[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-40305: Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed of two antiparallel protofilaments | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed of two antiparallel protofilaments. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | amyloid-like fibril / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / Insulin processing / regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst ...negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / Insulin processing / regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / alpha-beta T cell activation / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / negative regulation of protein secretion / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / fatty acid homeostasis / Signal attenuation / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / transport vesicle / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Insulin receptor recycling / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / positive regulation of glycolytic process / positive regulation of cytokine production / endosome lumen / acute-phase response / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of protein secretion / insulin receptor binding / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of insulin secretion / wound healing / positive regulation of neuron projection development / hormone activity / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Golgi lumen / vasodilation / cognition / glucose metabolic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / cell-cell signaling / glucose homeostasis / regulation of protein localization / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / positive regulation of cell growth / protease binding / secretory granule lumen / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / positive regulation of cell migration / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / Amyloid fiber formation / receptor ligand activity / Golgi membrane / negative regulation of gene expression / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / extracellular space / extracellular region / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
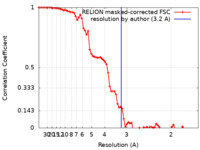
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang LW / Hall C / Uchikawa E / Chen DL / Choi E / Zhang XW / Bai XC | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of insulin fibrillation. Authors: Liwei Wang / Catherine E Hall / Emiko Uchikawa / Dailu Chen / Eunhee Choi / Xuewu Zhang / Xiao-Chen Bai /  Abstract: Insulin is a hormone responsible for maintaining normal glucose levels by activating insulin receptor (IR) and is the primary treatment for diabetes. However, insulin is prone to unfolding and ...Insulin is a hormone responsible for maintaining normal glucose levels by activating insulin receptor (IR) and is the primary treatment for diabetes. However, insulin is prone to unfolding and forming cross-β fibers. Fibrillation complicates insulin storage and therapeutic application. Molecular details of insulin fibrillation remain unclear, hindering efforts to prevent fibrillation process. Here, we characterized insulin fibrils using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), showing multiple forms that contain one or more of the protofilaments containing both the A and B chains of insulin linked by disulfide bonds. We solved the cryo-EM structure of one of the fibril forms composed of two protofilaments at 3.2-Å resolution, which reveals both the β sheet conformation of the protofilament and the packing interaction between them that underlie the fibrillation. On the basis of this structure, we designed several insulin mutants that display reduced fibrillation while maintaining native IR signaling activity. These designed insulin analogs may be developed into more effective therapeutics for type 1 diabetes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_40305.map.gz emd_40305.map.gz | 2.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-40305-v30.xml emd-40305-v30.xml emd-40305.xml emd-40305.xml | 20.5 KB 20.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
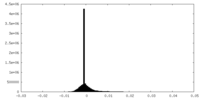
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_40305_fsc.xml emd_40305_fsc.xml | 7.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_40305.png emd_40305.png | 27.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-40305.cif.gz emd-40305.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_40305_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40305_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40305_half_map_2.map.gz emd_40305_half_map_2.map.gz | 25.6 MB 25.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40305 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40305 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40305 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40305 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8sbdMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_40305.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 33.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_40305.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 33.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed of two antiparallel protofilaments. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
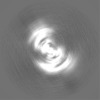
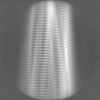
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.83 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
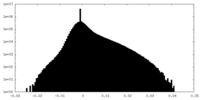
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is...
| File | emd_40305_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed of two antiparallel protofilaments. Half map 1. | ||||||||||||
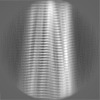
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
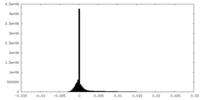
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is...
| File | emd_40305_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed of two antiparallel protofilaments. Half map 2. | ||||||||||||
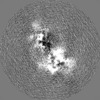
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed...
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed of two antiparallel protofilaments |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed...
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of insulin amyloid-like fibril that is composed of two antiparallel protofilaments type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Insulin B chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin B chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 16 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.433953 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: FVNQHLCGSH LVEALYLVCG ERGFFYTPKT UniProtKB: Insulin |
-Macromolecule #2: Insulin A chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin A chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 16 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.383698 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GIVEQCCTSI CSLYQLENYC N UniProtKB: Insulin |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 2 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 8.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.6 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8sbd: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)