+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Orphan receptor GPRC5D in complex with scFv150-18 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | orphan receptor / GPRC5D complex / scFv / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein kinase activator activity / electron transport chain / G protein-coupled receptor activity / periplasmic space / electron transfer activity / receptor complex / iron ion binding / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / heme binding / extracellular exosome / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yan P / Lin X / Xu F | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: The binding mechanism of an anti-multiple myeloma antibody to the human GPRC5D homodimer. Authors: Pengfei Yan / Xi Lin / Lijie Wu / Lu Xu / Fei Li / Junlin Liu / Fei Xu /  Abstract: GPRC5D is an atypical Class C orphan G protein-coupled receptor. Its high expression on the surface of multiple myeloma cells has rendered it an attractive target for therapeutic interventions, ...GPRC5D is an atypical Class C orphan G protein-coupled receptor. Its high expression on the surface of multiple myeloma cells has rendered it an attractive target for therapeutic interventions, including monoclonal antibodies, CAR-T cells, and T-cell engagers. Despite its therapeutic potential, the insufficient understanding regarding of the receptor's structure and antibody recognition mechanism has impeded the progress of effective therapeutic development. Here, we present the structure of GPRC5D in complex with a preclinical-stage single-chain antibody (scFv). Our structural analysis reveals that the GPRC5D presents a close resemblance to the typical Class C GPCRs in the transmembrane region. We identify a distinct head-to-head homodimer arrangement and interface mainly involving TM4, setting it apart from other Class C homo- or hetero-dimers. Furthermore, we elucidate the binding site engaging a sizable extracellular domain on GPRC5D for scFv recognition. These insights not only unveil the distinctive dimer organization of this unconventional Class C GPCR but also hold the potential to advance drug development targeting GPRC5D for the treatment of multiple myeloma. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_39696.map.gz emd_39696.map.gz | 56.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-39696-v30.xml emd-39696-v30.xml emd-39696.xml emd-39696.xml | 16.8 KB 16.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_39696.png emd_39696.png | 109.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-39696.cif.gz emd-39696.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_39696_half_map_1.map.gz emd_39696_half_map_1.map.gz emd_39696_half_map_2.map.gz emd_39696_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39696 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39696 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39696 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39696 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_39696_validation.pdf.gz emd_39696_validation.pdf.gz | 884.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_39696_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_39696_full_validation.pdf.gz | 883.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_39696_validation.xml.gz emd_39696_validation.xml.gz | 12.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_39696_validation.cif.gz emd_39696_validation.cif.gz | 14.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39696 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39696 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39696 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-39696 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 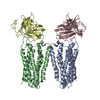 8yzkMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_39696.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_39696.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.832 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_39696_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_39696_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of Orphan GPRC5D with scFv150-18
| Entire | Name: Complex of Orphan GPRC5D with scFv150-18 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of Orphan GPRC5D with scFv150-18
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of Orphan GPRC5D with scFv150-18 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Soluble cytochrome b562,G-protein coupled receptor family C group...
| Macromolecule | Name: Soluble cytochrome b562,G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.822062 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKTIIALSYI FCLVFADYKD DDDAGRAADL EDNWETLNDN LKVIEKADNA AQVKDALTKM RAAALDAQKA TPPKLEDKSP DSPEMKDFR HGFDILVGQI DDALKLANEG KVKEAQAAAE QLKTTRNAYI QKYLMYKDCI ESTGDYFLLC DAEGPWGIIL E SLAILGIV ...String: MKTIIALSYI FCLVFADYKD DDDAGRAADL EDNWETLNDN LKVIEKADNA AQVKDALTKM RAAALDAQKA TPPKLEDKSP DSPEMKDFR HGFDILVGQI DDALKLANEG KVKEAQAAAE QLKTTRNAYI QKYLMYKDCI ESTGDYFLLC DAEGPWGIIL E SLAILGIV VTILLLLAFL FLMRKIQDCS QWNVLPTQLL FLLSVLGLFG LAFAFIIELN QQTAPVRYFL FGVLFALCFS CL LAHASNL VKLVRGCVSF SWTTILCIAI GCSLLQIIIA TEYVTLIMTR GMMFVNMTPC QLNVDFVVLL VYVLFLMALT FFV SKATFC GPCENWKQHG RLIFITVLFS IIIWVVWISM LLRGNPQFQR QPQWDDPVVC IALVTNAWVF LLLYIVPELC ILYR SEFLE VLFQGPHHHH HHHHHH UniProtKB: Soluble cytochrome b562, G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D |
-Macromolecule #2: scFv
| Macromolecule | Name: scFv / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 30.387537 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MLLVNQSHQG FNKEHTSKMV SAIVLYVLLA AAAHSAFASS ELTQDPAVSV ALGQTVRITC QGDSLRSYYA SWYQQKPGQA PVLVIYGKN NRPSGIPDRF SGSSSGNTAS LTITGAQAED EADYYCNSRD SSGNPPVVFG GGTKLTVLGS RGGGGSGGGG S GGGGSLEM ...String: MLLVNQSHQG FNKEHTSKMV SAIVLYVLLA AAAHSAFASS ELTQDPAVSV ALGQTVRITC QGDSLRSYYA SWYQQKPGQA PVLVIYGKN NRPSGIPDRF SGSSSGNTAS LTITGAQAED EADYYCNSRD SSGNPPVVFG GGTKLTVLGS RGGGGSGGGG S GGGGSLEM AQVQLVESGG GLVHPGGSLR LSCAASGFTF RSHSMNWVRQ APGKGLEWVS SISSDSTYTY YADSVKGRFT IS RDNAKNS LYLQMNSLRA EDTAVYYCAR SGGQWKYYDY WGQGTLVTVS S |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source: OTHER |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)