+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Oryza sativa HKT2;1 at 2.5 angstrom | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HKT / K+ transporter / Channel / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsodium ion transmembrane transporter activity / potassium ion homeostasis / symporter activity / monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / sodium ion transport / potassium ion transport / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.53 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang X / Shen X / Qu Y / Wang C / Shen H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Plants / Year: 2024Title: Structural insights into ion selectivity and transport mechanisms of Oryza sativa HKT2;1 and HKT2;2/1 transporters. Authors: Xiaohui Wang / Xiaoshuai Shen / Yannan Qu / Heng Zhang / Chu Wang / Fan Yang / Huaizong Shen /  Abstract: Plant high-affinity K transporters (HKTs) play a pivotal role in maintaining the balance of Na and K ions in plants, thereby influencing plant growth under K-depleted conditions and enhancing ...Plant high-affinity K transporters (HKTs) play a pivotal role in maintaining the balance of Na and K ions in plants, thereby influencing plant growth under K-depleted conditions and enhancing tolerance to salinity stress. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of Oryza sativa HKT2;1 and HKT2;2/1 at overall resolutions of 2.5 Å and 2.3 Å, respectively. Both transporters adopt a dimeric assembly, with each protomer enclosing an ion permeation pathway. Comparison between the selectivity filters of the two transporters reveals the critical roles of Ser88/Gly88 and Val243/Gly243 in determining ion selectivity. A constriction site along the ion permeation pathway is identified, consisting of Glu114, Asn273, Pro392, Pro393, Arg525, Lys517 and the carboxy-terminal Trp530 from the neighbouring protomer. The linker between domains II and III adopts a stable loop structure oriented towards the constriction site, potentially participating in the gating process. Electrophysiological recordings, yeast complementation assays and molecular dynamics simulations corroborate the functional importance of these structural features. Our findings provide crucial insights into the ion selectivity and transport mechanisms of plant HKTs, offering valuable structural templates for developing new salinity-tolerant cultivars and strategies to increase crop yields. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_36918.map.gz emd_36918.map.gz | 25.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-36918-v30.xml emd-36918-v30.xml emd-36918.xml emd-36918.xml | 19.6 KB 19.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_36918.png emd_36918.png | 117.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-36918.cif.gz emd-36918.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_36918_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36918_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36918_half_map_2.map.gz emd_36918_half_map_2.map.gz | 335.8 MB 335.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36918 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36918 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36918 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36918 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8k66MC  8k69C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_36918.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_36918.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.53865 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_36918_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
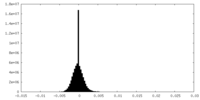
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_36918_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : OsHKT2;1 dimer
| Entire | Name: OsHKT2;1 dimer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: OsHKT2;1 dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: OsHKT2;1 dimer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Cation transporter HKT2;1
| Macromolecule | Name: Cation transporter HKT2;1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.822293 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADYKDDDDK GGRMTSIYHD FIHNKLQSFG RIGRYFVNFV VLAHRFIALH IHPFWIQLSY FLLISILGSV LLMFLKPSNP EFRPGYIDM LFLSTSALTL SSLITIEMEV LSSSQIVVIT LLMLLGGEVF VSFLGLMLRL NHKHNPEFSG DKVSSVPIEL D TINSASTV ...String: MADYKDDDDK GGRMTSIYHD FIHNKLQSFG RIGRYFVNFV VLAHRFIALH IHPFWIQLSY FLLISILGSV LLMFLKPSNP EFRPGYIDM LFLSTSALTL SSLITIEMEV LSSSQIVVIT LLMLLGGEVF VSFLGLMLRL NHKHNPEFSG DKVSSVPIEL D TINSASTV ISCEELQLEA AIPEVPSSTI KDLKRSKRLR WFLGFVVFSY FVVIHVAGFL LVLWYISRVS SAKAPLKKKG IN IALFSFS VTVSSFANVG LVPTNENMAI FSKNPGLLLL FIGQILAGNT LYPLFLRLLI WFLGKVTKLR ELKLMIKNPE ELQ YDYLLP KLPTAFLAST VIGLMASLVT LFGAVDWNSS VFDGLSSYQK IINALFMAVN ARHSGENSID CSLIAPAVLV LFII LMYLP PSTTFALSNG DEKTANKKAK RKLGLVVQNL AFSQLACISV FVIVAFITER SRLRNDPLNF SALNMIFEII SAYGN VGLS TGYSCSRLQK LHPGSICQDK PYSLSGWWSD EGKLLLVFVM LYGRLKAFTK GTGEYWRLW UniProtKB: Cation transporter HKT2;1 |
-Macromolecule #2: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: Y01 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 486.726 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-Y01: |
-Macromolecule #3: Phosphatidylinositol
| Macromolecule | Name: Phosphatidylinositol / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: T7X |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 887.128 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-T7X: |
-Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: PTY |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 734.039 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PTY: |
-Macromolecule #5: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Macromolecule #6: 1,2-DIACYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-DIACYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: PC1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 790.145 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PC1: |
-Macromolecule #7: SODIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: SODIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.99 Da |
-Macromolecule #8: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 130 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)