+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | XBB.1.5-K356T S-trimer (3 RBDs down) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Spike / SARS-CoV-2 / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.37 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yue C / Liu P | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Natl Sci Rev / Year: 2024 Journal: Natl Sci Rev / Year: 2024Title: Spike N354 glycosylation augments SARS-CoV-2 fitness for human adaptation through structural plasticity. Authors: Pan Liu / Can Yue / Bo Meng / Tianhe Xiao / Sijie Yang / Shuo Liu / Fanchong Jian / Qianhui Zhu / Yuanling Yu / Yanyan Ren / Peng Wang / Yixin Li / Jinyue Wang / Xin Mao / Fei Shao / Youchun ...Authors: Pan Liu / Can Yue / Bo Meng / Tianhe Xiao / Sijie Yang / Shuo Liu / Fanchong Jian / Qianhui Zhu / Yuanling Yu / Yanyan Ren / Peng Wang / Yixin Li / Jinyue Wang / Xin Mao / Fei Shao / Youchun Wang / Ravindra Kumar Gupta / Yunlong Cao / Xiangxi Wang /   Abstract: Selective pressures have given rise to a number of SARS-CoV-2 variants during the prolonged course of the COVID-19 pandemic. Recently evolved variants differ from ancestors in additional ...Selective pressures have given rise to a number of SARS-CoV-2 variants during the prolonged course of the COVID-19 pandemic. Recently evolved variants differ from ancestors in additional glycosylation within the spike protein receptor-binding domain (RBD). Details of how the acquisition of glycosylation impacts viral fitness and human adaptation are not clearly understood. Here, we dissected the role of N354-linked glycosylation, acquired by BA.2.86 sub-lineages, as a RBD conformational control element in attenuating viral infectivity. The reduced infectivity is recovered in the presence of heparin sulfate, which targets the 'N354 pocket' to ease restrictions of conformational transition resulting in a 'RBD-up' state, thereby conferring an adjustable infectivity. Furthermore, N354 glycosylation improved spike cleavage and cell-cell fusion, and in particular escaped one subset of ADCC antibodies. Together with reduced immunogenicity in hybrid immunity background, these indicate a single spike amino acid glycosylation event provides selective advantage in humans through multiple mechanisms. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_38701.map.gz emd_38701.map.gz | 118 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-38701-v30.xml emd-38701-v30.xml emd-38701.xml emd-38701.xml | 11.9 KB 11.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_38701.png emd_38701.png | 40.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-38701.cif.gz emd-38701.cif.gz | 3.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_38701_half_map_1.map.gz emd_38701_half_map_1.map.gz emd_38701_half_map_2.map.gz emd_38701_half_map_2.map.gz | 116.1 MB 116.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-38701 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-38701 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-38701 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-38701 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_38701_validation.pdf.gz emd_38701_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_38701_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_38701_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_38701_validation.xml.gz emd_38701_validation.xml.gz | 12.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_38701_validation.cif.gz emd_38701_validation.cif.gz | 14.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-38701 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-38701 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-38701 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-38701 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8whsC  8whuC  8whvC  8whwC  8whzC  8x4hC  8x4zC  8x50C  8x55C  8x56C  8x5qC  8x5rC  8xurC  8xusC  8xutC  8xuuC C: citing same article ( |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_38701.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_38701.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
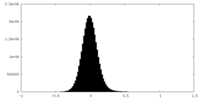
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_38701_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
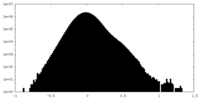
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : XBB.1.5-K356T S-trimer (3 RBDs down)
| Entire | Name: XBB.1.5-K356T S-trimer (3 RBDs down) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: XBB.1.5-K356T S-trimer (3 RBDs down)
| Supramolecule | Name: XBB.1.5-K356T S-trimer (3 RBDs down) / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.37 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 57082 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)