[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-36892: Structure of BtKY72 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) complexed... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
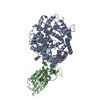
| Title | Structure of BtKY72 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) complexed with bat ACE2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | BtKY72 RBD ACE2 bat / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Rhinolophus landeri (Lander's horseshoe bat) Rhinolophus landeri (Lander's horseshoe bat) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Su C / Qi JX / Gao GF | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2024 Journal: mBio / Year: 2024Title: Structural characteristics of BtKY72 RBD bound to bat ACE2 reveal multiple key residues affecting ACE2 usage of sarbecoviruses. Authors: Chao Su / Juanhua He / Liang Wang / Yu Hu / Jian Cao / Bin Bai / Jianxun Qi / George Fu Gao / Mengsu Yang / Qihui Wang /  Abstract: Two different sarbecoviruses, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and SARS-CoV-2, have caused serious challenges to public health. Certain sarbecoviruses utilize angiotensin- ...Two different sarbecoviruses, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and SARS-CoV-2, have caused serious challenges to public health. Certain sarbecoviruses utilize angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as their cellular receptor, whereas some do not, speculatively due to the two deletions in their receptor-binding domain (RBD). However, it remains unclear whether sarbecoviruses with one deletion in the RBD can still bind to ACE2. Here, we showed that two phylogenetically related sarbecoviruses with one deletion, BtKY72 and BM48-31, displayed a different ACE2-usage range. The cryo-electron microscopy structure of BtKY72 RBD bound to bat ACE2 identified a key residue important for the interaction between RBD and ACE2. In addition, we demonstrated that the mutations involving four types of core residues enabled the sarbecoviruses with deletion(s) to bind to human ACE2 (hACE2) and broadened the ACE2 usage of SARS-CoV-2. Our findings help predict the potential hACE2-binding ability to emerge sarbecoviruses and develop pan-sarbecovirus therapeutic agents. IMPORTANCE: Many sarbecoviruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), possess the ability to bind to receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) through their ...IMPORTANCE: Many sarbecoviruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), possess the ability to bind to receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) through their receptor-binding domain (RBD). However, certain sarbecoviruses with deletion(s) in the RBD lack this capability. In this study, we investigated two closely related short-deletion sarbecoviruses, BtKY72 and BM48-31, and revealed that BtKY72 exhibited a broader ACE2-binding spectrum compared to BM48-31. Structural analysis of the BtKY72 RBD-bat ACE2 complex identifies a critical residue at position 493 contributing to these differences. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the mutations involving four core residues in the RBD enabled the sarbecoviruses with deletion(s) to bind to human ACE2 and expanded the ACE2 usage spectra of SARS-CoV-2. These findings offer crucial insights for accurately predicting the potential threat of newly emerging sarbecoviruses to human health. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_36892.map.gz emd_36892.map.gz | 167.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-36892-v30.xml emd-36892-v30.xml emd-36892.xml emd-36892.xml | 19.2 KB 19.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_36892.png emd_36892.png | 31 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-36892.cif.gz emd-36892.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_36892_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36892_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36892_half_map_2.map.gz emd_36892_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.4 MB 165.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36892 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36892 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36892 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36892 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_36892.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_36892.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.669 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
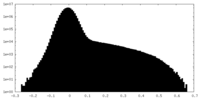
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_36892_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_36892_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of BtKY72 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) complexed...
| Entire | Name: Structure of BtKY72 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) complexed with bat ACE2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of BtKY72 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) complexed...
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of BtKY72 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) complexed with bat ACE2 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #2: BtKY72 RBD
| Supramolecule | Name: BtKY72 RBD / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Rhinolophus landeri (Lander's horseshoe bat) Rhinolophus landeri (Lander's horseshoe bat) |
-Supramolecule #3: Bat ACE2
| Supramolecule | Name: Bat ACE2 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: BtKY72
| Macromolecule | Name: BtKY72 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.514703 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: RVSPSTEVVR FPNITNLCPF GQVFNASNFP SVYAWERLRI SDCVADYAVL YNSSSSFSTF KCYGVSPTKL NDLCFSSVYA DYFVVKGDD VRQIAPAQTG VIADYNYKLP DDFTGCVLAW NTNSVDSKSG NNFYYRLFRH GKIKPYERDI SNVLYNSAGG T CSSISQLG ...String: RVSPSTEVVR FPNITNLCPF GQVFNASNFP SVYAWERLRI SDCVADYAVL YNSSSSFSTF KCYGVSPTKL NDLCFSSVYA DYFVVKGDD VRQIAPAQTG VIADYNYKLP DDFTGCVLAW NTNSVDSKSG NNFYYRLFRH GKIKPYERDI SNVLYNSAGG T CSSISQLG CYEPLKSYGF TPTVGVGYQP YRVVVLSFEL LNAPATVCGP KKSTELVKNK CVNFHHHHHH |
-Macromolecule #2: ACE2
| Macromolecule | Name: ACE2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Rhinolophus landeri (Lander's horseshoe bat) Rhinolophus landeri (Lander's horseshoe bat) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 69.443156 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: STPEDLAKTF LDDFNSAAEN LSYQSSLASW EYNTNISDEN IQKMDEAGAK WSDFYETQSK HAKNFSLEEI HNDTVKLQLQ ILQQSGSPV LSEDKSKRLN SILNAMSTIY STGKVCRPNN PQECLLLEPG LDNIMGTSKD YNERLWAWEG WRAEVGKQLR P LYEEYVVL ...String: STPEDLAKTF LDDFNSAAEN LSYQSSLASW EYNTNISDEN IQKMDEAGAK WSDFYETQSK HAKNFSLEEI HNDTVKLQLQ ILQQSGSPV LSEDKSKRLN SILNAMSTIY STGKVCRPNN PQECLLLEPG LDNIMGTSKD YNERLWAWEG WRAEVGKQLR P LYEEYVVL KNEMARGYHY EDYGDYWRRD YETEGSPDLE YSRDQLTKDV ERIFAEIKPL YEQLHAYVRA KLMDTYPFHI SP TGCLPAH LLGDMWGRFW TNLYPLTVPF GQKPNIDVTD AMLNQTWDAK RIFKEAEKFF VSIGLPHMTE GFWNNSMLTD PGD GRKVVC HPTAWDLGKG DFRIKMCTKV TMEDFLTAHH EMGHIQYDMA YASQPYLLRN GANEGFHEAV GEVMSLSVAT PKHL KTMGL LSPDFLEDNE TEINFLFKQA LTIVGTLPFT YMLEKWRWMV FKGEIPKEEW MTKWWEMKRK IVGVVEPVPH DETYC DPAS LFHVANDYSF IRYYTRTIFE FQFHEALCRI AKHDGPLHKC DISNSTDAGK KLHQMLSVGK SQPWTSVLKD FVDSKD MDV GPLLRYFEPL YTWLKEQNRN SFVGWNTDWS PHAD |
-Macromolecule #3: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


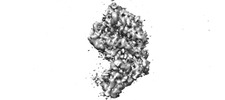
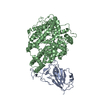
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)