+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Rubisco from Phaeodactylum tricornutum | |||||||||
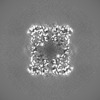
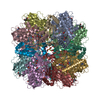
 Map data Map data | Main map of Rubisco from P. tricornutum | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Rubisco / phase separation / rubisco linker protein / condensation / pyrenoid / phaeodactylum tricornutum / PHOTOSYNTHESIS | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oh ZG / Ang WSL / Bhushan S / Mueller-Cajar O | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Singapore, 2 items Singapore, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023Title: A linker protein from a red-type pyrenoid phase separates with Rubisco via oligomerizing sticker motifs. Authors: Zhen Guo Oh / Warren Shou Leong Ang / Cheng Wei Poh / Soak-Kuan Lai / Siu Kwan Sze / Hoi-Yeung Li / Shashi Bhushan / Tobias Wunder / Oliver Mueller-Cajar /  Abstract: The slow kinetics and poor substrate specificity of the key photosynthetic CO-fixing enzyme Rubisco have prompted the repeated evolution of Rubisco-containing biomolecular condensates known as ...The slow kinetics and poor substrate specificity of the key photosynthetic CO-fixing enzyme Rubisco have prompted the repeated evolution of Rubisco-containing biomolecular condensates known as pyrenoids in the majority of eukaryotic microalgae. Diatoms dominate marine photosynthesis, but the interactions underlying their pyrenoids are unknown. Here, we identify and characterize the Rubisco linker protein PYCO1 from . PYCO1 is a tandem repeat protein containing prion-like domains that localizes to the pyrenoid. It undergoes homotypic liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) to form condensates that specifically partition diatom Rubisco. Saturation of PYCO1 condensates with Rubisco greatly reduces the mobility of droplet components. Cryo-electron microscopy and mutagenesis data revealed the sticker motifs required for homotypic and heterotypic phase separation. Our data indicate that the PYCO1-Rubisco network is cross-linked by PYCO1 stickers that oligomerize to bind to the small subunits lining the central solvent channel of the Rubisco holoenzyme. A second sticker motif binds to the large subunit. Pyrenoidal Rubisco condensates are highly diverse and tractable models of functional LLPS. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_35158.map.gz emd_35158.map.gz | 4.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-35158-v30.xml emd-35158-v30.xml emd-35158.xml emd-35158.xml | 20.5 KB 20.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_35158.png emd_35158.png | 307.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_35158_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35158_half_map_1.map.gz emd_35158_half_map_2.map.gz emd_35158_half_map_2.map.gz | 47.9 MB 47.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35158 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35158 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35158 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-35158 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_35158.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 67 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_35158.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 67 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Main map of Rubisco from P. tricornutum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.858 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_35158_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
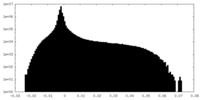
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_35158_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Phaeodactylu...
| Entire | Name: Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Phaeodactylum tricornutum |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Phaeodactylu...
| Supramolecule | Name: Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Phaeodactylum tricornutum type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 550 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSQSVSERTR IKSDRYESGV IPYAKMGYWD AAYAVKNTDV LALFRITPQP GVDPVEAAAA VAGESSTATW TVVWTDLLTA CDRYRAKAYR VDPVPNTTDQ YFAFIAYECD LFEEGSLANL TASIIGNVFG FKAVSALRLE DMRIPHSYLK TFQGPATGVI VERERLNKYG ...String: MSQSVSERTR IKSDRYESGV IPYAKMGYWD AAYAVKNTDV LALFRITPQP GVDPVEAAAA VAGESSTATW TVVWTDLLTA CDRYRAKAYR VDPVPNTTDQ YFAFIAYECD LFEEGSLANL TASIIGNVFG FKAVSALRLE DMRIPHSYLK TFQGPATGVI VERERLNKYG IPLLGATVKP KLGLSGKNYG RVVYEGLKGG LDFLKDDENI NSQPFMRWRE RFLYCMEGIN RASAATGETK GSYLNITAGT MEEVYKRAEY AKTVGSIVVM IDLVMGYTAI QSAAIWARDN DLILHLHRAG NSTYARQKNH GINFRVICKW MRMCGVDHIH AGTVVGKLEG DPLMIKGFYD TLLLTHLNVN LPYGIFFEMT WASLRKCMPV ASGGIHCGQM HQLVHYLGDD VVLQFGGGTI GHPDGIQAGA TANRVALEAM ILARNEGADY FNSDIGPQIL RNAAKTCGPL QTALDLWKDI SFNYTSTDTS DFSVTPTANV |
-Macromolecule #2: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MRLTQGCFSF LPDLTDQQIE KQIAYCITKG WAMNVEWTDD PHPRNSYWEL WGLPLFDVKD PASVMFELRE ARKSCAAGYI RINAFNAAYG TESCVMSFIV NRPSNEPGFY LERQELEGRR IAYTTKSYSV QANPEGGRY |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
Details: 20 mM Tris pH 8.0 20 mM NaCl | |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 2 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 20 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.6 kPa | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: Blotted for 2 sec with blot force of 1.. | |||||||||
| Details | 0.5 mg/mL Rubisco |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV / Details: Gatan EF |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 5760 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4092 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 8861 / Average exposure time: 5.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 65.0 e/Å2 Details: Images were collected in movie mode at 10 frames per second |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 165000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | Coot was used for model building |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)