer composed of five human cardiac myosin II tail of IHM-D.
+Additional map: Curved layer composed of five human cardiac myosin II tail of IHM-S.
+Additional map: Human cardiac myosin II tail of IHM-D segmented...
+Additional map: Human cardiac myosin II tail of IHM-S segmented...
+Additional map: Human cardiac myosin II tail of IHM-C segmented...
+Additional map: cMyBP-C domains C8, C9, C10
+Additional map: Eleven domains of C-zone titin-C
+Additional map: Eleven domains of C-zone titin-M
+Half map: Human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state even half map
+Half map: Human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state odd half map
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : In situ human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state
| Entire | Name: In situ human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: In situ human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state
| Supramolecule | Name: In situ human cardiac thick filament in the relaxed state type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | tissue |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 6.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 6.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)